Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
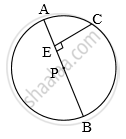
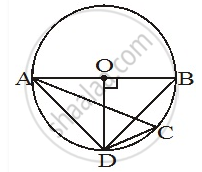
In the above figure, seg AB is a diameter of a circle with centre P. C is any point on the circle. seg CE ⊥ seg AB. Prove that CE is the geometric mean of AE and EB. Write the proof with the help of the following steps:
a. Draw ray CE. It intersects the circle at D.
b. Show that CE = ED.
c. Write the result using the theorem of the intersection of chords inside a circle. d. Using CE = ED, complete the proof.
Solution
The solution is not available
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the length of the tangent drawn from a point whose distance from the centre of a circle is 25 cm. Given that the radius of the circle is 7 cm.
In two concentric circles, prove that all chords of the outer circle which touch the inner circle are of equal length.
If PT is a tangent at T to a circle whose center is O and OP = 17 cm, OT = 8 cm. Find the length of tangent segment PT.
If AB, AC, PQ are tangents in Fig. and AB = 5cm find the perimeter of ΔAPQ.
Fill in the blank
A continuous piece of a circle is ............... of the circle
In the given figure, a triangle ABC is drawn to circumscribe a circle of radius 2 cm such that the segments BD and DC into which BC is divided by the point of contact D, are of lengths 4cm and 3cm respectively. If the area of 2 ABC 21cm then find the lengths of sides AB and AC.
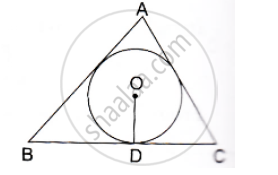
In the given figure, a cradle inscribed in a triangle ABC touches the sides AB, BC and CA at points D, E and F respectively. If AB = 14cm, BC = 8cm and CA=12 cm. Find the length AD, BE and CF.
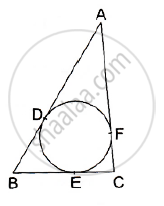
In Figure 3, a circle touches all the four sides of a quadrilateral ABCD whose sides are AB = 6 cm, BC = 9 cm and CD = 8 cm. Find the length of the side AD.
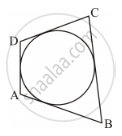
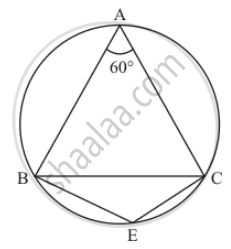
In the given figure, ΔABC is an equilateral triangle. Find m∠BEC.
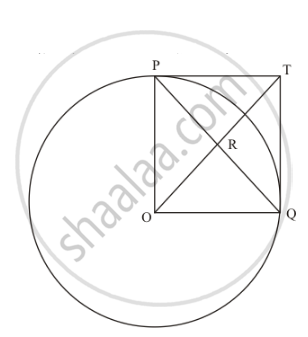
In the given figure, PO \[\perp\] QO. The tangents to the circle at P and Q intersect at a point T. Prove that PQ and OTare right bisector of each other.
Suppose you are given a circle. Describe a method by which you can find the center of this circle.
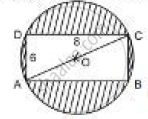
Find the area of the shaded region in the figure If ABCD is a rectangle with sides 8 cm and 6 cm and O is the centre of the circle. (Take π= 3.14)
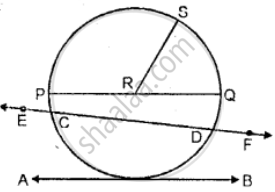
Use the figure given below to fill in the blank:
______ is a chord of the circle.
Construct a triangle ABC with AB = 4.2 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 5cm. Construct the circumcircle of the triangle drawn.
In the given figure, AB is the diameter of the circle. Find the value of ∠ACD.
If a number of circles pass through the endpoints P and Q of a line segment PQ, then their centres lie on the perpendicular bisector of PQ.
A circle of radius 3 cm with centre O and a point L outside the circle is drawn, such that OL = 7 cm. From the point L, construct a pair of tangents to the circle. Justify LM and LN are the two tangents.
A 7 m broad pathway goes around a circular park with a circumference of 352 m. Find the area of road.
AB is a chord of a circle with centre O. AOC is diameter of circle, AT is a tangent at A.
Write answers of the following questions:
- Draw the figure using the given information.
- Find the measures of ∠CAT and ∠ABC with reasons.
- Whether ∠CAT and ∠ABC are congruent? Justify your answer.
The circumcentre of a triangle is the point which is ______.
