Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the equation x2 – x + 2 = 0
उत्तर
The given quadratic equation is x2 – x + 2 = 0
On comparing the given equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we obtain
a = 1, b = –1, and c = 2
Therefore, the discriminant of the given equation is
D = b2 – 4ac = (–1)2 – 4 × 1 × 2 = 1 – 8 = –7
Therefore, the required solutions are
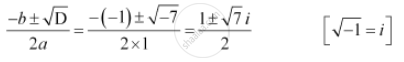
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Solve the equation x2 + 3 = 0
Solve the equation –x2 + x – 2 = 0
Solve the equation `sqrt2x^2 + x + sqrt2 = 0`
Solve the equation `x^2 + x/sqrt2 + 1 = 0`
Solve the equation 27x2 – 10x + 1 = 0
4x2 − 12x + 25 = 0
x2 + x + 1 = 0
\[4 x^2 + 1 = 0\]
\[x^2 - 4x + 7 = 0\]
\[x^2 - x + 1 = 0\]
\[17 x^2 + 28x + 12 = 0\]
\[13 x^2 + 7x + 1 = 0\]
\[2 x^2 + x + 1 = 0\]
\[x^2 + x + \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} = 0\]
\[x^2 + \frac{x}{\sqrt{2}} + 1 = 0\]
\[- x^2 + x - 2 = 0\]
Solve the following quadratic equation:
\[\left( 2 + i \right) x^2 - \left( 5 - i \right) x + 2 \left( 1 - i \right) = 0\]
Solve the following quadratic equation:
\[x^2 - \left( 3\sqrt{2} - 2i \right) x - \sqrt{2} i = 0\]
Solve the following quadratic equation:
\[2 x^2 - \left( 3 + 7i \right) x + \left( 9i - 3 \right) = 0\]
Write the number of real roots of the equation \[(x - 1 )^2 + (x - 2 )^2 + (x - 3 )^2 = 0\].
If a and b are roots of the equation \[x^2 - px + q = 0\], than write the value of \[\frac{1}{a} + \frac{1}{b}\].
If roots α, β of the equation \[x^2 - px + 16 = 0\] satisfy the relation α2 + β2 = 9, then write the value P.
If a and b are roots of the equation \[x^2 - x + 1 = 0\], then write the value of a2 + b2.
The complete set of values of k, for which the quadratic equation \[x^2 - kx + k + 2 = 0\] has equal roots, consists of
If α, β are roots of the equation \[4 x^2 + 3x + 7 = 0, \text { then } 1/\alpha + 1/\beta\] is equal to
The number of real roots of the equation \[( x^2 + 2x )^2 - (x + 1 )^2 - 55 = 0\] is
The number of real solutions of \[\left| 2x - x^2 - 3 \right| = 1\] is
If x is real and \[k = \frac{x^2 - x + 1}{x^2 + x + 1}\], then
If the equations \[x^2 + 2x + 3\lambda = 0 \text { and } 2 x^2 + 3x + 5\lambda = 0\] have a non-zero common roots, then λ =
The set of all values of m for which both the roots of the equation \[x^2 - (m + 1)x + m + 4 = 0\] are real and negative, is
The number of roots of the equation \[\frac{(x + 2)(x - 5)}{(x - 3)(x + 6)} = \frac{x - 2}{x + 4}\] is
Find the value of P such that the difference of the roots of the equation x2 – Px + 8 = 0 is 2.
Find the value of a such that the sum of the squares of the roots of the equation x2 – (a – 2)x – (a + 1) = 0 is least.
If 1 – i, is a root of the equation x2 + ax + b = 0, where a, b ∈ R, then find the values of a and b.
