Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State the law of radioactive decay.
Solution
Law of radioactive decay:
The number of nuclei undergoing the decay per unit time is proportional to the number of unchanged nuclei present at that instant.
If ‘N’ is the number of nuclei present at any instant ‘t’, ‘dN’ is the number of nuclei that disintegrated in short interval of time ‘dt’, then according to decay law,
`- (dN)/dt ∝ N`
`:.(dN)/dt = -lambda N`
where, `lambda` is known as decay constant or disintegration constant. The negative sign indicates disintegration of atoms.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Derive the mathematical expression for law of radioactive decay for a sample of a radioactive nucleus
How is the mean life of a given radioactive nucleus related to the decay constant?
A radioactive isotope has a half-life of T years. How long will it take the activity to reduce to a) 3.125%, b) 1% of its original value?
Obtain the amount of `""_27^60"Co"` necessary to provide a radioactive source of 8.0 mCi strength. The half-life of `""_27^60"Co"` is 5.3 years.
The radionuclide 11C decays according to
\[\ce{^11_6C -> ^11_5B + e+ + \text{v}}\] : T1/2 = 20.3 min
The maximum energy of the emitted positron is 0.960 MeV.
Given the mass values: `"m"(""_6^11"C") = 11.011434 u and "m"(""_6^11"B") = 11.009305 "u"`
Calculate Q and compare it with the maximum energy of the positron emitted.
The Q value of a nuclear reaction \[\ce{A + b → C + d}\] is defined by
Q = [ mA+ mb− mC− md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^1_1H + ^3_1H -> ^2_1H + ^2_1H}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12"C")` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
Represent Radioactive Decay curve using relation `N = N_o e^(-lambdat)` graphically
Using the equation `N = N_0e^(-lambdat)` obtain the relation between half-life (T) and decay constant (`lambda`) of a radioactive substance.
(a) Derive the relation between the decay constant and half life of a radioactive substance.
(b) A radioactive element reduces to 25% of its initial mass in 1000 years. Find its half life.
Define 'activity' of a radioactive substance ?
Two different radioactive elements with half lives T1 and T2 have N1 and N2 undecayed atoms respectively present at a given instant. Derive an expression for the ratio of their activities at this instant in terms of N1 and N2 ?
A radioactive nucleus ‘A’ undergoes a series of decays according to the following scheme:
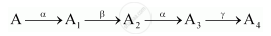
The mass number and atomic number of A are 180 and 72 respectively. What are these numbers for A4?
In a radioactive decay, neither the atomic number nor the mass number changes. Which of the following particles is emitted in the decay?
The decay constant of a radioactive sample is λ. The half-life and the average-life of the sample are respectively
The masses of 11C and 11B are respectively 11.0114 u and 11.0093 u. Find the maximum energy a positron can have in the β*-decay of 11C to 11B.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
28Th emits an alpha particle to reduce to 224Ra. Calculate the kinetic energy of the alpha particle emitted in the following decay:
`""^228"Th" → ""^224"Ra"^(∗) + alpha`
`""^224"Ra"^(∗) → ""^224"Ra" + γ (217 "keV")`.
Atomic mass of 228Th is 228.028726 u, that of 224Ra is 224.020196 u and that of `""_2^4H` is 4.00260 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the beta particle emitted in the following decay scheme:
12N → 12C* + e+ + v
12C* → 12C + γ (4.43MeV).
The atomic mass of 12N is 12.018613 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
The decay constant of `""_80^197`Hg (electron capture to `""_79^197`Au) is 1.8 × 10−4 S−1. (a) What is the half-life? (b) What is the average-life? (c) How much time will it take to convert 25% of this isotope of mercury into gold?
The decay constant of 238U is 4.9 × 10−18 S−1. (a) What is the average-life of 238U? (b) What is the half-life of 238U? (c) By what factor does the activity of a 238U sample decrease in 9 × 109 years?
57Co decays to 57Fe by β+- emission. The resulting 57Fe is in its excited state and comes to the ground state by emitting γ-rays. The half-life of β+- decay is 270 days and that of the γ-emissions is 10−8 s. A sample of 57Co gives 5.0 × 109 gamma rays per second. How much time will elapse before the emission rate of gamma rays drops to 2.5 × 109per second?
When charcoal is prepared from a living tree, it shows a disintegration rate of 15.3 disintegrations of 14C per gram per minute. A sample from an ancient piece of charcoal shows 14C activity to be 12.3 disintegrations per gram per minute. How old is this sample? Half-life of 14C is 5730 y.
A radioactive isotope is being produced at a constant rate dN/dt = R in an experiment. The isotope has a half-life t1/2. Show that after a time t >> t1/2 the number of active nuclei will become constant. Find the value of this constant.
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Suppose the production of the radioactive isotope starts at t = 0. Find the number of active nuclei at time t.
Obtain a relation between the half-life of a radioactive substance and decay constant (λ).
Identify the nature of the radioactive radiations emitted in each step of the decay process given below.
`""_Z^A X -> _Z^A _-1^-4 Y ->_Z^A _-1^-4 W`
A radioactive substance disintegrates into two types of daughter nuclei, one type with disintegration constant λ1 and the other type with disintegration constant λ2 . Determine the half-life of the radioactive substance.
What is the amount of \[\ce{_27^60Co}\] necessary to provide a radioactive source of strength 10.0 mCi, its half-life being 5.3 years?
The isotope \[\ce{^57Co}\] decays by electron capture to \[\ce{^57Fe}\] with a half-life of 272 d. The \[\ce{^57Fe}\] nucleus is produced in an excited state, and it almost instantaneously emits gamma rays.
(a) Find the mean lifetime and decay constant for 57Co.
(b) If the activity of a radiation source 57Co is 2.0 µCi now, how many 57Co nuclei does the source contain?
c) What will be the activity after one year?
Two radioactive materials X1 and X2 have decay constants 10λ and λ respectively. If initially, they have the same number of nuclei, then the ratio of the number of nuclei of X1 to that of X2 will belie after a time.
A radioactive element disintegrates for an interval of time equal to its mean lifetime. The fraction that has disintegrated is ______
Which one of the following nuclei has shorter meant life?
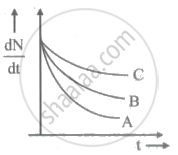
'Half-life' of a radioactive substance accounts for ______.
The half-life of a radioactive sample undergoing `alpha` - decay is 1.4 x 1017 s. If the number of nuclei in the sample is 2.0 x 1021, the activity of the sample is nearly ____________.
Two radioactive materials Y1 and Y2 have decay constants '5`lambda`' and `lambda` respectively. Initially they have same number of nuclei. After time 't', the ratio of number of nuclei of Y1 to that of Y2 is `1/"e"`, then 't' is equal to ______.
What percentage of radioactive substance is left after five half-lives?
Two electrons are ejected in opposite directions from radioactive atoms in a sample of radioactive material. Let c denote the speed of light. Each electron has a speed of 0.67 c as measured by an observer in the laboratory. Their relative velocity is given by ______.
The half-life of a radioactive nuclide is 20 hrs. The fraction of the original activity that will remain after 40 hrs is ______.
If 10% of a radioactive material decay in 5 days, then the amount of original material left after 20 days is approximately :
When a nucleus in an atom undergoes a radioactive decay, the electronic energy levels of the atom ______.
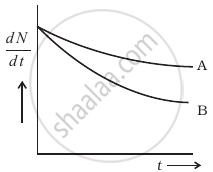
Which sample, A or B shown in figure has shorter mean-life?
A piece of wood from the ruins of an ancient building was found to have a 14C activity of 12 disintegrations per minute per gram of its carbon content. The 14C activity of the living wood is 16 disintegrations per minute per gram. How long ago did the tree, from which the wooden sample came, die? Given half-life of 14C is 5760 years.
Sometimes a radioactive nucleus decays into a nucleus which itself is radioactive. An example is :
\[\ce{^38Sulphur ->[half-life][= 2.48h] ^{38}Cl ->[half-life][= 0.62h] ^38Air (stable)}\]
Assume that we start with 1000 38S nuclei at time t = 0. The number of 38Cl is of count zero at t = 0 and will again be zero at t = ∞ . At what value of t, would the number of counts be a maximum?
The activity R of an unknown radioactive nuclide is measured at hourly intervals. The results found are tabulated as follows:
| t (h) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| R (MBq) | 100 | 35.36 | 12.51 | 4.42 | 1.56 |
- Plot the graph of R versus t and calculate the half-life from the graph.
- Plot the graph of ln `(R/R_0)` versus t and obtain the value of half-life from the graph.
The half-life of `""_82^210Pb` is 22.3 y. How long will it take for its activity 0 30% of the initial activity?
