Topics
Introduction to Microprocessors and Organization of 8085
Instruction Set and Programming of 8085
Introdcution to Inted X-86 Family
Introduction to Microcontroller
Networking Technology
- Introduction to Networking
- Types of Networks
- Multiplexing
- Study of Transmission media
- Coaxial cable (Cable Media)
- Twisted pair cable
- Fiber Optic Cable
- Unbounded (Wireless) Media
- Access Methods
- Network Topologies
- Ethernet (Network Architectures)
- Token-Ring (Network Architectures)
- Internet protocols
- Introduction to connectivity devices
- Advantages & Disadvantages over conventional cables
- System Of Fiber Optic Communications
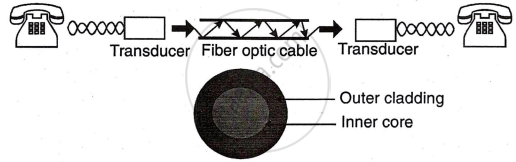
Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optic cables are ideal for data transmission due to their extremely high bandwidth, immunity to EMI, and ability to cover long distances. The core, made of refined glass or plastic, transmits light signals with minimal loss, while cladding reflects signals back into the fiber. Though offering superior performance, fiber optic cables are costly and difficult to install. Data signals are converted to light using lasers or LEDs and reconverted to electrical form at the receiving end. Fiber optic communication, which uses light waves instead of electrical signals, overcomes bandwidth limitations and noise interference, making it increasingly popular in modern networks.
Advantages & Disadvantages over conventional cables
Advantages: Fiber optic cables do not use electrical signals to transmit information hence are free from EMI interference. Attenuation is much lower than any other cable and hence it is used for long range communication.
Disadvantages: It is very expensive than other cables. Grater skill is required to install fiber - optic cable. They must be treated gently during installation. Every cable has minimum bend radius. They get damaged if bended sharply. The cable cannot be stretched.
System Of Fiber Optic Communications
Fiber optic communication uses light waves to transmit signals through a special cable called a light pipe or light guide. The light signal travels in a zigzag pattern through the cable due to multiple reflections. While some of the signal is absorbed inside the cable, it can still carry many signals, such as multiple telephone channels, without interference, like how radio waves work.