Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Chemical Bonding
3: Study Of Acids, Bases and Salts
4: Analytical Chemistry
5: Mole Concept And Stoichiometry
▶ 6: Electrolysis
7: Metallurgy
8: Study of Compounds-I: Hydrogen Chloride
9.1: Ammonia
9.2: Nitric Acid
10: Study of Sulphur Compound: Sulphuric Acid
11.1: Organic Compounds
11.2: Alkanes
11.3: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
11.4: Alkynes
11.5: Alcohols
11.6: Carboxylic Acid
12: Practical Work
![Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 6 - Electrolysis Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 6 - Electrolysis - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-part-2-english-class-10-icse_6:083608507a004841af01e3c142179570.PNG)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 6: Electrolysis
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 6 of CISCE Frank for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 6 Electrolysis Exercise 1 [Page 145]
Define the term : Electrolysis
Define the term : Electrolyte
The following question relate to the electroplating of an article with silver.
What should be the nature of the anode?
Define the term : Non-electrolyte
Define the following term:
Cation
Define the following term:
anion
From the given list :
NaCl, NaOH, H2O (pure), NH4OH, urea, dil.H2SO4, glucose, acetic acid, H2CO3.
Select :
a) Substances which will behave as strong electrolytes.
b) Substances which will behave as weak electrolytes.
c) Substances which are non-elctrolytes.
Write the difference between with examples:
A strong electrolyte and a weak electrolyte
Write the difference between with examples:
Electrolytic dissociation and ionization
Explain electrolysis of lead bromide.
Give three applications of electrolysis.
State your observation for the following electrolytic reaction:
Solid copper sulphate is electrolysed between platinum electrodes.
State your observation for the following electrolytic reaction
Aqueous copper sulphate is electrolysed between platinum electrodes.
State your observation for the following electrolytic reaction
Aqueous copper sulphate is electrolysed between copper electrodes.
Explain, why electrolysis is an example of redox reaction?
State the factors that influence the preferential discharge of ions at the electrodes.
With reference to the electrolysis of acidulated water, answer the following :
a) why distilled water is a non- electrolyte?
b) What is the electrolytic cell called?
c) State what you would observe at the (i) Cathode (ii) Anode
d) Summarize the electrode reactions.
e) why is electrolysis of acidulated water considered as an example of catalysis?
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 6 Electrolysis Exercise 2 [Page 146]
Make a neatly labeled sketch to show how a brass spoon can be plated with silver. Explain your choice of electrolyte used.
Explain the terms : Electro refining
Explain the term : Electro metallurgy
Explain the term : Anode mud
Fill in the black.
The metal plate trough which current enters into an electrolyte is called ___________. It has ____________ of electrons.
Fill in the black.
The metal plate through which ____________ leaves from an electrolyte is called ____________ .It has ______________ of electrons.
Fill in the blank.
The ions which discharge on the negative electrode during electrolysis _____________ electrons, Thus the ions are said to be __________.
Fill in the blank :
The ions which discharge on the positive electrode during electrolysis ____________electrons. Thus, the ions are said to be _____________.
Fill in the blank :
Hydrogen and metallic ions are ____________ because they ____________ electrons.
Fill in the blank :
Non-metallic ions are _____________ because they _____________ electrons.
Al+3 ,Cu+2 ,Na+ ,Zn+2 ions are present in aqueous solution, such that the concentration of ions is same, write the order of discharge of ions.
Amongst the OH- ions and Br- ions which are likely to discharge first?
How electrolysis can be used in extraction of aluminium? Why aluminium cannot be reduced by conventional reducing agents?
Explain, why during the electrolysis of copper sulphate using copper electrodes, the colour of solution does not fade?
How is impure copper purified by electrolysis ? Explain.
List out the main applications of electrolysis.
How is electrolytic dissociation different from thermal dissociation?
A solution of caustic soda (NaOH) in water or when fused, conducts an electric current. what is the similarity in these two cases?
Name : A salt which is a weak electrolyte.
Name : A base which is not alkali
Name an active electrode.
Name : A positively charged not metallic ion
Name : A non-metallic element which is a conductor of electricity.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
Which one is weak electrolyte?
HNO3
KOH
CuSO4
Cu(OH)2
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
Which among the following cations will discharge with ease at cathode?
Na+
Au3+
Cu2+
H+
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
Which among the following anions will discharge with ease at anode?
Cl-
I-
OH-
\[\ce{SO^{2-}_{4}}\]
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
In electrolysis of molten lead bromine anode is made up of
Steel rod
Platinum foil
Glass rod
Graphite rod
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
Electrolysis of acidulated water is used in the production of
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Hydrogen and oxygen
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 6 Electrolysis Exercise 3 [Page 147]
The following question relate to the electroplating of an article with silver.
Name the electrode formed by the article which is to be plated.
The following question relate to the electroplating of an article with silver.
What ions must be present in the electrolyte?
How is the passage of electricity through an electrolyte different from the passage of electricity through a copper wire?
The following questions are about electroplating of copper wire with silver.
(a) What ions must be present in the electrolyte?
(b) Of what substance must the anode be made up of?
(c) What will the cathode be made up of?
(d) Write the equation for the reaction which takes place at the cathode.
Define or explain the term: Electrolysis.
Why is it necessary to add acid to water before proceeding with electrolysis of 'water'?
Give one example of a substance which contain :
Ions only
Give one example of a substance which contain :
molecules only
Give one example of a substance which contain :
both ions and molecules.
What is meant by the term 'electrolyte'?
What are the particles present in a compound which is a non- electrolyte?
If an electrolyte is described as a 'strong electrolyte' what does this mean?
The following Question refer to the electrolysis of copper sulphate solution with copper electrodes:
(a) Compare the change in mass of the anode
(b) What is seen to happen to the colour of the copper sulphate solution if platinum electrodes are used? Explain the observation.
(c) What is the practical application of the electrolysis of copper sulphate solution? Briefly, describe one such application.
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 6 Electrolysis Exercise 4 [Page 148]
What should be the physical state of lead bromide if it is to conduct electricity?
What particles are present in pure lead bromide?
Write the equations for the reactions, which takes place at the electrodes during the electrolysis of lead bromide?
Choosing only words from the following list, write down the appropriate words to fill in the blanks (a) to (e) below:
anions, anode, cathode, cations, electrode, electrolyte, nickel, voltameter.
To electroplate an article with nickel requires an (a) ________ which must be a solution containing (b) ________ions. The article to be plated is placed as the (c) _________of the cell in which the plating is carried out. The (d)________ of the cell is made from pure nickel. The ions that are attracted to the negative electrode and discharged are called (e)________.
Correct the sentence by adding word(s)
The electrolysis of lead bromide liberates lead and bromine.
If a fused metallic chloride is electrolyzed, at which electrode would the metal be obtained?
Classify the following substance:
Acetic acid
Strong electrolyte
Weak electrolyte
Non-electrolyte
Classify the following substance:
Ammonium chloride
Strong electrolyte
Weak electrolyte
Non-electrolyte
Classify the following substance:
Ammonium hydroxide
Strong electrolyte
Weak electrolyte
Non-electrolyte
Classify the following substance:
Carbon tetrachloride
Strong electrolyte
Weak electrolyte
Non-electrolyte
Classify the following substance:
Dilute hydrochloric acid
Strong electrolyte
Weak electrolyte
Non-electrolyte
Classify the following substance:
Sodium acetate
Strong electrolyte
Weak electrolyte
Non-electrolyte
Classify the following substance:
Dilute sulphuric acid
Strong electrolyte
Weak electrolyte
Non-electrolyte
Write down the word or phrase from the given options that will correctly fill in the blanks in the following sentence:
Pure water consists entirely of ________
ions
molecules
Write down the word or phrase from the given options that will correctly fill in the blanks in the following sentence:
We can expect that pure water _______ normally conduct electricity.
Will
Will not
Copy and complete the following sentence :
With platinum electrodes, hydrogen is liberated at the ______and oxygen at the _________ during the electrolysis of acidified water.
To carry out the so-called "electrolysis of water", sulphuric acid is added to water. How does the addition of sulphuric acid produce a conducting solution?
Copy and complete the following table which refers to two practical applications of electrolysis.
| Anode | Electrolyte | Cathode | |
| Silver plating of a spoon | Solution of potassium argentocyanide | ||
| Purification of copper |
Complete the sentence by choosing correct words given in brackets.
Electrolysis is the passage of __________ (electricity/electrons) through a liquid or solution accompanied by a __________ ( physical/chemical ) change.
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 6 Electrolysis Exercise 5 [Page 149]
Element X is a metal with valency 2. Element Y is a non-metal with valency 3.
(a) Write equations to show how X and Y form ions.
(b) If Y is diatomic gas, write the equation for the direct combination of X and Y to form a compound.
(c) Write two applications of electrolysis in which anode diminish in mass.
(d) If the compound formed between X and Y is melted and an electric current passed through the molten compound, the element X will be obtained at the _____ and the Y at the ________of the electrolytic cell. (Provide the missing words).
What kind of particles will be found in a liquid compound which is a non- electrolyte?
If HX is a weak acid, what particles will be present in its dilute solution apart from those of water?
Choose the correct words to fill in the blanks.
Cations are formed by _______ (loss/ gain) of electrons and anions are formed by ________( loss/gain) of electrons.
What ions must be present in a solution used for electroplating a particular metal?
Explain how electrolysis is an example of Redox reaction.
Explain, why copper though a good conductor of electricity is, a non- electrolyte.
Name the gas released at the cathode when acidulated water is electrolyzed.
Explain, why solid sodium chloride does not allow electricity to pass through?
Fill in the blank.
As we descend the electrochemical series containing cations, the tendency of the cations to get ________ at the cathode increases.
oxidized
reduced
Fill in the blank :
The _______ the concentration of an ion in a solution, the greater is the probability of its being discharged at its appropriate electrode.
higher
lower
Study the diagram given alongside and answer the questions that follow :
(i) Give the names of the electrode A and B.
(ii) Which electrode is oxidizing electrode?
A strip of copper is placed in four different colourless salt solutions. They are KNO3, AgNO3, Zn(NO3)2, Ca(NO3)2. Which one of the solutions will finally turn blue?
Write the equations of the reactions which take place at the cathode and anode when acidified water is electrolyzed.
Write the equations of the reactions which take place at the cathode and anode when acidified water is electrolyzed.
A solution of silver nitrate is a good electrolyte but is not used for electroplating an article with silver.
Identify the following reactions as either oxidation or reduction : O + 2e- → O-2
Identify the following reactions as either oxidation or reduction : K - e- → K+
Identify the following reactions as either oxidation or reduction : Fe+3 + e- → Fe+2
Choose A, B, C or D to match the descriptions (i) to (v) below . Some alphabets may be repeated.
(A) Non-electrolyte, (B) Strong electrolyte, (C) Weak electrolyte, (D) Metallic conductor
(i) Molten ionic compound
(ii) Carbon tetrachloride
(iii) An aluminium wire
(iv) A solution containing solvent molecules, solute molecules and ions formed by the dissociation of solute molecules
(v) A sugar solution with sugar molecules and water molecules.
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 6 Electrolysis Exercise 6 [Page 150]
The following is an extract from metals in the service of man, Alexander and street /Pelican 1976': Alumina (aluminium oxide) has a very high melting point over 2000oC, so that I cannot readily be liquefied. However, conversion of alumina to aluminium and oxygen, by electrolysis, an occur when it is dissolved in some other substance.
(a) Which solution is used to react with bauxite as first step in obtaining pure aluminium oxide?
(b) The aluminium oxide for the electrolytic extraction of aluminium is obtained by heating aluminium hydroxide. Write the equation for this reaction.
(c) Name the element which serves both as the anode and the cathode in the extraction of aluminium.
(d) Write the equation for the reaction that occurs at the cathode during the extraction of aluminium.
(e) Write the equation for the reaction that occurs at the cathode during extraction of aluminium by electrolysis.
(f) Give the equation for the reaction that occurs at the anode when aluminium is purified by electrolysis.
Choose the correct answer:
During the electrolysis of molten lead bromide, which of the following takes place?
Bromine is released at the cathode.
Lead is deposited at the anode.
Bromine ions gain electrons.
Lead is deposited at the cathode.
Here is an electrode reaction:
\[\ce{Cu -> Cu^{2+} + 2e^-}\]
At which electrode (anode or cathode) would such a reaction take place? Is this an example of oxidation?
A solution contains magnesium ions (Mg+2), iron (II) ions (Fe+2) and copper ions (Cu+2). On passing an electric current through this solution, which ions will be the first to be discharged at the cathode? Write the equation for the cathode reaction.
Why is carbon tetrachloride, which is a liquid, a non-electrolyte?
The following is a sketch of an electrolytic cell used in the extraction of aluminium:

- What is the substance of which the electrodes A and B are made?
- At which electrode (A or B) is aluminium formed?
- What are the two aluminium compounds in the electrolyte C?
- Why is it necessary for electrode B to be continuously replaced?
A metal article is to be electroplated with silver. The electrolyte selected is sodium argentocyanide.
- What kind of salt is sodium argentocyanide?
- Why is it preferred to silver nitrate as an electrolyte?
- State one condition to ensure that the deposit is smooth, firm and long lasting.
- Write the reaction taking place at the cathode.
- Write the reaction taking place at the anode.
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 6 Electrolysis Exercise 7 [Page 151]
Find the odd one out from the following and explain your choice : Al(OH)3, Pb(OH)2,Mg(OH)2,Zn(OH)2
Correct the following statement:
Lead bromide conducts electricity.
Aqueous solution of nickel sulphate contains \[\ce{Ni^{+2}}\] and \[\ce{SO^{-2}_{4}}\] ions.
- Which ion moves towards the cathode?
- What is the product at the anode?
Select the correct answer from the choices a,b,c and d which are given. Write only the letter corresponding to the correct answer.
A compound which liberates reddish brown gas around the anode during the electrolysis in its molten state is:______________
Sodium chloride
Copper (II) oxide
Copper (II) sulphate
Lead (II) bromide
Select the correct answer from the choices a,b,c and d which are given. Write only the letter corresponding to the correct answer.
During ionization metals lose electrons, this change can be called _______________.
Oxidation
Reduction
Redox
Displacement
Mr Ramu wants electrolyte his key chain with nickel to prevent rusting. For this electroplating
(i) Name the electrolyte
(ii) Name the cathode
(iii) Name the anode
(iv) Give the reaction at the cathode
(v) Give the reaction at the anode
Three different electrolytic cells, A, B and C are connected in separate circuits. Electrolytic cell A contains a sodium chloride solution. When the circuit is completed, a bulb in the circuit glows brightly. Electrolytic cell B contains an acetic acid solution and in this case, the bulb in the circuit glows dimly. The electrolytic cell C contains a sugar solution and the bulb does not glow. Give a reason for each of these observations.
Give reasons as to why - the electrolysis of acidulated water is considered to be an example of catalysis.
Fill in the blank from the choices given below :
In covalent compounds, the bond is formed due to the ______ of electrons.
sharing
transfer
Fill in the blank from the choices given below :
Electro covalent compounds have a _____ boiling point
low
high
Fill in the blank from the choices given below :
A molecule of _____ contains a triple bond.
hydrogen
ammonia
nitrogen
Differentiate between the electrical conductivity of copper sulphate solution and copper metal.
During the electrolysis of copper (II) sulphate solution using platinum as cathode and carbon as anode:
- What do you observe at the cathode and at the anode?
- What change is noticed in the electrolyte?
- Write the reactions at the cathode and at the anode.
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 6 Electrolysis Exercise 8 [Page 152]
Copper sulphate solution is electrolyzed using copper electrodes. Study the diagram given alongside and answer the questions that follow.
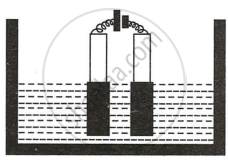
- Which electrode to your left or right is known as the oxidizing electrode and why?
- Write the equation representing the reaction that occurs.
- State two appropriate observations for the above electrolysis reactions.
Which of these will act as a non-electrolyte?
Liquid carbon tetrachloride
Acetic acid
Sodium hydroxide aqueous solution acid
Potassium chloride aqueous solution
State one observation when electricity is passed through molten lead bromide.
When fused lead bromide is electrolyzed we observe
A silver grey deposit at anode and a reddish brown deposit at cathode
A silver grey deposit at cathode and reddish brown deposit at anode
A silver grey deposit at cathode and reddish brown fumes at anode
Silver grey fumes at anode and reddish brown fumes at cathode
The electrolyte used for electroplating an article with silver is ______.
Silver nitrate solution
Silver cyanide solution
Sodium argentocyanide solution
Nickel sulphate solution
M is a metal above hydrogen in the activity series and its oxide has the formula M2O. The oxide when dissolved in water forms the corresponding hydroxide which is a good conductor of electricity. In the above context answer the following:
- What kind of combination exists between M and O?
- How many electrons are there in the outermost shell of M?
- Name the group to which M belongs.
- State the reaction taking place at the cathode.
- Name the product at the anode.
Give appropriate scientific reasons for the following statement :
Zinc oxide can be reduced to zinc by using carbon monoxide, but aluminium oxide cannot be reduced by a reducing agent.
Give appropriate scientific reasons for the following statement :
Carbon tetrachloride does not conduct electricity.
Give appropriate scientific reasons for the following statement:
During electrolysis of molten lead bromide, graphite anode is preferred to other electrodes.
Give appropriate scientific reasons for the following statement :
The electrical conductivity of acetic acid is less in comparision to the electrical conductivity of dilute sulphuric acid at a given concentration.
Give appropriate scientific reasons for the following statement :
Electrolysis of molten lead bromide is considered to be a redox reaction.
Differentiate between the terms strong electrolyte and weak electrolyte (stating any two differences)
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 6 Electrolysis Exercise 9 [Page 153]
Copy and complete the following table :
| Anode | Electrolyte | |
| Purification of copper |
Write the equation taking place at the anode.
Give reasons why sodium chloride will conduct electricity only in the fused or aqueous solution state.
Give reasons why in the electroplating of an article with silver, the electrolyte sodium argentocynide solution is preferred over silver nitrate solution.
Give reasons why although copper is a good conductor of electricity, it is a non-electrolyte.
Name the product formed at the anode during the electrolysis of acidified water using platinum electrodes
Name the metallic ions that should be present in the electrolyte when an article made copper is to be electroplated with silver
Identify the substance underlined in each of the following case :
he electrolyte used for electroplating an article with silver.
Identify the substance underlined in each of the following case :
The particles present in a liquid such as kerosene, that is non-electrolyte.
State the observation at the anode and at the cathode during the electrolysis of :
Fused lead bromide using graphite electrodes
State the observation at the anode and at the cathode during the electrolysis of :
Copper sulphate solution using copper electrodes.
Select the ion, that would get selectively discharge from the aqueous mixture of the ions listed below :
\[\ce{SO^{2-}_{4}}\], \[\ce{NO^{-}_{3}}\], \[\ce{OH-}\]
Select the ion, that would get selectively discharge from the aqueous mixture of the ions listed below :
Pb2+, Ag+, Cu+
Solutions for 6: Electrolysis
![Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 6 - Electrolysis Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 6 - Electrolysis - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-part-2-english-class-10-icse_6:083608507a004841af01e3c142179570.PNG)
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 6 - Electrolysis
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Frank solutions for Mathematics Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 6 (Electrolysis) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Frank textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 6 Electrolysis are Preferential Or Selective Discharge of Ions at Electrodes, Examples of Electrolysis, Electrolysis of Molten Lead Bromid, Electrolysis of Acidified Water Using Platinum Electrodes, Electrolysis of Copper Sulphate Solution Using Platinum Anode and Copper Or Platinum Cathode, Electrolysis of Aqueous Copper Sulphate - Using Copper Electrodes, Applications of Electrolysis, Electrolysis, Electrolytes, Nonelectrolyte, Electrochemical Cells, Electrodes, Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Reactions, Arrhenius Theory of Electrolytic Dissociation, Electrochemical Series.
Using Frank Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Electrolysis exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Frank Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Frank Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 6, Electrolysis Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
