Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
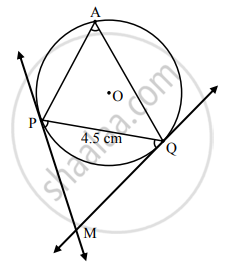
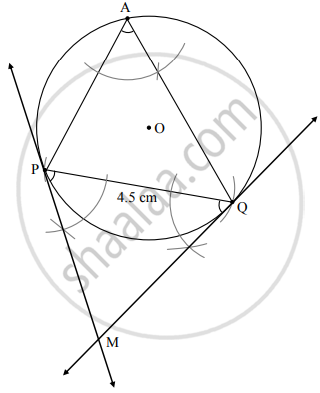
Draw a circle of radius 2.7 cm and draw a chord PQ of length 4.5 cm. Draw tangents at points P and Q without using centre.
उत्तर
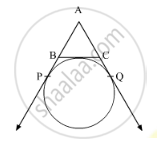
Rough Figure:
Steps of construction:
- Draw a circle of radius 2.7 cm.
- Draw a chord PQ of length 4.5 cm.
- Take a point A on the major arc, other than P and Q.
- Join PA and QA.
- Using P and Q as vertices and chord PQ as one side, draw ∠MPQ and ∠MQP equal to ∠PAQ.
- Lines containing the rays PM and QM are the tangents to the circle at P and Q respectively.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A circle can have ______ parallel tangents at the most.
A circle touches all the four sides of a quadrilateral ABCD. Prove that AB + CD = BC + DA.
In the given figure O is the centre of the circle. Tangents A and B meet at C. If ∠ACO = 30°, find
1) ∠BCO
2) ∠AOB
3) ∠APB
In the following figure, O is the centre of the circle and AB is a tangent to it at point B. ∠BDC = 65°. Find ∠BAO.
In the given figure, find TP if AT = 16 cm and AB = 12 cm.
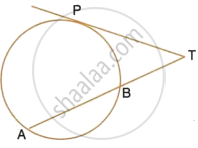
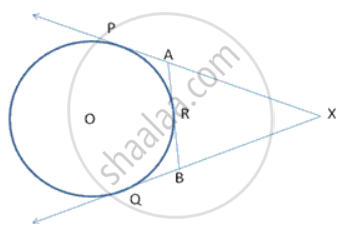
In Figure 2, XP and XQ are two tangents to the circle with centre O, drawn from an external point X. ARB is another tangent, touching the circle at R. Prove that XA + AR = XB + BR ?

In Figure 1, AP, AQ and BC are tangents to the circle. If AB = 5 cm, AC = 6 cm and BC
= 4 cm, then the length of AP (in cm) is
If Δ ABC is isosceles with AB = AC and C (O, r) is the incircle of the ΔABC touching BC at L,prove that L bisects BC.
AB is a diameter and AC is a chord of a circle with centre O such that ∠BAC = 30°. The tangent at C intersects extended AB at a point D. Prove that BC = BD.
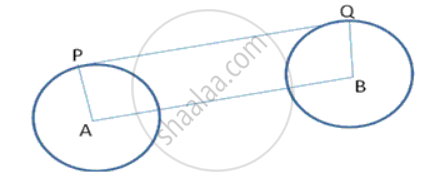
Calculate the length of direct common tangent to two circles of radii 3cm and Bern with their centres 13cm apart.
In the figure, XP and XQ are tangents from X to the circle with centre O. R is a point on the circle. Prove that XA + AR = XB + BR.
In a square ABCD, its diagonal AC and BD intersect each other at point O. The bisector of angle DAO meets BD at point M and bisector of angle ABD meets AC at N and AM at L. Show that - ALOB is a cyclic quadrilateral.
At one end A of a diameter AB of a circle of radius 5 cm, tangent XAY is drawn to the circle. The length of the chord CD parallel to XY and at a distance 8 cm from A is ______
In figure, AT is a tangent to the circle with centre O such that OT = 4 cm and ∠OTA = 30°. Then AT is equal to ______.

The distance between the centres of equal circles each of radius 3 cm is 10 cm. The length of a transverse tangent AB is ______
Construct a pair of tangents to a circle of radius 4 cm, which are inclined to each other at an angle of 60°.
Construct a pair of tangents to a circle of radius 5 cm which are inclined to each other at an angle of 60°.
ΔABC circumscribes a circle of radius r such that ∠B = 90°. If AB = 3 cm and BC = 4 cm, then find the value of r.
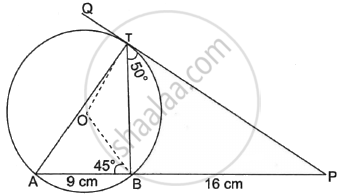
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. PQ is a tangent to the circle at T. Chord AB produced meets the tangent at P.
AB = 9 cm, BP = 16 cm, ∠PTB = 50° ∠OBA = 45°
Find:
- Length of PT
- ∠BAT
- ∠BOT
- ∠ABT
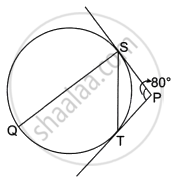
In the given diagram, PS and PT are the tangents to the circle. SQ || PT and ∠SPT = 80°. The value of ∠QST is ______.