Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the equation x2 + 3x + 9 = 0
उत्तर
The given quadratic equation is x2 + 3x + 9 = 0
On comparing the given equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we obtain
a = 1, b = 3, and c = 9
Therefore, the discriminant of the given equation is
D = b2 – 4ac = 32 – 4 × 1 × 9 = 9 – 36 = –27
Therefore, the required solutions are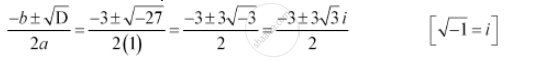
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Solve the equation x2 + 3 = 0
Solve the equation `sqrt2x^2 + x + sqrt2 = 0`
Solve the equation `sqrt3 x^2 - sqrt2x + 3sqrt3 = 0`
Solve the equation `x^2 + x + 1/sqrt2 = 0`
If z1 = 2 – i, z2 = 1 + i, find `|(z_1 + z_2 + 1)/(z_1 - z_2 + 1)|`
9x2 + 4 = 0
x2 + x + 1 = 0
\[x^2 - 4x + 7 = 0\]
\[5 x^2 - 6x + 2 = 0\]
\[21 x^2 + 9x + 1 = 0\]
\[x^2 - x + 1 = 0\]
\[17 x^2 - 8x + 1 = 0\]
\[13 x^2 + 7x + 1 = 0\]
\[\sqrt{5} x^2 + x + \sqrt{5} = 0\]
\[x^2 - 2x + \frac{3}{2} = 0\]
\[3 x^2 - 4x + \frac{20}{3} = 0\]
Solving the following quadratic equation by factorization method:
\[x^2 + 10ix - 21 = 0\]
Solving the following quadratic equation by factorization method:
\[6 x^2 - 17ix - 12 = 0\]
Solve the following quadratic equation:
\[\left( 2 + i \right) x^2 - \left( 5 - i \right) x + 2 \left( 1 - i \right) = 0\]
Solve the following quadratic equation:
\[x^2 - \left( 2 + i \right) x - \left( 1 - 7i \right) = 0\]
Solve the following quadratic equation:
\[2 x^2 + \sqrt{15}ix - i = 0\]
Solve the following quadratic equation:
\[x^2 - x + \left( 1 + i \right) = 0\]
If the difference between the roots of the equation \[x^2 + ax + 8 = 0\] is 2, write the values of a.
Write roots of the equation \[(a - b) x^2 + (b - c)x + (c - a) = 0\] .
For the equation \[\left| x \right|^2 + \left| x \right| - 6 = 0\] ,the sum of the real roots is
The values of x satisfying log3 \[( x^2 + 4x + 12) = 2\] are
The number of real roots of the equation \[( x^2 + 2x )^2 - (x + 1 )^2 - 55 = 0\] is
If the roots of \[x^2 - bx + c = 0\] are two consecutive integers, then b2 − 4 c is
The value of a such that \[x^2 - 11x + a = 0 \text { and } x^2 - 14x + 2a = 0\] may have a common root is
If the equations \[x^2 + 2x + 3\lambda = 0 \text { and } 2 x^2 + 3x + 5\lambda = 0\] have a non-zero common roots, then λ =
The number of roots of the equation \[\frac{(x + 2)(x - 5)}{(x - 3)(x + 6)} = \frac{x - 2}{x + 4}\] is
If the difference of the roots of \[x^2 - px + q = 0\] is unity, then
The equation of the smallest degree with real coefficients having 1 + i as one of the roots is
Find the value of P such that the difference of the roots of the equation x2 – Px + 8 = 0 is 2.
If 1 – i, is a root of the equation x2 + ax + b = 0, where a, b ∈ R, then find the values of a and b.
