Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Using Converse of basic proportionality theorem, prove that the line joining the mid-points of any two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side. (Recall that you have done it in Class IX).
उत्तर
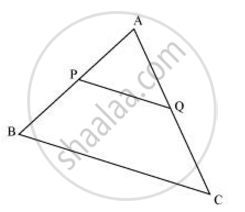
Consider the given figure in which PQ is a line segment joining the mid-points P and Q of line AB and AC respectively.
i.e., AP = PB and AQ = QC
It can be observed that
`("AP")/("PB") = 1/1`
and `("AQ")/("QC") = 1/1`
∴ `("AP")/("PB") = ("AQ")/("QC")`
Hence, by using basic proportionality theorem, we obtain
PQ || BC
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
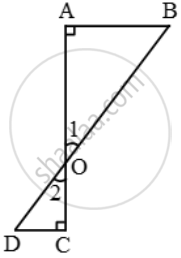
In figure, if ∠A = ∠C, then prove that ∆AOB ~ ∆COD
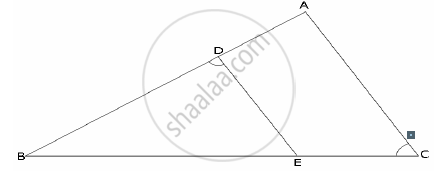
In the given figure ABC is a triangle with ∠EDB = ∠ACB. Prove that Δ ABC ~ Δ EBD. If BE = 6 cm, EC = 4 cm, BD = 5 cm. And area of Δ BED = 9 cm2. Calculate the
(1) length of AB
(2) area of Δ ABC
The perimeters of two similar triangles are 25 cm and 15 cm respectively. If one side of first triangle is 9 cm, what is the corresponding side of the other triangle?
In ΔABC and ΔDEF, it is being given that: AB = 5 cm, BC = 4 cm and CA = 4.2 cm; DE=10cm, EF = 8 cm and FD = 8.4 cm. If AL ⊥ BC and DM ⊥ EF, find AL: DM.
Given: ∠GHE = ∠DFE = 90°,
DH = 8, DF = 12,
DG = 3x – 1 and DE = 4x + 2.
Find: the lengths of segments DG and DE.
The ratio between the corresponding sides of two similar triangles is 2 is to 5. Find the ratio between the areas of these triangles.
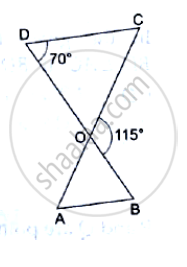
In the given figure, ΔODC~ΔOBA, ∠BOC = 115° and ∠CDO = 700.
Find (i) ∠DCO (ii) ∠DCO (iii) ∠OAB (iv) ∠OBA.
ΔABC ~ ΔDEF and their areas are respectively `100cm^2` and `49cm2`. If the altitude of ΔABC is 5cm, find the corresponding altitude of ΔDEF.
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle and PQ is a straight line meeting AB in P and AC in Q. If AP = 1cm, PB = 3cm, AQ = 1.5cm, QC = 4.5cm, prove that area of ΔAPQ is 116 of the area of ΔABC.
Are the triangles in the given figure similar? If yes, by which test?
In the given figure, ∠PQR = ∠PST = 90° ,PQ = 5cm and PS = 2cm.
(i) Prove that ΔPQR ~ ΔPST.
(ii) Find Area of ΔPQR : Area of quadrilateral SRQT.
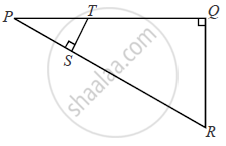
Figure shows Δ PQR in which ST || QR and SR and QT intersect each other at M. If `"PT"/"TR" = 5/3` find `("Ar" (triangle "MTS"))/("Ar" (triangle "MQR"))`
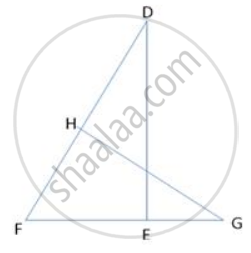
In figure , DEF is a right -angled triangle with ∠ E = 90 °.FE is produced to G and GH is drawn perpendicular to DE = 8 cm , DH = 8 cm ,DH = 6 cm and HF = 4 cm , find `("Ar" triangle "DEF")/("Ar" triangle "GHF")`
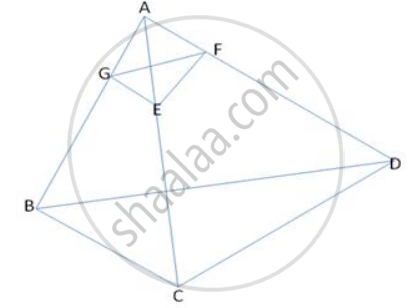
In the figure , ABCD is a quadrilateral . F is a point on AD such that AF = 2.1 cm and FD = 4.9 cm . E and G are points on AC and AB respectively such that EF || CD and GE || BC . Find `("Ar" triangle "BCD")/("Ar" triangle "GEF")`
In Δ PQR, MN is drawn parallel to QR. If PM = x, MQ = (x-2), PN = (x+2) and NR = (x-1), find the value of x.
The actual area of an island is 1872km2 . On a map, this area is 117 cm2. if the length of the coastline is 44cm on the map, find the length of its actual coastline.
On a map drawn to a scale of 1 : 25000, a triangular plot of a land is marked as ABC with AB= 6cm, BC = 8cm and ∠ ABC = 90° . Calculate the actual length of AB in km and the actual area of the plot in km2 .
A model of an aeroplane is made to a scale of 1 : 400. Calculate : the length, in cm, of the model; if the length of the aeroplane is 40 m.
The dimensions of the model of a multistorey building are 1.2 m × 75 cm × 2 m. If the scale factor is 1 : 30; find the actual dimensions of the building.
A line PQ is drawn parallel to the side BC of ΔABC which cuts side AB at P and side AC at Q. If AB = 9.0 cm, CA = 6.0 cm and AQ = 4.2 cm, find the length of AP.
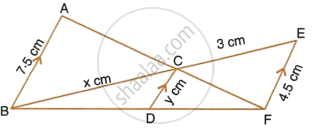
In the figure, given below, AB, CD and EF are parallel lines. Given AB = 7.5 cm, DC = y cm, EF = 4.5 cm, BC = x cm and CE = 3 cm, calculate the values of x and y.
Construct a ΔABC in which CA = 6 cm, AB = 5 cm and ∠BAC = 45°. Then construct a triangle whose sides are `3/5` of the corresponding sides of ΔABC.
If ΔABC ~ ΔDEF, then writes the corresponding congruent angles and also write the ratio of corresponding sides.
In ΔABC, D and E are the mid-point on AB and AC such that DE || BC.
If AD = 4x - 3, AE = 8x - 7, BD = 3x - 1 and CE = 5x - 3,Find x.
In figure, PQ is parallel to BC, AP : AB = 2 : 7. If QC = 0 and BC = 21,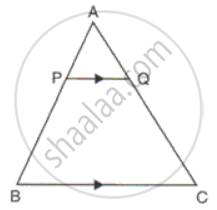
Find
(i) AQ
(ii) PQ
In ΔABC, DE is parallel to BC and DE = 3:8.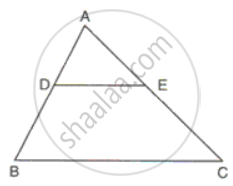
Find:
(i) AD : BD
(ii) AE, if AC = 16.
In ΔABC, point D divides AB in the ratio 5:7, Find: BC, If DE = 2.5cm
In ΔABC, point D divides AB in the ratio 5:7, Find: DE, If BC = 4.8cm
The sides PQ and PR of the ΔPQR are produced to S and T respectively. ST is drawn parallel to QR and PQ: PS = 3:4. If PT = 9.6 cm, find PR. If 'p' be the length of the perpendicular from P to QR, find the length of the perpendicular from P to ST in terms of 'p'.
In a right-angled triangle ABC, ∠B = 90°, P and Q are the points on the sides AB and AC such as PQBC, AB = 8 cm, AQ = 6 cm and PA:AB = 1:3. Find the lengths of AC and BC.
Given is a triangle with sides 3 cm, 5 cm and 6 cm. Find the sides of a triangle which is similar to the given triangle and its shortest side is 4.5 cm.
The areas of two similar triangles are 169cm2 and 121cm2 respectively. If one side of the larger triangle is 26cm, find the length of the corresponding side of the smaller triangle.
In ΔABC, DE is drawn parallel to BC cutting AB in the ratio 2 : 3. Calculate:
(i) `("area"(Δ"ADE"))/("area"(Δ"ABC")`
(i) `("area"("trapeziumEDBC"))/("area"(Δ"ABC"))`
ΔABC has been reduced by a scale factor 0.6 to ΔA'B'C'/ Calculate:Length of B' C', if BC = 8cm
ΔXYZ is enlarged to ΔX'Y'Z'. If XY = 12cm, YZ = 8cm and XZ = 14cm and the smallest side of ΔX'Y'Z' is 12cm, find the scale factor and use it to find the length of the other sides of the image ΔX'Y'Z'.
The scale of a map is 1 : 50000. The area of a city is 40 sq km which is to be represented on the map. Find: The length of a scale in km represented by 1cm on the map.
A plot of land of area 20km2 is represented on the map with a scale factor of 1:200000. Find: The area on the map that represented the plot of land.
A map is drawn to scale of 1:20000. Find: The distance covered by 6cm on the map
A map is drawn to scale of 1:20000. Find: The area of the lake on the map which has an actual area of 12km2
A model of cargo tuck is made to a scale of 1:40. The length of the model is 15cm. Calculate: The base area of the truck, if the base area of the model is 30m2
A model of a ship is made to a scale of 1:500. Find: The length of the ship, if length of the model is 1.2.
On a map drawn to a scale of 1:25000, a rectangular plot of land has sides 12cm x 16cm. Calculate: The diagonal distance of the plot in km
Check whether the triangles are similar and find the value of x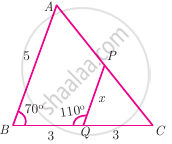
Two triangles QPR and QSR, right angled at P and S respectively are drawn on the same base QR and on the same side of QR. If PR and SQ intersect at T, prove that PT × TR = ST × TQ
D is the mid point of side BC and AE ⊥ BC. If BC = a, AC = b, AB = c, ED = x, AD = p and AE = h, prove that b2 + c2 = `2"p"^2 + "a"^2/2`
In any triangle _______ sides are opposite to equal angles
In the given figure, UB || AT and CU ≡ CB Prove that ΔCUB ~ ΔCAT and hence ΔCAT is isosceles.
Write the test of similarity for triangles given in figure.
In fig. BP ⊥ AC, CQ ⊥ AB, A−P−C, and A−Q−B then show that ΔAPB and ΔAQC are similar.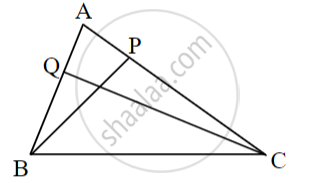
In ΔAPB and ΔAQC
∠APB = [ ]° ......(i)
∠AQC = [ ]° ......(ii)
∠APB ≅ ∠AQC .....[From (i) and (ii)]
∠PAB ≅ ∠QAC .....[______]
ΔAPB ~ ΔAQC .....[______]
In ΔABC, AP ⊥ BC and BQ ⊥ AC, B−P−C, A−Q−C, then show that ΔCPA ~ ΔCQB. If AP = 7, BQ = 8, BC = 12, then AC = ?
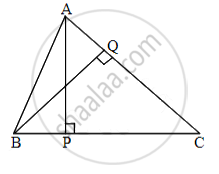
In ΔCPA and ΔCQB
∠CPA ≅ [∠ ______] ...[each 90°]
∠ACP ≅ [∠ ______] ...[common angle]
ΔCPA ~ ΔCQB ......[______ similarity test]
`"AP"/"BQ" = (["______"])/"BC"` .......[corresponding sides of similar triangles]
`7/8 = (["______"])/12`
AC × [______] = 7 × 12
AC = 10.5
In given fig., quadrilateral PQRS, side PQ || side SR, AR = 5 AP, then prove that, SR = 5PQ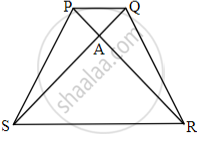
In Quadrilateral ABCD, side AD || BC, diagonal AC and BD intersect in point P, then prove that `"AP"/"PD" = "PC"/"BP"`
Prove that if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle intersecting the other two sides in distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
Using the above theorem prove that a line through the point of intersection of the diagonals and parallel to the base of the trapezium divides the non-parallel sides in the same ratio.
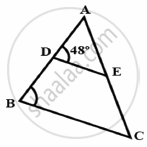
In figure, if AD = 6cm, DB = 9cm, AE = 8cm and EC = 12cm and ∠ADE = 48°. Find ∠ABC.