Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
We have,
Clearly, it is a linear differential equation of the form
Integrating both sides with respect to x, we get
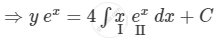
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the particular solution of the differential equation x (1 + y2) dx – y (1 + x2) dy = 0, given that y = 1 when x = 0.
Verify that the given function (explicit or implicit) is a solution of the corresponding differential equation:
y = x2 + 2x + C : y′ – 2x – 2 = 0
Verify that the given function (explicit or implicit) is a solution of the corresponding differential equation:
xy = log y + C :
Verify that the given function (explicit or implicit) is a solution of the corresponding differential equation:
If y = etan x+ (log x)tan x then find dy/dx
Solve the differential equation:
Write the order of the differential equation associated with the primitive y = C1 + C2 ex + C3 e−2x + C4, where C1, C2, C3, C4 are arbitrary constants.
The general solution of the differential equation
The solution of the differential equation x dx + y dy = x2 y dy − y2 x dx, is
The solution of the differential equation
The number of arbitrary constants in the general solution of differential equation of fourth order is
Which of the following differential equations has y = x as one of its particular solution?
For the following differential equation, find the general solution:-
For the following differential equation, find the general solution:-
For the following differential equation, find the general solution:-
For the following differential equation, find the general solution:-
Solve the following differential equation:-
Solve the following differential equation:-
Find the equation of a curve passing through the point (−2, 3), given that the slope of the tangent to the curve at any point (x, y) is
Solution of the differential equation
The general solution of the differential equation
y = x is a particular solution of the differential equation
Form the differential equation having y = (sin–1x)2 + Acos–1x + B, where A and B are arbitrary constants, as its general solution.
Solve:
Solve the differential equation (1 + y2) tan–1xdx + 2y(1 + x2)dy = 0.
If y = e–x (Acosx + Bsinx), then y is a solution of ______.
The general solution of ex cosy dx – ex siny dy = 0 is ______.
The solution of the differential equation
The solution of the differential equation
General solution of
The solution of differential equation coty dx = xdy is ______.
Number of arbitrary constants in the particular solution of a differential equation of order two is two.
The member of arbitrary constants in the particulars solution of a differential equation of third order as
The differential equation of all parabolas that have origin as vertex and y-axis as axis of symmetry is ______.
