Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If a line makes angles 90° and 60° respectively with the positive directions of x and y axes, find the angle which it makes with the positive direction of z-axis.
Solution
Let the direction cosines of the line be l, m and n.
We know that l2 + m2 + n2 = 1.
Let the line make angle θ with the positive direction of the z-axis.
α=90°, β=60°, γ=Θ
So, cos290°+cos260°+cos2θ=1
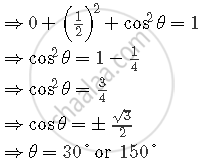
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Solve the equation for x:sin−1x+sin−1(1−x)=cos−1x
Find the principal values of the following:
`cos^-1(sin (4pi)/3)`
Find the principal values of the following:
`cos^-1(tan (3pi)/4)`
`sin^-1{(sin - (17pi)/8)}`
Evaluate the following:
`cos^-1{cos (5pi)/4}`
Evaluate the following:
`cos^-1(cos5)`
Evaluate the following:
`tan^-1(tan (9pi)/4)`
Evaluate the following:
`cot^-1(cot (4pi)/3)`
Write the following in the simplest form:
`sin{2tan^-1sqrt((1-x)/(1+x))}`
Evaluate the following:
`sin(sec^-1 17/8)`
Prove the following result
`tan(cos^-1 4/5+tan^-1 2/3)=17/6`
Evaluate:
`cot{sec^-1(-13/5)}`
Evaluate:
`sin(tan^-1x+tan^-1 1/x)` for x < 0
`2tan^-1 1/5+tan^-1 1/8=tan^-1 4/7`
`2tan^-1 3/4-tan^-1 17/31=pi/4`
If `sin^-1 (2a)/(1+a^2)+sin^-1 (2b)/(1+b^2)=2tan^-1x,` Prove that `x=(a+b)/(1-ab).`
Solve the following equation for x:
`3sin^-1 (2x)/(1+x^2)-4cos^-1 (1-x^2)/(1+x^2)+2tan^-1 (2x)/(1-x^2)=pi/3`
If x < 0, then write the value of cos−1 `((1-x^2)/(1+x^2))` in terms of tan−1 x.
If −1 < x < 0, then write the value of `sin^-1((2x)/(1+x^2))+cos^-1((1-x^2)/(1+x^2))`
Write the value of \[\tan^{- 1} \left\{ 2\sin\left( 2 \cos^{- 1} \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \right\}\]
The set of values of `\text(cosec)^-1(sqrt3/2)`
Wnte the value of\[\cos\left( \frac{\tan^{- 1} x + \cot^{- 1} x}{3} \right), \text{ when } x = - \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\]
If \[\cos\left( \sin^{- 1} \frac{2}{5} + \cos^{- 1} x \right) = 0\], find the value of x.
2 tan−1 {cosec (tan−1 x) − tan (cot−1 x)} is equal to
If \[\cos^{- 1} x > \sin^{- 1} x\], then
If x = a (2θ – sin 2θ) and y = a (1 – cos 2θ), find \[\frac{dy}{dx}\] When \[\theta = \frac{\pi}{3}\] .
Find : \[\int\frac{2 \cos x}{\left( 1 - \sin x \right) \left( 1 + \sin^2 x \right)}dx\] .
Prove that : \[\cot^{- 1} \frac{\sqrt{1 + \sin x} + \sqrt{1 - \sin x}}{\sqrt{1 + \sin x} - \sqrt{1 - \sin x}} = \frac{x}{2}, 0 < x < \frac{\pi}{2}\] .
Find the real solutions of the equation
`tan^-1 sqrt(x(x + 1)) + sin^-1 sqrt(x^2 + x + 1) = pi/2`
