Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the sum of integers from 1 to 100 that are divisible by 2 or 5.
Solution
The integers from 1 to 100, which are divisible by 2, are 2, 4, 6… 100.
This forms an A.P. with both the first term and common difference equal to 2.
⇒100 = 2 + (n –1) 2
⇒ n = 50

The integers from 1 to 100, which are divisible by 5, are 5, 10… 100.
This forms an A.P. with both the first term and common difference equal to 5.
∴100 = 5 + (n –1) 5
⇒ 5n = 100
⇒ n = 20
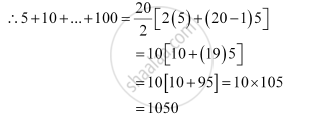
The integers, which are divisible by both 2 and 5, are 10, 20, … 100.
This also forms an A.P. with both the first term and common difference equal to 10.
∴100 = 10 + (n –1) (10)
⇒ 100 = 10n
⇒ n = 10
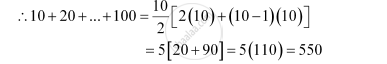
∴Required sum = 2550 + 1050 – 550 = 3050
Thus, the sum of the integers from 1 to 100, which are divisible by 2 or 5, is 3050.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the sum of odd integers from 1 to 2001.
The sums of n terms of two arithmetic progressions are in the ratio 5n + 4: 9n + 6. Find the ratio of their 18th terms
Insert five numbers between 8 and 26 such that the resulting sequence is an A.P.
Between 1 and 31, m numbers have been inserted in such a way that the resulting sequence is an A.P. and the ratio of 7th and (m – 1)th numbers is 5:9. Find the value of m.
The difference between any two consecutive interior angles of a polygon is 5°. If the smallest angle is 120°, find the number of the sides of the polygon.
Let the sum of n, 2n, 3n terms of an A.P. be S1, S2 and S3, respectively, show that S3 = 3 (S2– S1)
Show that the following sequence is an A.P. Also find the common difference and write 3 more terms in case.
9, 7, 5, 3, ...
Find:
18th term of the A.P.
\[\sqrt{2}, 3\sqrt{2}, 5\sqrt{2},\]
Which term of the A.P. 3, 8, 13, ... is 248?
Which term of the A.P. 4, 9, 14, ... is 254?
Is 302 a term of the A.P. 3, 8, 13, ...?
The 6th and 17th terms of an A.P. are 19 and 41 respectively, find the 40th term.
If 10 times the 10th term of an A.P. is equal to 15 times the 15th term, show that 25th term of the A.P. is zero.
The sum of 4th and 8th terms of an A.P. is 24 and the sum of the 6th and 10th terms is 34. Find the first term and the common difference of the A.P.
The first and the last terms of an A.P. are a and l respectively. Show that the sum of nthterm from the beginning and nth term from the end is a + l.
If the sum of three numbers in A.P. is 24 and their product is 440, find the numbers.
The angles of a quadrilateral are in A.P. whose common difference is 10°. Find the angles.
Find the sum of the following arithmetic progression :
50, 46, 42, ... to 10 terms
Find the sum of the following serie:
2 + 5 + 8 + ... + 182
Find the sum of all odd numbers between 100 and 200.
Solve:
1 + 4 + 7 + 10 + ... + x = 590.
If Sn = n2 p and Sm = m2 p, m ≠ n, in an A.P., prove that Sp = p3.
If \[\frac{1}{a}, \frac{1}{b}, \frac{1}{c}\] are in A.P., prove that:
a (b +c), b (c + a), c (a +b) are in A.P.
If a2, b2, c2 are in A.P., prove that \[\frac{a}{b + c}, \frac{b}{c + a}, \frac{c}{a + b}\] are in A.P.
If a, b, c is in A.P., then show that:
a2 (b + c), b2 (c + a), c2 (a + b) are also in A.P.
A farmer buys a used tractor for Rs 12000. He pays Rs 6000 cash and agrees to pay the balance in annual instalments of Rs 500 plus 12% interest on the unpaid amount. How much the tractor cost him?
Shamshad Ali buys a scooter for Rs 22000. He pays Rs 4000 cash and agrees to pay the balance in annual instalments of Rs 1000 plus 10% interest on the unpaid amount. How much the scooter will cost him.
A man is employed to count Rs 10710. He counts at the rate of Rs 180 per minute for half an hour. After this he counts at the rate of Rs 3 less every minute than the preceding minute. Find the time taken by him to count the entire amount.
A man saved ₹66000 in 20 years. In each succeeding year after the first year he saved ₹200 more than what he saved in the previous year. How much did he save in the first year?
If Sn denotes the sum of first n terms of an A.P. < an > such that
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
If in an A.P., the pth term is q and (p + q)th term is zero, then the qth term is
If second, third and sixth terms of an A.P. are consecutive terms of a G.P., write the common ratio of the G.P.
If a, b, c are in A.P. and x, y, z are in G.P., then the value of xb − c yc − a za − b is
The first three of four given numbers are in G.P. and their last three are in A.P. with common difference 6. If first and fourth numbers are equal, then the first number is
The first term of an A.P. is a, the second term is b and the last term is c. Show that the sum of the A.P. is `((b + c - 2a)(c + a))/(2(b - a))`.
The pth term of an A.P. is a and qth term is b. Prove that the sum of its (p + q) terms is `(p + q)/2[a + b + (a - b)/(p - q)]`.
If the sum of m terms of an A.P. is equal to the sum of either the next n terms or the next p terms, then prove that `(m + n) (1/m - 1/p) = (m + p) (1/m - 1/n)`
If the first term of an A.P. is 3 and the sum of its first 25 terms is equal to the sum of its next 15 terms, then the common difference of this A.P. is ______.
