Topics
Introduction to Microprocessors and Organization of 8085
Instruction Set and Programming of 8085
Introdcution to Inted X-86 Family
Introduction to Microcontroller
Networking Technology
- Introduction to Networking
- Types of Networks
- Multiplexing
- Study of Transmission media
- Coaxial cable (Cable Media)
- Twisted pair cable
- Fiber Optic Cable
- Unbounded (Wireless) Media
- Access Methods
- Network Topologies
- Ethernet (Network Architectures)
- Token-Ring (Network Architectures)
- Internet protocols
- Introduction to connectivity devices
- Unbounded media communication
- Advantage and disadvantage
Unbounded (Wireless) Media
Unbounded media communication
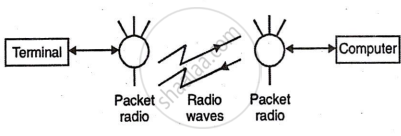
i.Packet Radio: A packet radio system transmits data between terminals and a computer using separate transmitters and receivers. Information is sent from the terminal, processed by the computer, and the results are returned via the same system.
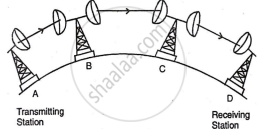
ii. Microwave Media: Microwave communication uses waveguides and repeaters to transmit high-frequency signals, around 100 GHz. Repeaters are placed in a line of sight between obstacles like hills to help the signal bend or pass around them.
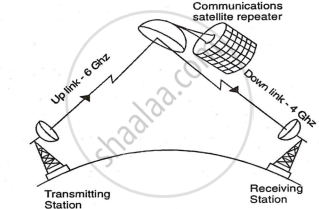
iii.Communication Satellite Media: Microwave signals, like TV signals, cannot be reflected by the ionosphere and must be transmitted directly from towers to receivers. Due to the Earth's curvature, these signals only cover limited line-of-sight areas, leading TV towers to be placed on hills. The coverage area can be extended using repeaters between towers, but this increases cost and weakens signal strength. Satellite microwave systems use satellites positioned 22,300 miles above the Earth, communicating via satellite dishes. These systems operate in the 11-14 GHz range, offering data rates of 1-10 Mbps, but are costly and sensitive to EMI and atmospheric conditions.
Advantage and disadvantage
Advantage: Wireless media offers several advantages, including high data rates through large bandwidth, providing transmission speeds of up to 24 Kbps. This type of communication is especially beneficial for reaching rural and hilly areas where wired infrastructure may be challenging. Additionally, wireless media supports digital data transmission with bandwidths ranging from 1 to 10 Mbps.
Disadvantage: VHF waves are prone to atmospheric noise, which can introduce errors and be affected by EMI. They lack security, as radio waves can be intercepted by anyone. Installation is expensive and complex, and the high attenuation requires repeaters to minimize signal loss.
