Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give examples of two functions f: N → Z and g: Z → Z such that g o f is injective but gis not injective.
(Hint: Consider f(x) = x and g(x) =|x|)
उत्तर
Define f: N → Z as f(x) = x and g: Z → Z as g(x) =|x|.
We first show that g is not injective.
It can be observed that:
g(−1) = `|-1| = 1`
g(1) = `|1| = 1`
∴ g(−1) = g(1), but −1 ≠ 1.
∴ g is not injective.
Now, gof: N → Z is defined as
`gof(x) = g(f(x)) = g(x) = |x|`
Let x, y ∈ N such that gof(x) = gof(y).
⇒ |x| = |y|
Since x and y ∈ N, both are positive.
`:. |x| = |y| => x = y`
Hence, gof is injective
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Following the case, state whether the function is one-one, onto, or bijective. Justify your answer.
f : R → R defined by f(x) = 3 − 4x
Show that function f: R `rightarrow` {x ∈ R : −1 < x < 1} defined by f(x) = `x/(1 + |x|)`, x ∈ R is one-one and onto function.
Let S = {a, b, c} and T = {1, 2, 3}. Find F−1 of the following functions F from S to T, if it exists.
F = {(a, 3), (b, 2), (c, 1)}
Give an example of a function which is one-one but not onto ?
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : N → N given by f(x) = x2
If f : R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 4x3 + 7, show that f is a bijection.
Given A = {2, 3, 4}, B = {2, 5, 6, 7}. Construct an example of each of the following:
(i) an injective map from A to B
(ii) a mapping from A to B which is not injective
(iii) a mapping from A to B.
Show that f : R→ R, given by f(x) = x — [x], is neither one-one nor onto.
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = x2 + 8 and g(x) = 3x3 + 1 .
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = x2 + 2x − 3 and g(x) = 3x − 4 .
If f : A → B and g : B → C are one-one functions, show that gof is a one-one function.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = x2 g(x) = cos x .
If f(x) = 2x + 5 and g(x) = x2 + 1 be two real functions, then describe each of the following functions:
(1) fog
(2) gof
(3) fof
(4) f2
Also, show that fof ≠ f2
Let f be a real function given by f (x)=`sqrt (x-2)`
Find each of the following:
(i) fof
(ii) fofof
(iii) (fofof) (38)
(iv) f2
Also, show that fof ≠ `f^2` .
If f, g : R → R be two functions defined as f(x) = |x| + x and g(x) = |x|- x, ∀x∈R" .Then find fog and gof. Hence find fog(–3), fog(5) and gof (–2).
Find f −1 if it exists : f : A → B, where A = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}; B = {0, 1, 9, 25, 49, 81} and f(x) = x2
If f : Q → Q, g : Q → Q are two functions defined by f(x) = 2 x and g(x) = x + 2, show that f and g are bijective maps. Verify that (gof)−1 = f−1 og −1.
Let f be a function from R to R, such that f(x) = cos (x + 2). Is f invertible? Justify your answer.
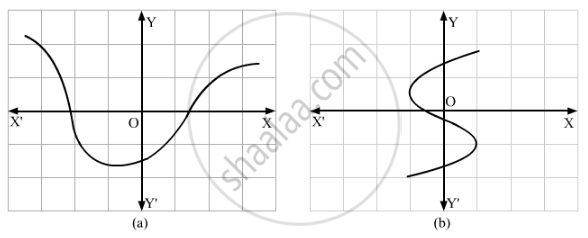
Which one of the following graphs represents a function?
Let f be a function from C (set of all complex numbers) to itself given by f(x) = x3. Write f−1 (−1).
Let A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {a, b} be two sets. Write the total number of onto functions from A to B.
The function f : R → R defined by
`f (x) = 2^x + 2^(|x|)` is
The function
f : A → B defined by
f (x) = - x2 + 6x - 8 is a bijection if
Let
\[A = \left\{ x : - 1 \leq x \leq 1 \right\} \text{and} f : A \to \text{A such that f}\left( x \right) = x|x|\]
The function f : [-1/2, 1/2, 1/2] → [-π /2,π/2], defined by f (x) = `sin^-1` (3x - `4x^3`), is
If \[F : [1, \infty ) \to [2, \infty )\] is given by
\[f\left( x \right) = x + \frac{1}{x}, then f^{- 1} \left( x \right)\]
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let A = {1, 2, ... , n} and B = {a, b}. Then the number of subjections from A into B is
Let f: R → R be defined by f(x) = 3x – 4. Then f–1(x) is given by ______.
Let f: R → R be defined by f(x) = x2 + 1. Then, pre-images of 17 and – 3, respectively, are ______.
For sets A, B and C, let f: A → B, g: B → C be functions such that g o f is injective. Then both f and g are injective functions.
Let f: R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 2x – 3 ∀ x ∈ R. write f–1
Let A = [–1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions defined on A are one-one, onto or bijective:
k(x) = x2
If the set A contains 5 elements and the set B contains 6 elements, then the number of one-one and onto mappings from A to B is ______.
Let A = {0, 1} and N be the set of natural numbers. Then the mapping f: N → A defined by f(2n – 1) = 0, f(2n) = 1, ∀ n ∈ N, is onto.
Let R be a relation on the set L of lines defined by l1 R l2 if l1 is perpendicular to l2, then relation R is ____________.
If f: R → R given by f(x) =(3 − x3)1/3, find f0f(x)
Function f: R → R, defined by f(x) = `x/(x^2 + 1)` ∀ x ∈ R is not
Consider a function f: `[0, pi/2] ->` R, given by f(x) = sinx and `g[0, pi/2] ->` R given by g(x) = cosx then f and g are
Difference between the greatest and least value of f(x) = `(1 + (cos^-1x)/π)^2 - (1 + (sin^-1x)/π)^2` is ______.
A function f : [– 4, 4] `rightarrow` [0, 4] is given by f(x) = `sqrt(16 - x^2)`. Show that f is an onto function but not a one-one function. Further, find all possible values of 'a' for which f(a) = `sqrt(7)`.
