Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is metamerism?
Solution 1
The ethers with the same molecular formula but different alkyl groups attached on either side of the oxygen atom are called metamers of each other, and the phenomenon is called metamerism
Solution 2
Metamerism (positional isomerism): Ethers having same molecular formula but different alkyl groups attached on either side of the oxygen atom are called metamers of each other. This phenomenon is called metamerism (positional isomerism).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain metamerism with suitable examples of ethers
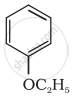
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound:
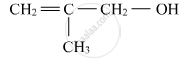
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H2C = CH - CH - CH2 - CH2 - CH3}\\
|\phantom{..........}\\
\ce{OH}\phantom{........}
\end{array}\]
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - C = C - CH2OH}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\ce{Br}\phantom{...}
\end{array}\]
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{................}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{.............}|\\
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - C - CH3}\\
|\phantom{......}|\phantom{......}|\\
\phantom{...}\ce{CH3\phantom{.}}\phantom{..}\ce{OH}\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H3C - CH - CH2 - CH - CH - CH2 - CH3}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{.............}|\phantom{......}|\phantom{.........}\\
\phantom{}\ce{OH}\phantom{..........}\ce{OH}\phantom{...}\ce{C2H5}\phantom{......}
\end{array}\]
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{HO - CH2 - CH - CH2 - OH}\\
|\phantom{..}\\
\ce{OH}
\end{array}\]
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
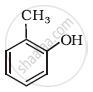
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
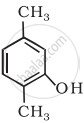
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
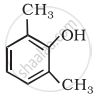
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - O - CH2 - CH - CH3}\\
\phantom{..........}|\\
\phantom{............}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
C6H5 – O – C2H5
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - O - CH - CH2 - CH3}\\
\phantom{...}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
- Draw the structures of all isomeric alcohols of molecular formula C5H12O and give their IUPAC names.
- Classify the isomers of alcohols in the above question as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Give IUPAC name of the following ether:
Ethylidene dichloride when boiled with aqueous solution of NaOH yields _______.
(A) formaldehyde
(B) acetaldehyde
(C) acetone
(D) ethyl methyl ketone
Write the structure and IUPAC name of 'methyl-n-propyl ether'.
What is the action of hot HI on it?
3-Methylbutane-2-ol on heating with HI gives ______
How is phenol converted into the following?
benzoquinone
How is phenol converted into the following?
picric acid
Write IUPAC name of the following compound (CH3)2 N − CH2CH3
Give reasons Fluoride ion has higher hydration enthalpy than chloride ion.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
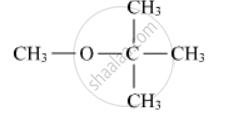
Write the IUPAC name of the following :
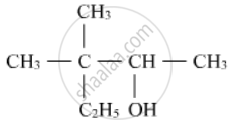
What.will be the product fonned when chlorobenzene is heated with sodium metal in the presence of dry ether?
Resorcinol on distillation with zinc dust gives _________.
Write structural formulae for Methyl vinyl ether.
Write structural formulae for Cyclohex-2-en-1-ol.
Write IUPAC name of the following
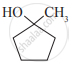
Write IUPAC name of the following
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3-CH-CH-CH2-OH}\\|\phantom{.....}|\phantom{.......}\\\ce{OH}\phantom{..}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}\end{array}\]
Write IUPAC names of the following
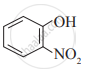
Write IUPAC names of the following
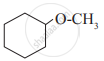
Glycerol is ____________.
Isopropyl alcohol on oxidation forms:
Give IUPAC names of the following compound:
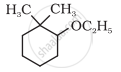
Give IUPAC names of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\ce{H}\phantom{..}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{}\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{}\\
\phantom{.}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{OH}\phantom{.}\ce{H}\phantom{.}\\
\end{array}\]
C6H5OCH2CH3 is called:
One of the following is not a dihydroxy derivative of benzene.
The compound HOCH2 – CH2OH is __________.
An example of a compound with functional group – O – is ____________.
Butane-2-ol is ____________.
Cresol has ____________.
Ethyl alcohol is industrially prepared from ethylene by:
Which of the following compounds is oxidised to prepare methyl ethyl ketone?
n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?
When ethyl alcohol reacts with acetic acid, the products formed are:
1-Propanol and 2-propanol can be best distinguished by:
Which of the following is most acidic?
The IUPAC name of the ether CH2 = CH–CH2OCH3 is:
\[\ce{HC ≡ CH ->[HgSO4][H2SO4] ->[CH3MgBr][H2O] ->[PBr3]}\]
The heating of phenyl methyl ether with HI produces:
\[\ce{Phenol ->[Zn, dust] 'X' ->[CH3Cl][Anhy. AlCl3] 'Y' ->[Alkaline][KMnO4] 'Z'}\]
The product ‘Z’ is:
Among the following sets of reactants which one produces anisole?
IUPAC name of the compound is:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3-CH-OCH3}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}
\end{array}\]
The correct acidic strength order of the following is:
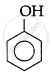
(I)

(II)
(III)
Which of the following compounds will react with sodium hydroxide solution in water?
Write the IUPAC name of the compound given below.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - CH2 - C = C - OH}\\
\phantom{........}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{}\\
\phantom{..............}\ce{CH3 CH2OH}
\end{array}\]
Match the starting materials given in Column I with the products formed by these (Column II) in the reaction with HI.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | CH3—O—CH3 | (a) | 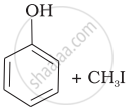 |
| (ii) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{..................}\\ \backslash\phantom{.............}\\ \ce{CH-O-CH3}\\ /\phantom{..............}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{..................} \end{array}\] |
(b) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{....}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3-C-I + CH3OH}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{....} \end{array}\] |
| (iii) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\\ |\phantom{....}\\ \ce{H3C-C-O-CH3}\\ |\phantom{....}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{..} \end{array}\] |
(c) | 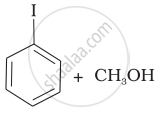 |
| (iv) | 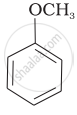 |
(d) | CH3—OH + CH3—I |
| (e) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................}\\ \backslash\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH-OH + CH3I}\\ /\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................} \end{array}\] |
||
| (f) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................}\\ \backslash\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH-I + CH3OH}\\ /\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................} \end{array}\] |
||
| (g) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{....}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3-C-OH + CH3I}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{....} \end{array}\] |
Assertion: Addition reaction of water to but-1-ene in acidic medium yields butan-1-ol.
Reason: Addition of water in acidic medium proceeds through the formation of primary carbocation.
Assertion: p-nitrophenol is more acidic than phenol.
Reason: Nitro group helps in the stabilisation of the phenoxide ion by dispersal of negative charge due to resonance.
Assertion: IUPAC name of the compound
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH - O - CH2 - CH2 - CH3}\\
|\phantom{....................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}
\end{array}\] is 2-Ethoxy-2-methylethane.
Reason: In IUPAC nomenclature, ether is regarded as hydrocarbon derivative in which a hydrogen atom is replaced by —OR or —OAr group [where R = alkyl group and Ar = aryl group]
Assertion: Like bromination of benzene, bromination of phenol is also carried out in the presence of Lewis acid.
Reason: Lewis acid polarises the bromine molecule.
Assertion: Phenols give o- and p-nitrophenol on nitration with conc. \[\ce{HNO3}\] and \[\ce{H2SO4}\] mixture.
Reason: –OH group in phenol is o–, p– directing.
Explain why Lewis acid is not required in bromination of phenol?
How can phenol be converted to aspirin?
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound.
Convert the following:
Ethyl alcohol into ethyl acetate
Write chemical reactions for the following conversion:
Acetic acid into ethyl alcohol
Identify A and B in the following:

Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{................}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{.............}|\\
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - C - CH3}\\
|\phantom{......}|\phantom{......}|\\
\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\ce{OH}\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
Draw structure of the following compound.
2. 5-Diethylphenol
Draw structure of the following compound.
2-Methoxypropane
Give the structures of Thiosulphuric acid and Peroxy monosulphuric acid.
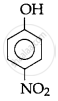
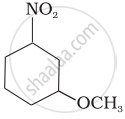
The IUPAC name of  is ______.
is ______.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..............}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{............}|\\
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - C - CH3}\\
|\phantom{.....}|\phantom{......}|\\
\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\ce{OH}\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
Write the IUPAC name.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{................}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{.............}|\\
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - C -CH3}\\
\phantom{.}|\phantom{......}|\phantom{......}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{CH3\phantom{...}\ce{OH}\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}}\
\end{array}\]
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{...............}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{.............}|\\
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - C - CH3}\\
|\phantom{......}|\phantom{......}|\\
\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\ce{OH}\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
