Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The difference between any two consecutive interior angles of a polygon is 5°. If the smallest angle is 120°, find the number of the sides of the polygon.
उत्तर
The angles of the polygon will form an A.P. with common difference d as 5° and first term a as 120°.
It is known that the sum of all angles of a polygon with n sides is 180° (n – 2).
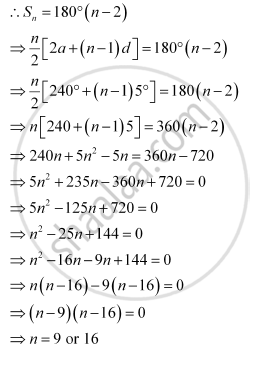
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Sum of the first p, q and r terms of an A.P. are a, b and c, respectively.
Prove that `a/p (q - r) + b/q (r- p) + c/r (p - q) = 0`
The ratio of the sums of m and n terms of an A.P. is m2: n2. Show that the ratio of mth and nthterm is (2m – 1): (2n – 1)
Find the sum of integers from 1 to 100 that are divisible by 2 or 5.
Find the sum of all two digit numbers which when divided by 4, yields 1 as remainder.
A sequence is defined by an = n3 − 6n2 + 11n − 6, n ϵ N. Show that the first three terms of the sequence are zero and all other terms are positive.
The nth term of a sequence is given by an = 2n2 + n + 1. Show that it is not an A.P.
Find:
10th term of the A.P. 1, 4, 7, 10, ...
Is 302 a term of the A.P. 3, 8, 13, ...?
If the nth term of the A.P. 9, 7, 5, ... is same as the nth term of the A.P. 15, 12, 9, ... find n.
The sum of 4th and 8th terms of an A.P. is 24 and the sum of the 6th and 10th terms is 34. Find the first term and the common difference of the A.P.
The first and the last terms of an A.P. are a and l respectively. Show that the sum of nthterm from the beginning and nth term from the end is a + l.
If < an > is an A.P. such that \[\frac{a_4}{a_7} = \frac{2}{3}, \text { find }\frac{a_6}{a_8}\].
If the sum of three numbers in A.P. is 24 and their product is 440, find the numbers.
Find the sum of the following arithmetic progression :
3, 9/2, 6, 15/2, ... to 25 terms
Find the sum of all integers between 50 and 500 which are divisible by 7.
Find the sum of the series:
3 + 5 + 7 + 6 + 9 + 12 + 9 + 13 + 17 + ... to 3n terms.
Find an A.P. in which the sum of any number of terms is always three times the squared number of these terms.
If the sum of n terms of an A.P. is nP + \[\frac{1}{2}\] n (n − 1) Q, where P and Q are constants, find the common difference.
If a2, b2, c2 are in A.P., prove that \[\frac{a}{b + c}, \frac{b}{c + a}, \frac{c}{a + b}\] are in A.P.
If a, b, c is in A.P., then show that:
b + c − a, c + a − b, a + b − c are in A.P.
If \[\frac{b + c}{a}, \frac{c + a}{b}, \frac{a + b}{c}\] are in A.P., prove that:
bc, ca, ab are in A.P.
If a, b, c is in A.P., prove that:
(a − c)2 = 4 (a − b) (b − c)
If a, b, c is in A.P., prove that:
a3 + c3 + 6abc = 8b3.
Insert five numbers between 8 and 26 such that the resulting sequence is an A.P.
A manufacturer of radio sets produced 600 units in the third year and 700 units in the seventh year. Assuming that the product increases uniformly by a fixed number every year, find (i) the production in the first year (ii) the total product in 7 years and (iii) the product in the 10th year.
A man is employed to count Rs 10710. He counts at the rate of Rs 180 per minute for half an hour. After this he counts at the rate of Rs 3 less every minute than the preceding minute. Find the time taken by him to count the entire amount.
If the sums of n terms of two arithmetic progressions are in the ratio 2n + 5 : 3n + 4, then write the ratio of their m th terms.
If \[\frac{3 + 5 + 7 + . . . + \text { upto n terms }}{5 + 8 + 11 + . . . . \text { upto 10 terms }}\] 7, then find the value of n.
If m th term of an A.P. is n and nth term is m, then write its pth term.
If a1, a2, a3, .... an are in A.P. with common difference d, then the sum of the series sin d [cosec a1cosec a2 + cosec a1 cosec a3 + .... + cosec an − 1 cosec an] is
In the arithmetic progression whose common difference is non-zero, the sum of first 3 n terms is equal to the sum of next n terms. Then the ratio of the sum of the first 2 n terms to the next 2 nterms is
The first and last term of an A.P. are a and l respectively. If S is the sum of all the terms of the A.P. and the common difference is given by \[\frac{l^2 - a^2}{k - (l + a)}\] , then k =
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let Sn denote the sum of first n terms of an A.P. If S2n = 3Sn, then S3n : Sn is equal to
The pth term of an A.P. is a and qth term is b. Prove that the sum of its (p + q) terms is `(p + q)/2[a + b + (a - b)/(p - q)]`.
Show that (x2 + xy + y2), (z2 + xz + x2) and (y2 + yz + z2) are consecutive terms of an A.P., if x, y and z are in A.P.
If the sum of m terms of an A.P. is equal to the sum of either the next n terms or the next p terms, then prove that `(m + n) (1/m - 1/p) = (m + p) (1/m - 1/n)`
A man accepts a position with an initial salary of Rs 5200 per month. It is understood that he will receive an automatic increase of Rs 320 in the very next month and each month thereafter. Find his salary for the tenth month
Any term of an A.P. (except first) is equal to half the sum of terms which are equidistant from it.
If the sum of n terms of a sequence is quadratic expression then it always represents an A.P
The number of terms in an A.P. is even; the sum of the odd terms in lt is 24 and that the even terms is 30. If the last term exceeds the first term by `10 1/2`, then the number of terms in the A.P. is ______.
