Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Express (sin 67° + cos 75°) in terms of trigonometric ratios of the angle between 0° and 45°.
उत्तर
(sin 67° + cos 75°)
= (sin (90°−23°) + cos (90°−15°)) .....(∵ sin(90°−θ) = cosθ and cos(90°−θ) = sinθ)
= (cos 23°+ sin 15°)
संबंधित प्रश्न
Prove the following trigonometric identities:
`(1 - cos^2 A) cosec^2 A = 1`
Prove the following identities:
`tan^2A - tan^2B = (sin^2A - sin^2B)/(cos^2A * cos^2B)`
Prove the following identities:
(1 + cot A – cosec A)(1 + tan A + sec A) = 2
Prove the following identities:
`sqrt((1 - cosA)/(1 + cosA)) = sinA/(1 + cosA)`
If x = a cos θ and y = b cot θ, show that:
`a^2/x^2 - b^2/y^2 = 1`
If 3 `cot theta = 4 , "write the value of" ((2 cos theta - sin theta))/(( 4 cos theta - sin theta))`
If `sqrt(3) sin theta = cos theta and theta ` is an acute angle, find the value of θ .
`If sin theta = cos( theta - 45° ),where theta " is acute, find the value of "theta` .
What is the value of \[\frac{\tan^2 \theta - \sec^2 \theta}{\cot^2 \theta - {cosec}^2 \theta}\]
Prove the following identity :
`sin^4A + cos^4A = 1 - 2sin^2Acos^2A`
Prove the following identity :
`(1 + cosA)/(1 - cosA) = tan^2A/(secA - 1)^2`
Prove that cosec2 (90° - θ) + cot2 (90° - θ) = 1 + 2 tan2 θ.
Prove that (cosec A - sin A)( sec A - cos A) sec2 A = tan A.
Prove the following identities.
cot θ + tan θ = sec θ cosec θ
If (sin α + cosec α)2 + (cos α + sec α)2 = k + tan2α + cot2α, then the value of k is equal to
a cot θ + b cosec θ = p and b cot θ + a cosec θ = q then p2 – q2 is equal to
Choose the correct alternative:
sin θ = `1/2`, then θ = ?
tan2θ – sin2θ = tan2θ × sin2θ. For proof of this complete the activity given below.
Activity:
L.H.S = `square`
= `square (1 - (sin^2theta)/(tan^2theta))`
= `tan^2theta (1 - square/((sin^2theta)/(cos^2theta)))`
= `tan^2theta (1 - (sin^2theta)/1 xx (cos^2theta)/square)`
= `tan^2theta (1 - square)`
= `tan^2theta xx square` .....[1 – cos2θ = sin2θ]
= R.H.S
Prove that `(1 + sec theta - tan theta)/(1 + sec theta + tan theta) = (1 - sin theta)/cos theta`
Find the value of sin2θ + cos2θ
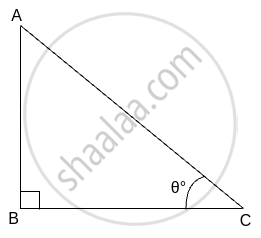
Solution:
In Δ ABC, ∠ABC = 90°, ∠C = θ°
AB2 + BC2 = `square` .....(Pythagoras theorem)
Divide both sides by AC2
`"AB"^2/"AC"^2 + "BC"^2/"AC"^2 = "AC"^2/"AC"^2`
∴ `("AB"^2/"AC"^2) + ("BC"^2/"AC"^2) = 1`
But `"AB"/"AC" = square and "BC"/"AC" = square`
∴ `sin^2 theta + cos^2 theta = square`
