Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The ligand triethylenetetramine is _______.
Options
monodentate
bidentate
tridentate
tetradentate
Solution
The ligand triethylenetetramine is tetradentate.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Classify the following ligands into monodentate and polydentate —
- Ammonia
- Carbon monoxide
- Ethylene diamine
- Ethylene diamine tetra acetate ion
What is the coordination entity formed when excess of aqueous KCN is added to an aqueous solution of copper sulphate? Why is it that no precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained when H2S(g) is passed through this solution?
Give the oxidation state, d-orbital occupation and coordination number of the central metal ion in the following complex:
K3[Co(C2O4)3]
Give the oxidation state, d-orbital occupation and coordination number of the central metal ion in the following complex:
cis-[CrCl2(en)2]Cl
Give the oxidation state, d-orbital occupation and coordination number of the central metal ion in the following complex:
(NH4)2[CoF4]
Amongst the following, the most stable complex is:
Predict the co-ordination No. of cs+ ion if `r_(Cs)^+` = 1.69Å and `r_(Cl)^-` = 1.81Å.
Write the structures of compounds A, B and C in the following reactions
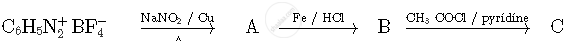
Ligand (en) is an example of ___________.
The coordination number of the central ion may be obtained from:
When 0.1 mol \[\ce{CoCl3 (NH3)5}\] is treated with excess of \[\ce{AgNO3}\], 0.2 mol of \[\ce{AgCl}\] are obtained. The conductivity of solution will correspond to ______.
A complex of the type \[\ce{[M(AA)2X2]^{n+}}\] is known to be optically active. What does this indicate about the structure of the complex? Give one example of such complex.
Match the coordination compounds given in Column I with the central metal atoms given in Column II and assign the correct code:
| Column I (Coordination Compound) | Column II (Central metal atom) |
| A. Chlorophyll | 1. rhodium |
| B. Blood pigment | 2. cobalt |
| C. Wilkinson catalyst | 3. calcium |
| D. Vitamin B12 | 4. iron |
| 5. magnesium |
Match the compounds given in Column I with the oxidation state of cobalt present in it (given in Column II) and assign the correct code:
| Column I (Compound) | Column II (Oxidation state of Co) |
| A. \[\ce{[Co(NCS)(NH3)5](SO3)}\] | 1. + 4 |
| B. \[\ce{[Co(NH3)4 CL2]SO4}\] | 2. 0 |
| C. \[\ce{Na4[Co(S2O3)3]}\] | 3. + 1 |
| D. \[\ce{[Co2(CO)8]}\] | 4. + 2 |
| 5. + 3 |
Assertion: \[\ce{Cr(H2O)6]Cl2 and [Fe(H2O)6]Cl2}\] are reducing in nature.
Reason: Unpaired electrons are present in their d-orbitals.
What is the relationship between observed colour of the complex and the wavelength of light absorbed by the complex?
Which one of the following does not achieve an octet of electrons in the central atom?
Oxidation number of cobalt in K[Co(CO)4] is
Oxidation number of carbon in CH2Cl2 is
The oxidation number d-arbitral occupation and co-ordination number of Cr in the complex cis [Cr(en)2Cl2]Cl are respectively.
The most stable ion is:-
Is the central metal atom in coordination complexes a Lewis acid or a Lewis base? Explain.
What is meant by the chelate effect? Give an example.
Explain the following, giving two examples:
Ligand
Give two examples of unidentate ligand.
What is meant by ambidentate ligand?
Give two examples of ambidentate ligand.
