Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
ABC is an isosceles right-angled triangle. Assuming of AB = BC = x, find the value of each of the following trigonometric ratios: sin 45°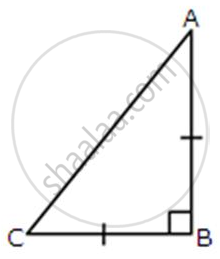
उत्तर
Given that AB = BC = x
∴ AC = `sqrt(AB^2+BC^2) = sqrt(x^2 + x^2) = xsqrt2`
sin 45° = `"AB"/"AC" = x/(xsqrt2) = 1/sqrt2`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Evaluate the following in the simplest form: sin 60º cos 45º + cos 60º sin 45º
Show that tan 48° tan 23° tan 42° tan 67° = 1
Evaluate the following:
`(sin 20^@)/(cos 70^@)`
Express each one of the following in terms of trigonometric ratios of angles lying between 0° and 45°
tan 65° + cot 49°
Express each one of the following in terms of trigonometric ratios of angles lying between 0° and 45°
cos 78° + sec 78°
Prove that tan 20° tan 35° tan 45° tan 55° tan 70° = 1
Prove the following :
`(cos(90^@ - theta) sec(90^@ - theta)tan theta)/(cosec(90^@ - theta) sin(90^@ - theta) cot (90^@ - theta)) + tan (90^@ - theta)/cot theta = 2`
Evaluate:
`2/3 (cos^4 30° - sin^4 45°) - 3(sin^2 60° - sec^2 45°) + 1/4 cot^2 30°`.
Evaluate: `sin 50^@/cos 40^@ + (cosec 40^@)/sec 50^@ - 4 cos 50^@ cosec 40^@`
Evaluate: `(3 cos 55^@)/(7 sin 35^@) - (4(cos 70 cosec 20^@))/(7(tan 5^@ tan 25^@ tan 45^@ tan 65^@ tan 85^@))`
Without using trigonometric tables, prove that:
cos54° cos36° − sin54° sin36° = 0
Prove that
cosec (67° + θ) − sec (23° − θ) = 0
Prove that:
sin 60° = 2 sin 30° cos 30°
Given A = 60° and B = 30°,
prove that : sin (A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B
find the value of: cos2 60° + sin2 30°
If sin x = cos y; write the relation between x and y, if both the angles x and y are acute.
For any angle θ, state the value of: sin2 θ + cos2 θ
Evaluate :
`(3 sin 3"B" + 2 cos(2"B" + 5°))/(2 cos 3"B" – sin (2"B" – 10°)` ; when "B" = 20°.
If A =30o, then prove that :
cos 2A = cos2A - sin2A = `(1 – tan^2"A")/(1+ tan^2"A")`
Without using table, find the value of the following:
`(sin30° - sin90° + 2cos0°)/(tan30° tan60°)`
Prove that : cos60° . cos30° - sin60° . sin30° = 0
Find the value of x in the following: tan x = sin45° cos45° + sin30°
If A = 30° and B = 60°, verify that: sin (A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B
If A = 30° and B = 60°, verify that: `(sin("A" + "B"))/(cos"A" . cos"B")` = tanA + tanB
Verify the following equalities:
sin 30° cos 60° + cos 30° sin 60° = sin 90°
Find the value of the following:
`(tan45^circ)/("cosec"30^circ) + (sec60^circ)/(cot45^circ) - (5sin90^circ)/(2cos0^circ)`
The value of `(1 - tan^2 45^circ)/(1 + tan^2 45^circ)` is
If A and B are acute angles such that sin (A – B) = 0 and 2 cos (A + B) – 1 = 0, then find angles A and B.
