Advertisements
Chapters
2: Data Handling
3: Square-Square Root and Cube-Cube Root
4: Linear Equation In One Variable
5: Understanding Quadrilaterals and Practical Geometry
6: Visualising Solid Shapes
7: Algebraic Expression, Identities and Factorisation
8: Exponents and Powers
9: Comparing Quantities
10: Direct and Inverse Proportions
▶ 11: Mensuration
12: Introduct To Graphs
13: Playing With Numbers
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 11 - Mensuration NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 11 - Mensuration - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-8_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 11: Mensuration
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 11 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Mathematics [English] Class 8.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 11 Mensuration Exercise [Pages 344 - 360]
Choose the correct alternative:
A cube of side 5 cm is painted on all its faces. If it is sliced into 1 cubic centimetre cubes, how many 1 cubic centimetre cubes will have exactly one of their faces painted?
27
42
54
142
A cube of side 4 cm is cut into 1 cm cubes. What is the ratio of the surface areas of the original cubes and cut-out cubes?
1 : 2
1 : 3
1 : 4
1 : 6
A circle of maximum possible size is cut from a square sheet of board. Subsequently, a square of maximum possible size is cut from the resultant circle. What will be the area of the final square?
`3/4` of original square.
`1/2` of original square.
`1/4` of original square.
`2/3` of original square.
What is the area of the largest triangle that can be fitted into a rectangle of length l units and width w units?
`(lw)/2`
`(lw)/3`
`(lw)/6`
`(lw)/4`
If the height of a cylinder becomes `1/4` of the original height and the radius is doubled, then which of the following will be true?
Volume of the cylinder will be doubled.
Volume of the cylinder will remain unchanged.
Volume of the cylinder will be halved.
Volume of the cylinder will be `1/4` of the original volume.
If the height of a cylinder becomes `1/4` of the original height and the radius is doubled, then which of the following will be true?
Curved surface area of the cylinder will be doubled.
Curved surface area of the cylinder will remain unchanged.
Curved surface area of the cylinder will be halved.
Curved surface area will be `1/4` of the original curved surface.
If the height of a cylinder becomes `1/4` of the original height and the radius is doubled, then which of the following will be true?
Total surface area of the cylinder will be doubled.
Total surface area of the cylinder will remain unchanged.
Total surface of the cylinder will be halved.
None of the above.
The surface area of the three coterminus faces of a cuboid are 6, 15 and 10 cm2 respectively. The volume of the cuboid is ______.
30 cm3
40 cm3
20 cm3
35 cm3
A regular hexagon is inscribed in a circle of radius r. The perimeter of the regular hexagon is ______.
3r
6r
9r
12r
The dimensions of a godown are 40 m, 25 m and 10 m. If it is filled with cuboidal boxes each of dimensions 2 m × 1.25 m × 1 m, then the number of boxes will be ______.
1800
2000
4000
8000
The volume of a cube is 64 cm3. Its surface area is ______.
16 cm2
64 cm2
96 cm2
128 cm2
If the radius of a cylinder is tripled but its curved surface area is unchanged, then its height will be ______.
tripled
constant
one sixth
one third
How many small cubes with edge of 20 cm each can be just accommodated in a cubical box of 2 m edge?
10
100
1000
10000
The volume of a cylinder whose radius r is equal to its height is ______.
`1/4 pir^3`
`(pir^3)/32`
`pir^3`
`r^3/8`
The volume of a cube whose edge is 3x is ______.
27x3
9x3
6x3
3x3
The figure ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AB = CD and BC = AD. Its area is ______.

72 cm2
36 cm2
24 cm2
18 cm2
What is the area of the rhombus ABCD below if AC = 6 cm and BE = 4 cm?
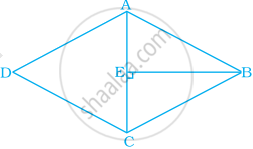
36 cm2
16 cm2
24 cm2
13 cm2
The area of a parallelogram is 60 cm2 and one of its altitudes is 5 cm. The length of its corresponding side is ______.
12 cm
6 cm
4 cm
2 cm
The perimeter of a trapezium is 52 cm and its each non-parallel side is equal to 10 cm with its height 8 cm. Its area is ______.
124 cm2
118 cm2
128 cm2
112 cm2
Area of a quadrilateral ABCD is 20 cm2 and perpendiculars on BD from opposite vertices are 1 cm and 1.5 cm. The length of BD is ______.
4 cm
15 cm
16 cm
18 cm
A metal sheet 27 cm long, 8 cm broad and 1 cm thick is melted into a cube. The side of the cube is ______.
6 cm
8 cm
12 cm
24 cm
Three cubes of metal whose edges are 6 cm, 8 cm and 10 cm respectively are melted to form a single cube. The edge of the new cube is ______.
12 cm
24 cm
18 cm
20 cm
A covered wooden box has the inner measures as 115 cm, 75 cm and 35 cm and thickness of wood as 2.5 cm. The volume of the wood is ______.
85,000 cm3
80,000 cm3
82,125 cm3
84,000 cm3
The ratio of radii of two cylinders is 1 : 2 and heights are in the ratio 2 : 3. The ratio of their volumes is ______.
1 : 6
1 : 9
1 : 3
2 : 9
Two cubes have volumes in the ratio 1 : 64. The ratio of the area of a face of first cube to that of the other is ______.
1 : 4
1 : 8
1 : 16
1 : 32
The surface areas of the six faces of a rectangular solid are 16, 16, 32, 32, 72 and 72 square centimetres. The volume of the solid, in cubic centimetres, is ______.
192
384
480
2592
Ramesh has three containers.
- Cylindrical container A having radius r and height h,
- Cylindrical container B having radius 2r and height 1/2 h, and
- Cuboidal container C having dimensions r × r × h
The arrangement of the containers in the increasing order of their volumes is
A, B, C
B, C, A
C, A, B
cannot be arranged
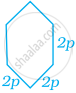
If R is the radius of the base of the hat, then the total outer surface area of the hat is ______.

πr(2h + R)
2πr(h + R)
2πrh + πR2
None of these
Fill in the blanks:
A cube of side 4 cm is painted on all its sides. If it is sliced in 1 cubic cm cubes, then number of such cubes that will have exactly two of their faces painted is ______.
A cube of side 5 cm is cut into 1 cm cubes. The percentage increase in volume after such cutting is ______.
The surface area of a cuboid formed by joining two cubes of side a face to face is ______.
If the diagonals of a rhombus get doubled, then the area of the rhombus becomes ______ its original area.
If a cube fits exactly in a cylinder with height h, then the volume of the cube is ______ and surface area of the cube is ______.
The volume of a cylinder becomes ______ the original volume if its radius becomes half of the original radius.
The curved surface area of a cylinder is reduced by ______ per cent if the height is half of the original height.
The volume of a cylinder which exactly fits in a cube of side a is ______.
The surface area of a cylinder which exactly fits in a cube of side b is ______.
If the diagonal d of a quadrilateral is doubled and the heights h1 and h2 falling on d are halved, then the area of quadrilateral is ______.
The perimeter of a rectangle becomes ______ times its original perimeter, if its length and breadth are doubled.
A trapezium with 3 equal sides and one side double the equal side can be divided into ______ equilateral triangles of ______ area.
All six faces of a cuboid are ______ in shape and of ______ area.
Opposite faces of a cuboid are ______ in area.
Curved surface area of a cylinder of radius h and height r is ______.
Total surface area of a cylinder of radius h and height r is ______.
Volume of a cylinder with radius h and height r is ______.
Area of a rhombus = `1/2` product of ______.
Two cylinders A and B are formed by folding a rectangular sheet of dimensions 20 cm × 10 cm along its length and also along its breadth respectively. Then volume of A is ______ of volume of B.
In the above question, curved surface area of A is ______ curved surface area of B.
______ of a solid is the measurement of the space occupied by it.
______ surface area of room = area of 4 walls.
Two cylinders of equal volume have heights in the ratio 1 : 9. The ratio of their radii is ______.
Two cylinders of same volume have their radii in the ratio 1 : 6, then ratio of their heights is ______.
State whether the following statement is True or False:
The areas of any two faces of a cube are equal.
True
False
The areas of any two faces of a cuboid are equal.
True
False
The surface area of a cuboid formed by joining face to face 3 cubes of side x is 3 times the surface area of a cube of side x.
True
False
Two cuboids with equal volumes will always have equal surface areas.
True
False
The area of a trapezium become 4 times if its height gets doubled.
True
False
A cube of side 3 cm painted on all its faces, when sliced into 1 cubic centimetre cubes, will have exactly 1 cube with none of its faces painted.
True
False
Two cylinders with equal volume will always have equal surface areas.
True
False
The surface area of a cube formed by cutting a cuboid of dimensions 2 × 1 × 1 in 2 equal parts is 2 sq. units.
True
False
Ratio of area of a circle to the area of a square whose side equals radius of circle is 1 : π.
True
False
Solve the following:
The area of a rectangular field is 48 m2 and one of its sides is 6 m. How long will a lady take to cross the field diagonally at the rate of 20 m/minute?
The circumference of the front wheel of a cart is 3 m long and that of the back wheel is 4 m long. What is the distance travelled by the cart, when the front wheel makes five more revolutions than the rear wheel?
Four horses are tethered with equal ropes at 4 corners of a square field of side 70 metres so that they just can reach one another. Find the area left ungrazed by the horses.
The walls and ceiling of a room are to be plastered. The length, breadth and height of the room are 4.5 m, 3 m, and 350 cm respectively. Find the cost of plastering at the rate of Rs 8 per m2.
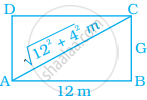
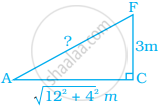
Most of the sailboats have two sails, the jib and the mainsail. Assume that the sails are triangles. Find the total area sail of the sailboats to the nearest tenth.
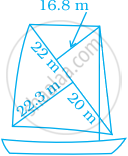
Most of the sailboats have two sails, the jib and the mainsail. Assume that the sails are triangles. Find the total area sail of the sailboats to the nearest tenth.
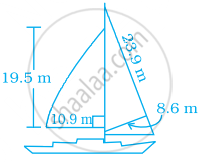
Most of the sailboats have two sails, the jib and the mainsail. Assume that the sails are triangles. Find the total area of sail of the sailboats to the nearest tenth.
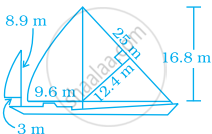
The area of a trapezium with equal non-parallel sides is 168 m2. If the lengths of the parallel sides are 36 m and 20 m, find the length of the non-parallel sides.
Mukesh walks around a circular track of radius 14 m with a speed of 4 km/hr. If he takes 20 rounds of the track, for how long does he walk?
The areas of two circles are in the ratio 49 : 64. Find the ratio of their circumferences.
There is a circular pond and a footpath runs along its boundary. A person walks around it, exactly once keeping close to the edge. If his step is 66 cm long and he takes exactly 400 steps to go around the pond, find the diameter of the pond.
A running track has 2 semicircular ends of radius 63 m and two straight lengths. The perimeter of the track is 1000 m. Find each straight length.
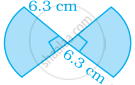
Find the perimeter of the given figure.
A bicycle wheel makes 500 revolutions in moving 1 km. Find the diameter of the wheel.
A boy is cycling such that the wheels of the cycle are making 140 revolutions per hour. If the diameter of the wheel is 60 cm, calculate the speed in km/h with which the boy is cycling.
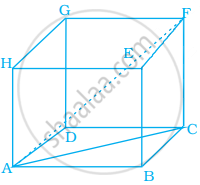
Find the length of the largest pole that can be placed in a room of dimensions 12 m × 4 m × 3 m.
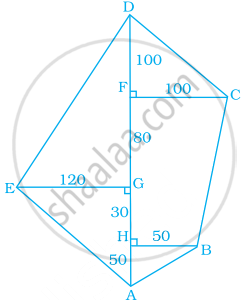
Find the area of the following fields. All dimensions are in metres.
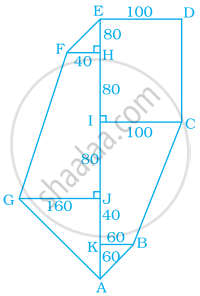
Find the area of the following fields. All dimensions are in metres.
Find the area of the shaded portion in the following figure.
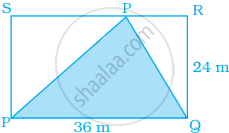
Find the area of the shaded portion in the following figure.
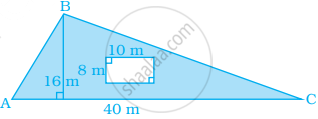
Find the area of the shaded portion in the following figure.
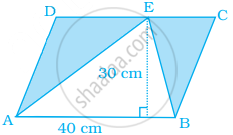
Find the area of the shaded portion in the following figure.
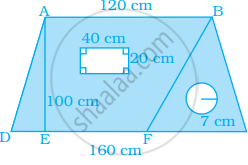
Find the area of the shaded portion in the following figure.
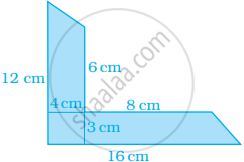
Find the area of the shaded portion in the following figure.
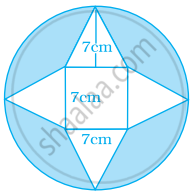
Find the area of the shaded portion in the following figure.
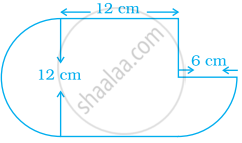
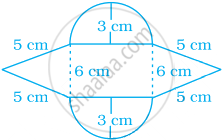
Find the area of the shaded portion in the following figure.
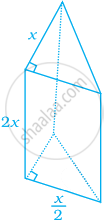
Find the volume of the given figure if volume = base area × height.
Find the volume of the given figure if volume = base area × height.
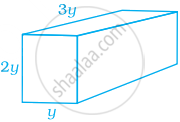
Find the volume of the given figure if volume = base area × height.
A cube of side 5 cm is cut into as many 1 cm cubes as possible. What is the ratio of the surface area of the original cube to that of the sum of the surface areas of the smaller cubes?
A square sheet of paper is converted into a cylinder by rolling it along its side. What is the ratio of the base radius to the side of the square?
How many cubic metres of earth must be dug to construct a well 7 m deep and of diameter 2.8 m?
The radius and height of a cylinder are in the ratio 3 : 2 and its volume is 19,404 cm3. Find its radius and height.
The thickness of a hollow metallic cylinder is 2 cm. It is 70 cm long with outer radius of 14 cm. Find the volume of the metal used in making the cylinder, assuming that it is open at both the ends. Also find its weight if the metal weighs 8 g per cm3.
Radius of a cylinder is r and the height is h. Find the change in the volume if the height is doubled.
Radius of a cylinder is r and the height is h. Find the change in the volume if the height is doubled and the radius is halved.
Radius of a cylinder is r and the height is h. Find the change in the volume if the height remains same and the radius is halved.
If the length of each edge of a cube is tripled, what will be the change in its volume?
A carpenter makes a box which has a volume of 13,400 cm3. The base has an area of 670 cm2. What is the height of the box?
A cuboidal tin box opened at the top has dimensions 20 cm × 16 cm × 14 cm. What is the total area of metal sheet required to make 10 such boxes?
Find the capacity of water tank, in litres, whose dimensions are 4.2 m, 3 m and 1.8 m?
How many cubes each of side 0.5 cm are required to build a cube of volume 8 cm3?
A wooden box (including the lid) has external dimensions 40 cm by 34 cm by 30 cm. If the wood is 1 cm thick, how many cm3 of wood is used in it?
A river 2 m deep and 45 m wide is flowing at the rate of 3 km per hour. Find the amount of water in cubic metres that runs into the sea per minute.
Find the area to be painted in the following block with a cylindrical hole. Given that length is 15 cm, width 12 cm, height 20 cm and radius of the hole 2.8 cm.

A truck carrying 7.8 m3 concrete arrives at a job site. A platform of width 5 m and height 2 m is being contructed at the site. Find the length of the platform, constructed from the amount of concrete on the truck?
A hollow garden roller of 42 cm diameter and length 152 cm is made of cast iron 2 cm thick. Find the volume of iron used in the roller.
Three cubes each of side 10 cm are joined end to end. Find the surface area of the resultant figure.
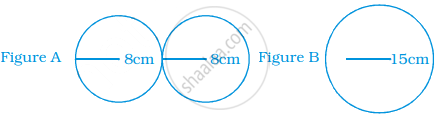
Below are the drawings of cross sections of two different pipes used to fill swimming pools. Figure A is a combination of 2 pipes each having a radius of 8 cm. Figure B is a pipe having a radius of 15 cm. If the force of the flow of water coming out of the pipes is the same in both the cases, which will fill the swimming pool faster?
A swimming pool is 200 m by 50 m and has an average depth of 2 m. By the end of a summer day, the water level drops by 2 cm. How many cubic metres of water is lost on the day?
A housing society consisting of 5,500 people needs 100 L of water per person per day. The cylindrical supply tank is 7 m high and has a diameter 10 m. For how many days will the water in the tank last for the society?
Metallic discs of radius 0.75 cm and thickness 0.2 cm are melted to obtain 508.68 cm3 of metal. Find the number of discs melted (use π = 3.14).
The ratio of the radius and height of a cylinder is 2:3. If its volume is 12,936 cm3, find the total surface area of the cylinder.
External dimensions of a closed wooden box are in the ratio 5:4:3. If the cost of painting its outer surface at the rate of Rs 5 per dm2 is Rs 11,750, find the dimensions of the box.
The capacity of a closed cylindrical vessel of height 1 m is 15.4 L. How many square metres of metal sheet would be needed to make it?
What will happen to the volume of the cube, if its edge is tripled?
What will happen to the volume of the cube, if its edge is reduced to one-fourth?
A rectangular sheet of dimensions 25 cm × 7 cm is rotated about its longer side. Find the volume and the whole surface area of the solid thus generated.
From a pipe of inner radius 0.75 cm, water flows at the rate of 7 m per second. Find the volume in litres of water delivered by the pipe in 1 hour.
Four times the area of the curved surface of a cylinder is equal to 6 times the sum of the areas of its bases. If its height is 12 cm, find its curved surface area.
A cylindrical tank has a radius of 154 cm. It is filled with water to a height of 3 m. If water to a height of 4.5 m is poured into it, what will be the increase in the volume of water in kl?
The length, breadth and height of a cuboidal reservoir is 7 m, 6 m and 15 m respectively. 8400 L of water is pumped out from the reservoir. Find the fall in the water level in the reservoir.
How many bricks of size 22 cm × 10 cm × 7 cm are required to construct a wall 11 m long, 3.5 m high and 40 cm thick, if the cement and sand used in the construction occupy (1/10)th part of the wall?
A rectangular examination hall having seats for 500 candidates has to be built so as to allow 4 cubic metres of air and 0.5 square metres of floor area per candidate. If the length of hall be 25 m, find the height and breadth of the hall.
The ratio between the curved surface area and the total surface area of a right circular cylinder is 1 : 2. Find the ratio between the height and radius of the cylinder.
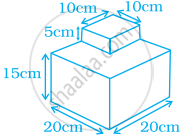
A birthday cake has two tiers as shown in the figure below. Find the volume of the cake.
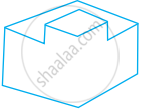
Work out the surface area of following shape (use π = 3.14).
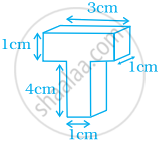
Work out the surface area of following shape (use π = 3.14).
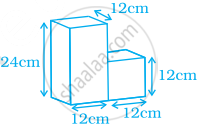
Work out the surface area of following shape (use π = 3.14).
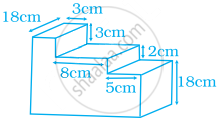
Work out the surface area of following shape (use π = 3.14).
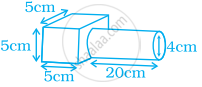
Water flows from a tank with a rectangular base measuring 80 cm by 70 cm into another tank with a square base of side 60 cm. If the water in the first tank is 45 cm deep, how deep will it be in the second tank?
A rectangular sheet of paper is rolled in two different ways to form two different cylinders. Find the volume of cylinders in each case if the sheet measures 44 cm × 33 cm.
Solutions for 11: Mensuration
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 11 - Mensuration NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 11 - Mensuration - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-8_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 11 - Mensuration
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 8 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 8 CBSE 11 (Mensuration) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 8 chapter 11 Mensuration are Area of a Polygon, Plane Figures and Solid Shapes, Mensuration, Area of a Rhombus, Surface Area of a Cube, Surface Area of a Cuboid, Surface Area of Cylinder, Concept of Surface Area, Volume, and Capacity, Volume of a Cuboid, Volume of Cube, Volume of a Cylinder, Area of Trapezium, Area of a General Quadrilateral.
Using NCERT Exemplar Mathematics [English] Class 8 solutions Mensuration exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Mathematics [English] Class 8 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 11, Mensuration Mathematics [English] Class 8 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 8 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
