Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
∠ACD is an exterior angle of Δ ABC. If ∠B = 40o, ∠A = 70o find ∠ACD.
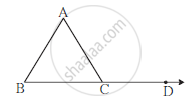
उत्तर
∠ ACD = ∠ B + ∠ A .............. (theorem of remote interior angle)
= 40 + 70
= 110˚
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the angle θ = -60° , find the value of sinθ .
If `cosθ=1/sqrt(2)`, where θ is an acute angle, then find the value of sinθ.
If A, B, C are the interior angles of a triangle ABC, prove that `\tan \frac{B+C}{2}=\cot \frac{A}{2}`
If tan A = cot B, prove that A + B = 90
if `cos theta = 4/5` find all other trigonometric ratios of angles θ
Evaluate.
sin(90° - A) cosA + cos(90° - A) sinA
Evaluate:
`(sin35^circ cos55^circ + cos35^circ sin55^circ)/(cosec^2 10^circ - tan^2 80^circ)`
Use tables to find the acute angle θ, if the value of tan θ is 0.7391
Prove that:
`1/(1 + cos(90^@ - A)) + 1/(1 - cos(90^@ - A)) = 2cosec^2(90^@ - A)`
Find A, if 0° ≤ A ≤ 90° and 2 cos2 A – 1 = 0
If tanθ = 2, find the values of other trigonometric ratios.
What is the maximum value of \[\frac{1}{\sec \theta}\]
Write the value of cos 1° cos 2° cos 3° ....... cos 179° cos 180°.
If θ and 2θ − 45° are acute angles such that sin θ = cos (2θ − 45°), then tan θ is equal to
Without using trigonometric tables, prove that:
sec70° sin20° + cos20° cosec70° = 2
A triangle ABC is right-angled at B; find the value of `(sec "A". sin "C" - tan "A". tan "C")/sin "B"`.
Find the value of the following:
`((cos 47^circ)/(sin 43^circ))^2 + ((sin 72^circ)/(cos 18^circ))^2 - 2cos^2 45^circ`
If sin A = `3/5` then show that 4 tan A + 3 sin A = 6 cos A
In ∆ABC, `sqrt(2)` AC = BC, sin A = 1, sin2A + sin2B + sin2C = 2, then ∠A = ? , ∠B = ?, ∠C = ?
If x and y are complementary angles, then ______.
