Topics
Introduction to Microprocessors and Organization of 8085
Instruction Set and Programming of 8085
Introdcution to Inted X-86 Family
Introduction to Microcontroller
Networking Technology
- Introduction to Networking
- Types of Networks
- Multiplexing
- Study of Transmission media
- Coaxial cable (Cable Media)
- Twisted pair cable
- Fiber Optic Cable
- Unbounded (Wireless) Media
- Access Methods
- Network Topologies
- Ethernet (Network Architectures)
- Token-Ring (Network Architectures)
- Internet protocols
- Introduction to connectivity devices
- BUS topology
- Ring topology
- Star topology
- Mesh topology
Network Topologies
A topology defines the arrangement of nodes, cables and connectivity devices that make up the network. There are two categories -
- Physical topology: It describes actual layout of the network transmission media. It defines the way the network looks.
- Logical topology: It describes the logical pathway a signal follows as it passes among the network nodes. It defines the data passes among the nodes.
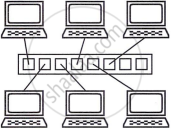
BUS topology
In a bus topology, all devices connect to a shared backbone cable. It supports contention-based access methods and broadcasts signals in both directions, allowing all devices to receive them. Unidirectional buses send signals one way, reaching only downstream devices, and use terminators to prevent signal reflection.
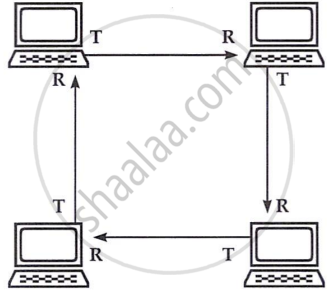
Ring topology
In ring topologies, devices are connected in a circle, with data passing in one direction. Each device acts as a repeater, transmitting the signal to the next. This topology is ideal for token passing methods, where only the token-holding node can transmit. Though rare as a physical setup, it is often used as a logical topology.
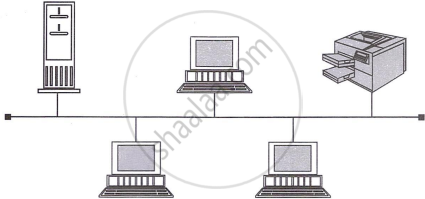
Star topology
In star topologies, all devices connect to a central hub, which receives and routes signals to their destinations. This physical setup is often used to implement bus or ring logical topologies.
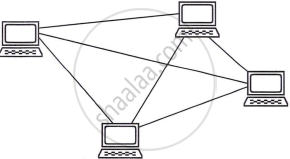
Mesh topology
Mesh topology connects every device to each other, enhancing fault tolerance by providing alternate data routes in case of failure. However, it requires complex cabling and setup.