Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Let f and g be two functions given by
f = {(2, 4), (5, 6), (8, −1), (10, −3)} and g = {(2, 5), (7, 1), (8, 4), (10, 13), (11, −5)}.
Find the domain of f + g
Solution
It is given that f and g are two functions such that
f = {(2, 4), (5, 6), (8, −1), (10, −3)}
and g = {(2, 5), (7, 1), (8, 4), (10, 13), (11, −5)}
Now,
Domain of f = Df = {2, 5, 8, 10}
Domain of g = Dg = {2, 7, 8, 10, 11}
∴ Domain of f + g = Df ∩ Dg = {2, 8, 10}
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which of the following relations are functions? Give reasons. If it is a function, determine its domain and range.
- {(2, 1), (5, 1), (8, 1), (11, 1), (14, 1), (17, 1)}
- {(2, 1), (4, 2), (6, 3), (8, 4), (10, 5), (12, 6), (14, 7)}
- {(1, 3), (1, 5), (2, 5)}
Find the domain of the function f(x) = `(x^2 + 2x + 1)/(x^2 - 8x + 12)`
Let A = {9, 10, 11, 12, 13} and let f: A → N be defined by f(n) = the highest prime factor of n. Find the range of f.
Let A = {−2, −1, 0, 1, 2} and f : A → Z be a function defined by f(x) = x2 − 2x − 3. Find:
(a) range of f, i.e. f(A).
et A = (12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17) and f : A → Z be a function given by
f(x) = highest prime factor of x.
Find range of f.
The function f is defined by \[f\left( x \right) = \begin{cases}x^2 , & 0 \leq x \leq 3 \\ 3x, & 3 \leq x \leq 10\end{cases}\]
The relation g is defined by \[g\left( x \right) = \begin{cases}x^2 , & 0 \leq x \leq 2 \\ 3x, & 2 \leq x \leq 10\end{cases}\]
Show that f is a function and g is not a function.
If \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{x + 1}{x - 1}\] , show that f[f[(x)]] = x.
If \[f\left( x \right) = x^3 - \frac{1}{x^3}\] , show that
Let f and g be two real functions defined by \[f\left( x \right) = \sqrt{x + 1}\] and \[g\left( x \right) = \sqrt{9 - x^2}\] . Then, describe function:
(v) \[\frac{g}{f}\]
If f(x) = loge (1 − x) and g(x) = [x], then determine function:
(iv) \[\frac{g}{f}\] Also, find (f + g) (−1), (fg) (0),
If f, g and h are real functions defined by
Let f and g be two real functions given by
f = {(0, 1), (2, 0), (3, −4), (4, 2), (5, 1)} and g = {(1, 0), (2, 2), (3, −1), (4, 4), (5, 3)}
Find the domain of fg.
The function f : R → R is defined by f(x) = cos2 x + sin4 x. Then, f(R) =
The domain of definition of \[f\left( x \right) = \sqrt{x - 3 - 2\sqrt{x - 4}} - \sqrt{x - 3 + 2\sqrt{x - 4}}\] is
The range of the function \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{x}{\left| x \right|}\] is
Let \[f\left( x \right) = \sqrt{x^2 + 1}\ ] . Then, which of the following is correct?
The range of \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{1 - 2\cos x}\] is
A function f is defined as follows: f(x) = 5 − x for 0 ≤ x ≤ 4. Find the value of x such that f(x) = 3
If f(m) = m2 − 3m + 1, find f(−3)
Find x, if g(x) = 0 where g(x) = x3 − 2x2 − 5x + 6
Express the area A of a square as a function of its side s
Express the area A of circle as a function of its diameter d
Express the following exponential equation in logarithmic form
e2 = 7.3890
Express the following exponential equation in logarithmic form
`"e"^(1/2)` = 1.6487
Express the following logarithmic equation in exponential form
`log_(1/2) (8)` = – 3
Write the following expression as sum or difference of logarithm
In `[(root(3)(x - 2)(2x + 1)^4)/((x + 4)sqrt(2x + 4))]^2`
Solve for x.
log2 x + log4 x + log16 x = `21/4`
If f(x) = 3x + 5, g(x) = 6x − 1, then find (f + g) (x)
Answer the following:
If f(x) = ax2 + bx + 2 and f(1) = 3, f(4) = 42, find a and b
Answer the following:
Find the domain of the following function.
f(x) = `(x^2 + 4x + 4)/(x^2 + x - 6)`
A graph representing the function f(x) is given in it is clear that f(9) = 2
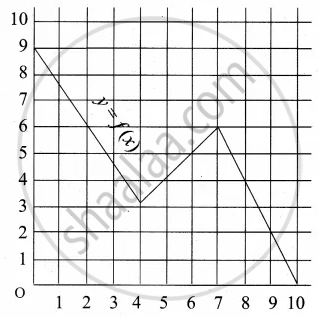
What is the image of 6 under f?
A function f is defined by f(x) = 2x – 3 find `("f"(0) + "f"(1))/2`
A function f is defined by f(x) = 3 – 2x. Find x such that f(x2) = (f(x))2
The range of the function f(x) = `(x - 3)/(5 - x)`, x ≠ 5 is ______.
The range of the function f(x) = `(x^2 - 3x + 2)/(x^3 - 4x^2 + 5x - 2)` is ______
Let f : R → R be defined by
f(x) = `{(3x; x > 2),(2x^2; 1 ≤ x ≤ 2), (4x; x < 1):}`
Then f(-2) + f(1) + f(3) is ______
Find the domain for which the functions f(x) = 2x2 – 1 and g(x) = 1 – 3x are equal.
Let A and B be any two sets such that n(B) = p, n(A) = q then the total number of functions f : A → B is equal to ______.
Let f(x) = `sqrt(x)` and g(x) = x be two functions defined in the domain R+ ∪ {0}. Find (f + g)(x)
