Topics
Introduction to Microprocessors and Organization of 8085
Instruction Set and Programming of 8085
Introdcution to Inted X-86 Family
Introduction to Microcontroller
Networking Technology
- Introduction to Networking
- Types of Networks
- Multiplexing
- Study of Transmission media
- Coaxial cable (Cable Media)
- Twisted pair cable
- Fiber Optic Cable
- Unbounded (Wireless) Media
- Access Methods
- Network Topologies
- Ethernet (Network Architectures)
- Token-Ring (Network Architectures)
- Internet protocols
- Introduction to connectivity devices
- Direct Addressing
- Register Addressing Mode
- Register Indirect Addressing
- Immediate Addressing
- Implied Addressing
Addressing Modes in 8085
A microprocessor only understands binary code, not assembly language instructions. Assembly instructions are converted into binary code, known as machine code. Instructions can be 1, 2, or 3 bytes long. The first byte specifies the operation, while the second and third bytes indicate the operand or its address.
Direct Addressing
The direct addressing mode, the address of the operand is specified within the instruction itself. For example, LDA 06C2H. This means Load accumulator with the contents of memory location 06C2H. Here all instructions are three-byte instructions.
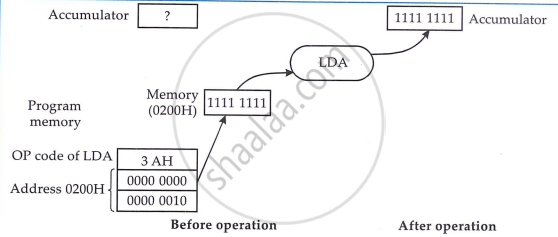
Register Addressing Mode
In this mode the register name is specified in the instruction. Address is not required for this type. These are single byte instructions.
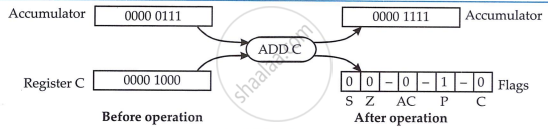
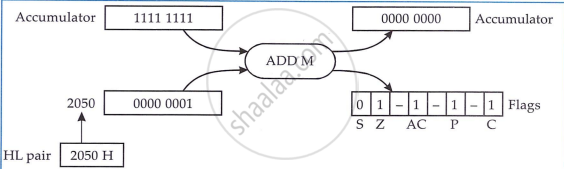
Register Indirect Addressing
In register indirect addressing, the contents of register pair point to the address of the operand. Some of the instructions of 8085 use combined addressing modes from the ones mentioned above.
Immediate Addressing
When data (operand) is directly transferred to register then it is known as immediate Addressing. One or two byte instructions are used for this type of addressing. In this mode, operand is specified within the instruction itself. Data is specified after immediate Mnemonic
Implied Addressing
The addressing mode of certain 8085 instructions is implied by the instruction's functions. For example, the STC (set carry flag) instruction deals with the carry flag only. Here there is no need to specify the address as it is inherent.
