Topics
Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land
- Natural Resources
- Atmosphere and Its Layers
- Air Around Us
- Composition and Components of Air
- Importance of Air
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Water: Our Lifeline
- Availability of Water
- Composition of Water
- Importance of Water
- Scarcity of Water
- Land
- Soil Formation
- The Importance of Conserving Earth’s Natural Resources
The Living World
Diversity in Living Things and Their Classification
Disaster Management
Substances in the Surroundings –Their States and Properties
Substances in Daily Use
Nutrition and Diet
- Nutrients and Nutrition
- Component of Food
- Carbohydrates
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Carbohydrates
- Fats (Lipids)
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Fats
- Proteins
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Proteins
- Vitamin and Minerals
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Vitamin
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Minerals
- Fibre
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Fibre
- Water
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Water
- A Balanced Diet
- Nourishment and Malnutrition
- Food Adulteration
Our Skeletal System and the Skin
Motion and Types of Motion
Force and Types of Force
Work and Energy
- Force, displacement and work
- Energy
- The relationship between work and energy
- Forms of Energy
- Mechanical Energy
- Power Plants Based on Thermal Energy
- Light Energy
- Sound energy
- Chemical Energy
- Transformation of Energy
- Energy Resources
- Conventional energy resources or non-renewable energy resources
- Non-conventional energy resources or renewable energy resources
- Energy saving and green energy
Simple Machines
Sound
Light and the Formation of Shadows
Fun with Magnets
The Universe
- Introduction
- Water Cycle
Introduction
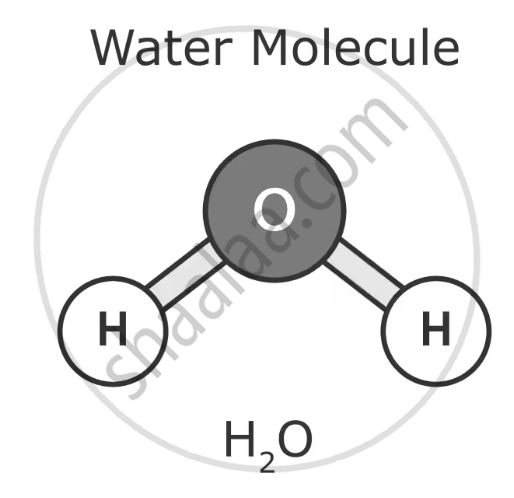
The chemical formula of water is H₂O, which consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom.
1. Molecular Structure
- Covalent bonds: hydrogen and oxygen atoms held together by shared electrons, forming a stable molecule.
- Polar Molecule: Water has a positive charge near the hydrogen atoms and a negative charge near the oxygen atom.
2. Properties Due to Composition
- Cohesion and Adhesion: Water molecules stick together due to hydrogen bonding, leading to high surface tension and capillary action.
- High Specific Heat: Water absorbs significant heat before it gets hot, regulating environmental and biological temperatures.
- Solvent Abilities: Water is the "universal solvent." It can dissolve more substances than any other liquid due to its polarity.
3. States of Water
- Solid (Ice): Water expands and becomes less dense upon freezing, allowing ice to float on liquid water.
- Liquid: Water is fluid in this state, conforming to the shape of its container.
- Gas (Water Vapour): Water vaporises into the atmosphere, contributing to the water cycle when heated.
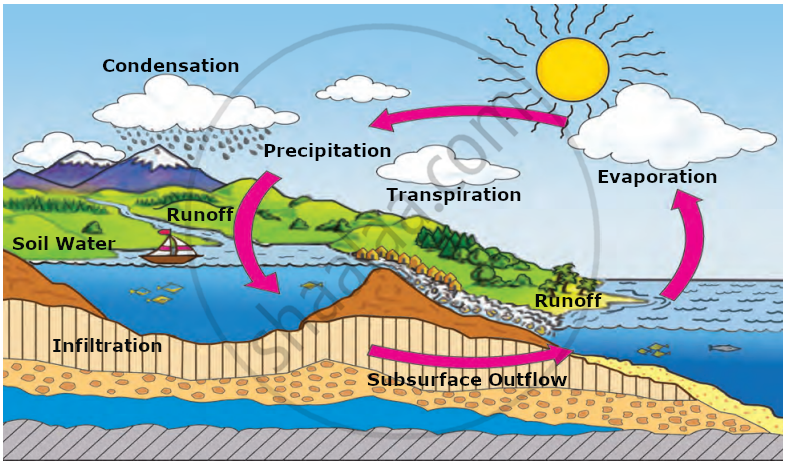
Water Cycle:
We use water in large quantities. Water on the earth is regulated through the water cycle. The water vapour formed from oceans is the main source of water in the water cycle. It gets converted into rain, creating freshwater sources on earth.
- Evaporation: Water from oceans, rivers, and lakes heats up by the sun, turning into vapour or steam that rises into the air.
- Condensation: Water vapour cools in the sky, forming tiny droplets that come together to form clouds.
- Precipitation: When clouds become too heavy, water falls to Earth as rain, snow, or hail, depending on the temperature.
- Collection: Water gathers in rivers, lakes, and oceans, with some seeping into the ground to become groundwater.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
