Advertisements
Advertisements
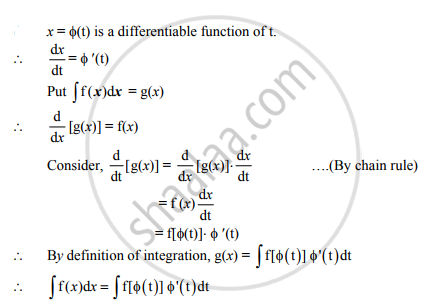
Question
If x = Φ(t) differentiable function of ‘ t ' then prove that `int f(x) dx=intf[phi(t)]phi'(t)dt`
Solution
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Solve the differential equation cos(x +y) dy = dx hence find the particular solution for x = 0 and y = 0.
The solution of the differential equation dy/dx = sec x – y tan x is:
(A) y sec x = tan x + c
(B) y sec x + tan x = c
(C) sec x = y tan x + c
(D) sec x + y tan x = c
Find the general solution of the following differential equation :
`(1+y^2)+(x-e^(tan^(-1)y))dy/dx= 0`
Verify that the given function (explicit or implicit) is a solution of the corresponding differential equation:
y = ex + 1 : y″ – y′ = 0
Verify that the given function (explicit or implicit) is a solution of the corresponding differential equation:
y = Ax : xy′ = y (x ≠ 0)
Verify that the given function (explicit or implicit) is a solution of the corresponding differential equation:
`y = sqrt(a^2 - x^2 ) x in (-a,a) : x + y dy/dx = 0(y != 0)`
The number of arbitrary constants in the general solution of a differential equation of fourth order are ______.
Find a particular solution of the differential equation`(x + 1) dy/dx = 2e^(-y) - 1`, given that y = 0 when x = 0.
If y = etan x+ (log x)tan x then find dy/dx
Solve the differential equation `cos^2 x dy/dx` + y = tan x
The population of a town grows at the rate of 10% per year. Using differential equation, find how long will it take for the population to grow 4 times.
How many arbitrary constants are there in the general solution of the differential equation of order 3.
The solution of the differential equation \[\frac{dy}{dx} + \frac{2y}{x} = 0\] with y(1) = 1 is given by
Write the solution of the differential equation \[\frac{dy}{dx} = 2^{- y}\] .
cos (x + y) dy = dx
\[\frac{dy}{dx} - y \tan x = e^x\]
\[y^2 + \left( x + \frac{1}{y} \right)\frac{dy}{dx} = 0\]
`(dy)/(dx)+ y tan x = x^n cos x, n ne− 1`
Find the general solution of the differential equation \[\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{x + 1}{2 - y}, y \neq 2\]
For the following differential equation, find the general solution:- `y log y dx − x dy = 0`
For the following differential equation, find a particular solution satisfying the given condition:
\[x\left( x^2 - 1 \right)\frac{dy}{dx} = 1, y = 0\text{ when }x = 2\]
For the following differential equation, find a particular solution satisfying the given condition:- \[\frac{dy}{dx} = y \tan x, y = 1\text{ when }x = 0\]
Solve the following differential equation:-
\[\frac{dy}{dx} + 2y = \sin x\]
Solve the following differential equation:-
\[\left( x + 3 y^2 \right)\frac{dy}{dx} = y\]
Solve the differential equation: `(d"y")/(d"x") - (2"x")/(1+"x"^2) "y" = "x"^2 + 2`
Solve the differential equation: ` ("x" + 1) (d"y")/(d"x") = 2e^-"y" - 1; y(0) = 0.`
Form the differential equation having y = (sin–1x)2 + Acos–1x + B, where A and B are arbitrary constants, as its general solution.
Find the general solution of the differential equation `(1 + y^2) + (x - "e"^(tan - 1y)) "dy"/"dx"` = 0.
Find the general solution of (1 + tany)(dx – dy) + 2xdy = 0.
If y = e–x (Acosx + Bsinx), then y is a solution of ______.
Integrating factor of the differential equation `cosx ("d"y)/("d"x) + ysinx` = 1 is ______.
The solution of `("d"y)/("d"x) + y = "e"^-x`, y(0) = 0 is ______.
Integrating factor of the differential equation `("d"y)/("d"x) + y tanx - secx` = 0 is ______.
The integrating factor of the differential equation `("d"y)/("d"x) + y = (1 + y)/x` is ______.
The solution of the differential equation cosx siny dx + sinx cosy dy = 0 is ______.
The general solution of the differential equation `("d"y)/("d"x) = "e"^(x^2/2) + xy` is ______.
Which of the following is the general solution of `("d"^2y)/("d"x^2) - 2 ("d"y)/("d"x) + y` = 0?
The member of arbitrary constants in the particulars solution of a differential equation of third order as
Find the general solution of the differential equation:
`(dy)/(dx) = (3e^(2x) + 3e^(4x))/(e^x + e^-x)`
