Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Chemical Bonding
3: Study Of Acids, Bases and Salts
4: Analytical Chemistry
5: Mole Concept And Stoichiometry
6: Electrolysis
▶ 7: Metallurgy
8: Study of Compounds-I: Hydrogen Chloride
9.1: Ammonia
9.2: Nitric Acid
10: Study of Sulphur Compound: Sulphuric Acid
11.1: Organic Compounds
11.2: Alkanes
11.3: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
11.4: Alkynes
11.5: Alcohols
11.6: Carboxylic Acid
12: Practical Work
![Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Metallurgy Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Metallurgy - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-part-2-english-class-10-icse_6:083608507a004841af01e3c142179570.PNG)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 7: Metallurgy
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 7 of CISCE Frank for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Metallurgy Exercise 1 [Page 179]
Name the following:
Two metals which are found in the free or native state.
Name the following:
The mixture of materials fed into a furnace to extract a metal.
Name the following:
The rocky impurities present in an ore.
Name the following:
The substance added to get rid of gangue in the extraction of metal.
Name the following:
The process of heating a substance very strongly in such a way that it does not combine with oxygen.
Name the following:
The process in which an ore is heated in air so that oxygen gets added to it to form the oxides.
Name the following :
Ore of iron referred to as "fool's gold".
Name the following:
The chief ore of aluminium.
Name the following:
The substance added along with aluminium in the Hall-Heroult's process.
Name the following:
The materials used as electrodes in the electrolytic extraction of aluminium.
Name the following:
The kind of welding in which aluminium powder is used.
Name the following:
The chief metal which occur in nature in free state as well as in combined state.
Name the following:
The chief metal present in magnalium and duralumin
Name the following:
Two metals which occur in nature in free state as well as in combined state.
Name the following:
Name two metals always find in combined state.
Give reason for the following:
Zinc is used in galvanization and dry cells.
Give reason for the following:
Nitric acid can be stored in aluminium containers.
Give reason for the following:
Aluminium oxide cannot be reduced by carbon.
Give reason for the following:
A neutral gas other than oxygen is formed at the anode during electrolysis of fused alumina.
Give reason for the following:
Extraction of aluminium was very difficult in the beginning.
Give reason for the following:
Carbon anodes are used in the electrolytic extraction of aluminium.
Give reason for the following:
Galvanized metal ions should not be used for storing food.
Define the term : Mineral
Define the term : Ore
Define the term : Gangue
Define the term : Charge
Define the term : Flux
Define the term : Slag
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Metallurgy Exercise 2 [Page 180]
What is meant by concentration of ores?
Name the process of concentration
(a) Based on densities
(b) Based on magnetic nature.
How an ore is concentrated by froth floatation process?
Name one metal occurring as a : Sulphide ore
Name one metal occurring as a : Halide ore
Name one metal occurring as a : Carbonate ore
Name one metal occurring as a : Oxide ore
Comment on the statement that- "All ores are minerals but all minerals are not ores".
Write the name and formula of two ores of the following: Iron
Write the name and formula of two ores of the following: Zinc
Write the name and formula of two ores of the following: Aluminium
Compare the process of calcination and roasting.
What is meant by refining of metals? Name the three common methods used for refining.
How are metals refined by the electrolytic methods?
Name the ore from which aluminium is extracted.
How is ore purified (give equations also)
How is aluminium obtained from pure ore?
Which method of refining is used to get 99.8% pure aluminium?
In the Hall's process for extraction of aluminium, Give the formula and purpose of fluorspar and cryolite
In the Hall's process for extraction of aluminium, Sate the location of cathode and anode and explain what occurs at each electrode.
What is the role of cryolite (NaAlF6) in the electrolytic reduction of alumina in the Hall's process?
Aluminium is a more active metal than iron, but suffers less corrosion. Why?
Explain and give reasons why aluminium vessels should not be cleaned with powders containing alkalis.
Why is food containing iron salts should not be cooked in aluminium utensils?
Give equation for the following conversion: Ferric oxide to iron.
Give equation for the following conversion: Aluminium hydroxide to aluminium oxide.
Give equation for the following conversion: Aluminium to aluminium nitride.
Give equation for the following conversion:Aluminium to sodium aluminate.
What is an alloy? Give three reasons why alloys are made.
Give two properties of alloys which are different from constituent metals.
What is an amalgam? Name one metal which does not form amalgam? State one use of amalgam.
Give composition and uses of the following alloys. Mention the reason for its use.
Stainless steel
Give composition and uses of the following alloys. Mention the reason for its use.
Duralumin
Give composition and uses of the following alloys. Mention the reason for its use.
Brass
Give composition and uses of the following alloys. Mention the reason for its use.
Magnalium
Give composition and uses of the following alloys. Mention the reason for its use.
Solder
Give composition and uses of the following alloys. Mention the reason for its use.
Bronze
Explain the following:
Galvanization protects iron from rusting.
Explain the following:
Stainless steel is more useful than steel.
Explain the following:
Aluminium is extensively used for making aircraft parts.
Explain the following:
Cold water has no action on aluminium.
Complete and balance the following equation:
Al + O2 →
Complete and balance the following equation:
Al + N2 →
Complete and balance the following equation:
Al + KOH + H2O →
Complete and balance the following equation:
Fe2O3 + → Al2O3 +
Complete and balance the following equation:
Fe2O3 + CO →
Name oxide of one metal which is reduced by (give equation): Reduction with carbon
Name oxide of one metal which is reduced by (give equation): Electrolytic reduction
Name oxide of one metal which is reduced by (give equation): Reduction with heat alone
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Metallurgy Exercise 3 [Page 181]
An aqueous solution of sodium chloride is not used for electrolytic reduction of sodium metal. Why?
For the reaction of a metal oxide. Suggest a reducing agent other than carbon
What is galvanized iron.
What is passive iron?
Name the alloy of zinc used in simple voltaic cells.
Complete and balance the following equation :
Al + NaOH →
Give the chemical name and formula of 'cryolite'
what is the function of cryolite in the extraction of aluminium, other than acting as a solvent for bauxite?
Name a non-metallic element which forms acidic and neutral oxides
Name a non-metallic element which has a metallic lustre
Name a non-metallic element which is a liquid at ordinary temperatures
Name a non-metallic element which is a conductor of electricity.
Name a metal which occurs free in nature.
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Metallurgy Exercise 4 [Page 182]
Give the name and formula of an ore of zinc.:
Roasting of the ore
Give the name and formula of an ore of zinc.
Reduction of the zinc compound which is the product of above reaction.
Give the name and formula of an ore of zinc.
What in addition to a zinc compound, is put into the furnace? State one large scale use of zinc.
Arrange the metals:
calcium, iron, magnesium and sodium in order of their reactivity with water placing the most reactive first.
Write equations for each of the above metal which reacts with water.
The following question refer to the extraction of aluminium and iron from their ores :
Name the principle ore from which i. iron, and ii. Aluminium is extracted.
The following question refer to the extraction of aluminium and iron from their ores:
What is the most important chemical process in the extraction of any metal? State how this essential step is carried out in the extraction of: i. iron, and ii. Aluminium.
The following question refer to the extraction of aluminium and iron from their ores:
Iron and aluminum ores both, contain impurities. Explain briefly how these impurities are removed in each case.
The following question refer to the extraction of aluminium and iron from their ores:
What is the major impurity present in iron when it is removed from the furnace?
Name an alloy of zinc which is used in simple voltaic cells.
For the substance listed below, explain its role in the extraction of aluminium: Bauxite
For the substance listed below, explain its role in the extraction of aluminium: Sodium hydroxide
For the substance listed below, explain its role in the extraction of aluminium: Cryolite
For the substance listed below, explain its role in the extraction of aluminium: Graphite
The following question relate to the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis.
Give the equation for the reaction which takes place at the cathode.
The following questions relate to the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis.
Explain why it is necessary to renew the anode periodically.
What is an alloy? An alloy usually has some property which makes it useful in a specific way.
What is the special property of: Duralumin
What is an alloy? An alloy usually has some property which makes it useful in a specific way.
What is the special property of : type metal?
What is added to steel to make it stainless steel?
Define and explain the meaning of the term ore.
Complete the incomplete statement with missing words:
Metals are ______ while non-metals are ______ conductors of heat.
Complete the incomplete statement with missing word:
Metals are malleable while non-metals are ______.
Complete the incomplete statement with missing word:
Metals form positive ions while non- metals ______.
Complete the incomplete statement with missing word:
Non-metals form acidic oxides while metals form ______.
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Metallurgy Exercise 5 [Page 183]
Name : The metal which is liquid at room temperature.
Name:
The allotrope of the non-metal carbon which conducts electricity.
How many valence electrons are present in metals ?
How many valence electrons are present in non- metals?
With reference to the reduction of copper (II) oxide , iron (II) oxide, lead (II) oxide and magnesium oxide; place the oxides in order of increasing ease of reduction.[i.e. first write the oxide that is most difficult to reduce and at last, the oxide, that is most easily reduced.]
Write balanced equation for the following reaction:
Reduction of copper oxide by hydrogen.
Write balanced equation for the following reaction:
Reduction of iron (III) oxide by carbon monoxide.
Write balanced equation for the following reaction:
Reduction of lead (II) oxide by carbon.
What is the type of bonding expected in a metallic chloride?
If fused metallic chloride is electrolyzed, at which electrode would the metal be obtained?
What metallic property is shown by the non-metal graphite?
X is an element in the form of a powder. X burns in oxygen and the product is soluble in water. The solution is tested with litmus. Write down only the word which will correctly complete each of the following sentences:
(a) If X is a metal, then the litmus will turn ______.
(b) If X is a non-metal, then the litmus will turn ______.
(c) If X is a reactive metal, then ______ will be evolved, when X reacts with dilute sulphuric acid.
(d) If X is a non -metal, it will form _ oxide, which will form ______ solution with water.
(e) If X is a non -metal, it will not conduct electricity unless it is carbon in the form of ______.
From the metals copper, iron, magnesium, sodium and zinc, select a different metal in each case which:
(a) Does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid
(b) Can form 2+ and 3+ ions
(c) Has a hydroxide that reacts with both acid and alkalis.
(d) Does not react with cold water, but reacts with steam when heated.
Arrange the metals of copper, iron, magnesium, sodium and zinc in the decreasing order of reactivity.
List 1 contains the meta ls I alloys (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ) and list 2 contains their uses (A, B, C, D, E).
| List 1 Metal/Alloy |
List 2 Uses |
| 1. Aluminium | A. Steel making |
| 2. Lead | B. aeroplane wings |
| 3. Brass | C. galvanizing |
| 4. Iron | D. radiation shield |
| 5. Zinc | E. electricaI fittings |
Copy and complete the following table, write down the correct letter against the numbers representing metals. An answer may be used only once. The first has been done for you.
| Metal | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Use | B |
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Metallurgy Exercise 6 [Page 184]
4 tones of bauxite, 150 Kg of sodium hydroxide and 600 Kg of graphite.
The aluminium compound in bauxite is aluminium oxide and the main impurity is iron (II) oxide. Aluminium is obtained by the electrolysis of aluminium oxide dissolved in cryolite.
(a) When bauxite is treated with sodium hydroxide solution, what happens to:
(i) the aluminium oxide?
(ii) The iron (III) oxide?
In order to obtain one tone of aluminium, the following inputs are required:
4 tones of bauxite, 150 Kg of sodium hydroxide and 600 Kg of graphite.
The aluminium compound in bauxite is aluminium oxide and the main impurity is iron (II) oxide. Aluminium is obtained by the electrolysis of aluminium oxide dissolved in cryolite.
(i) Name the process used for purification of bauxite.
(ii) Write the equation to show the action of heat on aluminium hydroxide.
In order to obtain one tone of aluminium, the following inputs are required:
4 tones of bauxite, 150 Kg of sodium hydroxide and 600 Kg of graphite.
The aluminium compound in bauxite is aluminium oxide and the main impurity is iron (II) oxide. Aluminium is obtained by the electrolysis of aluminium oxide dissolved in cryolite.
(i) Write the formula of cryolite.
(ii) Write down the word which correctly completes the following sentence.
"By dissolving aluminium oxide in cryolite, a ______ (conducting / non- conducting) solution is produced.
(iii) Why so much graphite required for this electrolytic process.
(iv) Write the equation for the reaction which takes place at cathode.
In order to obtain one tone of aluminium, the following inputs are required:
4 tones of bauxite, 150 Kg of sodium hydroxide and 600 Kg of graphite.
The aluminium compound in bauxite is aluminium oxide and the main impurity is iron (II) oxide. Aluminium is obtained by the electrolysis of aluminium oxide dissolved in cryolite.
In construction work, why is the alloy of aluminium, duralumin used rather than pure aluminium.
Compare the properties of a typical metal and a non- metal on the basis of the following:
(a) electronic configuration
(b) nature of oxides
(c) oxidizing or reducing action
(d) conductivity of heat and electricity
Name a non- metal that has a metallic luster and sublimes on heating.
Write balanced equation for the following reaction:
Aluminium powder is warmed with hot and concentrated caustic soda solution.
Name the ore of zinc containing its sulphide.
Write the equation for the reaction of zinc with following: Sodium hydroxide solution
Write the equation for the reaction of zinc with following: Dilute sulphuric acid
Write the equation for the reaction of zinc of the following: Copper sulphate solution
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Metallurgy Exercise 7 [Page 185]
To protect iron from rusting, it is coated with a thin layer of zinc. Name the process.
Aluminium is extracted from its chief ore bauxite. The ore is first purified and then the metal is extracted from it by electrolytic reduction.
Write three balanced equations for the purification of bauxite by Hall's process.
Aluminium is extracted from its chief ore bauxite. The ore is first purified and then the metal is extracted from it by electrolytic reduction.
Name a chemicals used for dissolving aluminium oxide. In which state of sub-division is the chemical used?
Aluminium is extracted from its chief ore bauxite. The ore is first purified and then the metal is extracted from it by electrolytic reduction.
Write an equation for the reaction which takes place at the anode during the extraction of aluminium by the electrolytic process.
Aluminium is extracted from its chief ore bauxite. The ore is first purified and then the metal is extracted from it by electrolytic reduction.
Mention one reason for the use of aluminium in thermite welding. Which particular property of cast iron makes it unsuitable for the construction of bridges?
A to F below relate to the source and extraction of either zinc or aluminium.
- Bauxite
- Coke
- Cryolite
- Froth floatation
- Sodium hydroxide solution
- Zinc blende
Write down the three letters each from the above list which are relevant to:
- Zinc
- Aluminium
A to F below relate to the source and extraction of either zinc or aluminium.
- Bauxite
- Coke
- Cryolite
- Froth floatation
- Sodium hydroxide solution
- Zinc blende
Fill in the blanks using the most appropriate words from A to F:
(i) The ore from which aluminium is extracted must be treated with ______ so that pure aluminium oxide can be obtained.
(ii) Pure aluminium oxide is dissolved in ______ to make a conducting solution.
A to F below relate to the source and extraction of either zinc or aluminium.
- Bauxite
- Coke
- Cryolite
- Froth floatation
- Sodium hydroxide solution
- Zinc blende
Write the formula of cryolite.
Calcium, copper, lead, aluminium, zinc, chromium, magnesium, iron.
Choose the major metals from the list given above to make the following alloys:
(a) Stainless steel
(b) brass
Name the following:
or
With reference to the physical properties of metals and non-metals, state the following exception.
A metal which is liquid at room temperature.
Name the following:
A compound which is added to lower the fusion temperature of the electrolytic bath in the extraction of aluminium.
Name the following:
The process of heating an ore to a high temperature in the presence of air.
Name the following:
The compound formed by the reaction between calcium oxide and silica.
Name the following:
The middle region of the blast furnace.
The following is an extract from 'Metals in the Service of Man, Alexander and Street/Pelican 1976':
| 'Alumina (aluminium oxide) has a very high melting point of over 2000°C so that it cannot readily be liquefied. However, conversion of alumina to aluminium and oxygen, by electrolysis, can occur when it is dissolved in some other substance.' |
- Which solution is used to react with bauxite as a first step in obtaining pure aluminium oxide?
- The aluminium oxide for the electrolytic extraction of aluminium is obtained by heating aluminium hydroxide. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
- Name the element which serves both as the anode and the cathode in the extraction of aluminium.
- Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction that occurs at the cathode during the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis.
- Give the balanced chemical equation for the reaction which occurs at the anode when aluminium is purified by electrolysis.
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Metallurgy Exercise 8 [Page 186]
Find the odd one out of the following and explain your choice.
Sulphur, Phosphorous, Carbon, Iodine
Find the odd one out of the following and explain your choice : Copper, Lead, Zinc, Mercury
Correct the following statement :
Copper reacts with nitric acid to produce nitrogen dioxide.
Correct the following statement :
Haematite is the chief ore of aluminium.
The sketch below illustrates the refin ing of aluminium by Hoope's process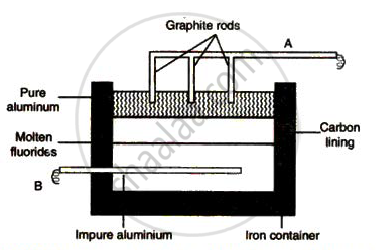
(a) Which of A and B is th e cathode and which one is the anode?
(b) What is the electroly te in the tank?
( c) What material is used for th e cathode?
State the property of the metal being utilized in the following :
| Use of metal | Property |
| Zinc in Galvanization | |
| Aluminium in Thermite welding |
Choose the correct answer:
Brass is an alloy of ______.
Copper and tin
Copper and zinc
Zinc and lead
Lead and tin
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Metallurgy Exercise 9 [Page 187]
Which one of the following is not true of metal :
Metals are good conductors of electricity.
True
False
Which one of the following is not true of metal :
Metals are malleable and ductile
True
False
Which one of the following is not true of metal :
Metals form non-polar covalent compounds
True
False
Which one of the following is not true of metal :
Metal will have 1 or 2 or 3 electrons in their valence shell.
True
False
Name the main constituent metal in the following alloy:
Duralumin
Name the main constituent metal in the following alloy:
Brass
Name the main constituent metal in the following alloy:
Stainless steel
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The metal is a liquid at room temperature.
Potassium
Zinc
Gold
Mercury
Answer the following question :
Name a metal which is found abundantly in earth's crust.
Answer the following question :
What is the difference between calcination and roasting.
Answer the following question :
Name the process used for the enrichment of sulphide ore.
Write the chemical formulae of the main ore of aluminium.
Write the chemical formulae of the main ore of iron.
Answer the following question :
Write the constituents of electrolyte for the extraction of aluminum.
| X | Y | |
| Normal Electronic Configuration | 2, 8, 7 | 2, 8, 2 |
| Nature of Oxide | Dissolves in water and truns blue litmus red. | Very low solubility in water. Dissolves in hydrochloric acid. |
| Tendency for Oxidising and reducing reactions | Tends to oxidise elements and compound. | Tends to act as a reducing agent. |
| Electrical and Thermal Conductivity | Very poor electrical conductor. Poor thermal conductivity. |
Good electrical conductor. Good thermal conductor. |
| Tendency to form Alloys and Amalgams | No tendency to form alloys. | Forms alloys. |
Using the information above, complete the following:
- _________ is the metallic element.
- Metal atoms tend to have a maximum of ________ electrons in the outermost energy level.
- Non-metallic elements tend to form _________ oxides while metals tend to form _______ oxides.
- Non-metallic elements tend to be ______ conductors of heat and electricity.
- Metals tend to _______ electrons and act as ________ agents in their reactions with elements and compounds.
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Metallurgy Exercise 10 [Page 188]
The metals zinc and tin are present in the alloy
Solder
Brass
Bronze
Duralumin
The following question relate to the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis.
Name the other aluminium containing compound added to alumina and state the significance.
The following question relate to the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis.
Give the equation for the reaction that takes place at the cathode
The following question relate to the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis.
Explain why is it necessary to renew the anode periodically.
State the main components of the following alloy:
Brass
State the main components of the following alloy:
Duralumin
State the main components of the following alloy:
Bronze
Name the following.
The property possessed by metals by which they can be beaten into sheets.
Name the following :
A compound added to lower the fusion temperature of electrolytic bath in the extracton of aluminium.
Name the following:
The ore of zinc containing its sulphide.
The main ore used for the extraction of iron is ______.
Haematite
Calamine
Bauxite
Cryolite
Heating an ore in a limited supply of air or in the absence of air at a temperature just below its melting point is known as ______.
Smelting
Ore dressing
Calcination
bessemerisation
Aluminium powder is used in thermite welding because
It is a strong reducing agent
It is a strong oxidizing agent
It is corrosion resistant
It is a good conductor of heat
This is not an alloy of copper:
Brass
Bronze
Solder
Durlamium
Describe the role played in the extraction of aluminum:
Cryolite
Describe the role played in the extraction of aluminum:
Sodium hydroxide
Describe the role played in the extraction of aluminum : Graphite
Explain why :
In the electrolysis of alumina using the Hall Heroult's Process the electrolyte is covered with powdered coke.
Explain why :
Iron sheets are coated with zinc during galvanization.
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Metallurgy Exercise 11 [Page 189]
Name the solution used to react with bauxite as a first step in obtaining pure aluminium oxide, in the Baeyer's process.
Write the equation for the reaction where the aluminium oxide for the electrolytic extraction of aluminium is obtained by heating aluminium hydroxide.
Name the compound added to pure alumina to lower the fusion temperature during the electrolytic reduction of alumina.
Write the equation for the reaction that occurs at the cathode during the extraction by aluminium by electrolysis.
Explain why it is preferably to use a number of graphite electrodes as anode instead of a single electrode, during the above electrolysis.
The two main metals in bronze are
Copper and zinc
Copper and lead
Copper and nickel
Copper and tin
Name the following :
The process of coating of iron with zinc.
Name the following :
An alloy of lead and tin that is use in electrical circuits.
Name the following :
An ore of zinc containing its sulphide.
Name the following :
A metal oxide that can be reduced by hydrogen
Answer the following question with respect by hydrogen : Identify the components of the electrolyte other than pure alumina and the role played by each.
Answer the following question with respect by hydrogen :
Explain why powdered coke is sprinkled over than electrolytic mixture.
Complete the following by selecting the correct option from the choices given:
The metal which does not react with water or dilute H2SO4 but reacts with concentrated H2SO4 is _________
Al
Cu
Zn
Fe
Complete the following by selecting the correct option from the choices given :
The metal whose oxide, which is amphoteric, is reduced to metal by carbon reduction ________
Fe
Mg
Pb
Al
Complete the following by selecting the correct option from the choices given :
The diavalent metal whose oxide is reduced to metal by electrolysis of its fused salt is ________
Al
Na
Mg
K
choose the most appropriate term to match the given description.
Crushing of the ore into a fine powder
Calcination
roasting
pulverization
smelting
choose the most appropriate term to match the given description.
Heating of the ore in the absence of air to high temperature
Calcination
roasting
pulverization
smelting
Solutions for 7: Metallurgy
![Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Metallurgy Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Metallurgy - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-part-2-english-class-10-icse_6:083608507a004841af01e3c142179570.PNG)
Frank solutions for Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Metallurgy
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Frank solutions for Mathematics Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 7 (Metallurgy) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Frank textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 Metallurgy are Mineral Resources, Types of Element: Non-metal, Ores, Extraction of Reactive Metals, Types of Element: Metals, Corrosion of Metals, Metallurgy, Types of Separation or Concentration of an Ore, Conversion of Concentrated Ore to Its Oxide, Reactivity Series of Metals, Reduction of Metal Oxides to Metals, Refining of Metals, Metallurgy of Aluminium, Extraction of Aluminium, Refining of Aluminium, Alloy, Making Alloys, Some Common Alloys, Prevention of Corrosion.
Using Frank Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Metallurgy exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Frank Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Frank Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 7, Metallurgy Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry - Part 2 [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
