Topics
Introduction to Microprocessors and Organization of 8085
Instruction Set and Programming of 8085
Introdcution to Inted X-86 Family
Introduction to Microcontroller
Networking Technology
- Introduction to Networking
- Types of Networks
- Multiplexing
- Study of Transmission media
- Coaxial cable (Cable Media)
- Twisted pair cable
- Fiber Optic Cable
- Unbounded (Wireless) Media
- Access Methods
- Network Topologies
- Ethernet (Network Architectures)
- Token-Ring (Network Architectures)
- Internet protocols
- Introduction to connectivity devices
- Contention
- Polling
- Token passing
Access Methods
Contention
Contention occurs when multiple computers compete to use the transmission medium, leading to collisions when two transmit simultaneously. Collisions increase with network activity but can be reduced by carrier sensing, where computers listen before transmitting, and carrier detection, where they monitor the network while transmitting and stop if interference is detected. After a collision, computers wait a random time before retrying. Contention methods are common in LANs, but they don't guarantee transmission priority, and collisions increase as more computers join the network. All computers are treated equally in this probabilistic system. 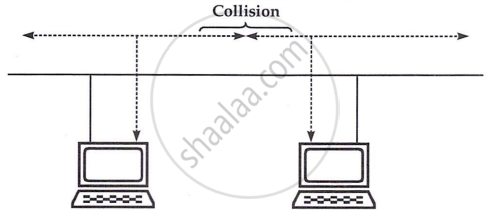
Polling
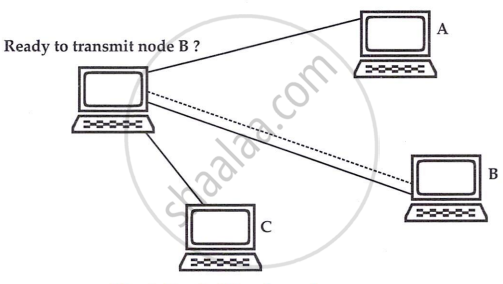
In polling-based systems, a controller or master device checks other devices on the network to see if they are ready to transmit or receive data. However, polling generates significant network traffic, making it less common. A typical example is a computer polling a printer for print jobs.
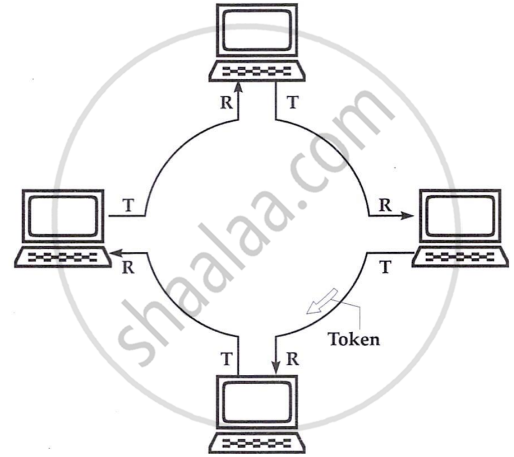
Token passing
Token passing involves a token frame circulating the network, allowing only the computer holding the token to transmit. Once done, the token is passed to the next station. This method is more suitable than contention when handling time-sensitive data, as it provides predictable delivery, making it deterministic. It also handles heavy network traffic better by preventing gridlock from collisions and allows for priority assignments among stations.
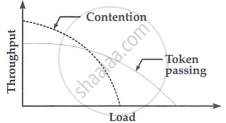
Token passing requires complex control mechanisms and costly hardware. It outperforms contention networks under heavy traffic, but contention networks perform better under light traffic loads.