Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If ∆ABC ~ ∆QRP, `(ar(ABC))/(ar(PQR)) = 9/4`, AB = 18 cm and BC = 15 cm, then PR is equal to ______.
Options
10 cm
12 cm
`20/3` cm
8 cm
Solution
If ∆ABC ~ ∆QRP, `(ar(ABC))/(ar(PQR)) = 9/4`, AB = 18 cm and BC = 15 cm, then PR is equal to 10 cm.
Explanation:
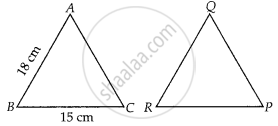
Given, ∆ABC ~ ∆QRP,
AB = 18 cm
And BC = 15 cm
We know that, the ratio of the area of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of square of their corresponding sides.
∴ `("ar(∆ABC)")/("ar(∆QRP)") = ("BC")^2/("RP")^2`
But, `("ar(∆ABC)")/("ar(∆PQR)") = 9/4` ...[Given]
⇒ `(15)^2/("RP")^2 = 9/4` ...[∵ BC = 15 cm, given]
⇒ (RP)2 = `(225 xx 4)/9` = 100
∴ RP = 10 cm
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC and its diagonals intersect each other at the point O. Show that `("AO")/("BO") = ("CO")/("DO")`
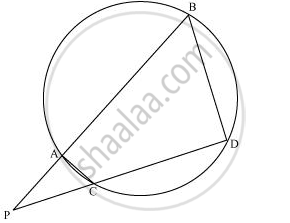
In the given figure, two chords AB and CD of a circle intersect each other at the point P (when produced) outside the circle. Prove that
(i) ΔPAC ∼ ΔPDB
(ii) PA.PB = PC.PD
`triangleDEF ~ triangleMNK`. If DE = 5 and MN = 6, then find the value of `(A(triangleDEF))/(A(triangleMNK))`
Given `triangle ABC ~ triangle PQR`, if `(AB)/(PQ) = 1/3`, then find `(ar triangle ABC)/(ar triangle PQR)`
State, true or false:
Two similar polygons are necessarily congruent.
In the given figure, ΔOAB ~ ΔOCD. If AB = 8cm, BO = 6.4cm, OC = 3.5cm and CD = 5cm, find (i) OA (ii) DO.
Two chords AB and CD of a circle intersect at a point P outside the circle.
Prove that: (i) Δ PAC ~ Δ PDB (ii) PA. PB = PC.PD

The areas of two similar triangles are `81cm^2` and `49cm^2` respectively. If the altitude of the first triangle is 6.3cm, find the corresponding altitude of the other.
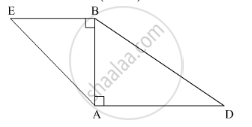
In the following figure, seg BE ⊥ seg AB and seg BA ⊥ seg AD. If BE = 6 and \[\text{AD} = 9 \text{ find} \frac{A\left( \Delta ABE \right)}{A\left( \Delta BAD \right)} \cdot\]
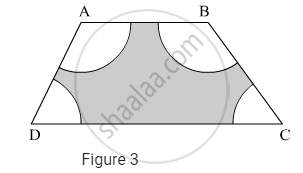
In Figure 3, ABCD is a trapezium with AB || DC, AB = 18 cm, DC = 32 cm and the distance between AB and DC is 14 cm. If arcs of equal radii 7 cm have been drawn, with centres A,B, C and D, then find the area of the shaded region.
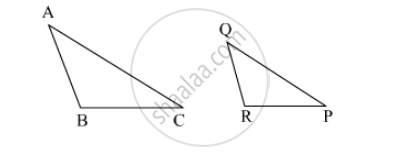
Select the appropriate alternative.
In ∆ABC and ∆PQR, in a one to one correspondence \[\frac{AB}{QR} = \frac{BC}{PR} = \frac{CA}{PQ}\]

O is any point in the interior of ΔABC. Bisectors of ∠AOB, ∠BOC and ∠AOC intersect side AB, side BC, side AC in
F, D and E respectively.
Prove that
BF × AE × CD = AF × CE × BD
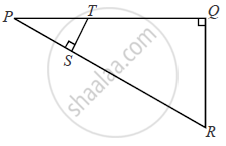
In the given figure, ∠PQR = ∠PST = 90° ,PQ = 5cm and PS = 2cm.
(i) Prove that ΔPQR ~ ΔPST.
(ii) Find Area of ΔPQR : Area of quadrilateral SRQT.
Δ ABC ∼ Δ PQR. AD and PS are altitudes from A and P on sides BC and QR respectively. If AD : PS = 4 : 9 , find the ratio of the areas of Δ ABC and Δ PQR.
A ship is 400m laig and 100m wide. The length of its model is 20 cm. find the surface area of the deck of the model.
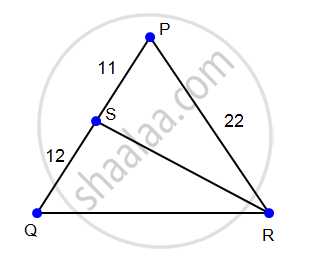
In the following figure, in Δ PQR, seg RS is the bisector of ∠PRQ.
PS = 11, SQ = 12, PR = 22. Find QR.
In the following figure, point D divides AB in the ratio 3 : 5. Find : `(AD)/(AB)`
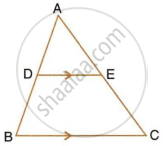
In the figure, given below, AB, CD and EF are parallel lines. Given AB = 7.5 cm, DC = y cm, EF = 4.5 cm, BC = x cm and CE = 3 cm, calculate the values of x and y.
Construct a ΔABC in which CA = 6 cm, AB = 5 cm and ∠BAC = 45°. Then construct a triangle whose sides are `3/5` of the corresponding sides of ΔABC.
Choose the correct alternative:
If ΔABC ~ ΔPQR and 4A (ΔABC) = 25 A(ΔPQR), then AB : PQ = ?
In ΔABC, DE is parallel to BC and DE = 3:8.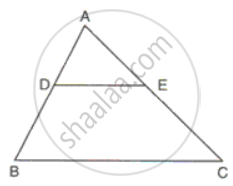
Find:
(i) AD : BD
(ii) AE, if AC = 16.
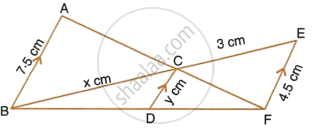
ABCD is a parallelogram whose sides AB and BC are 18cm and 12cm respectively. G is a point on AC such that CG : GA = 3 : 5 BG is produced to meet CD at Q and AD produced at P. Prove that ΔCGB ∼ ΔAGP. Hence, fi AP.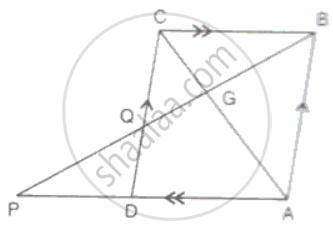
In a quadrilateral PQRS, the diagonals PR and QS intersect each other at the point T. If PT:TR = QT :TS = 1:2, show that TP:TQ = TR:TS
In ΔABC, DE is drawn parallel to BC cutting AB in the ratio 2 : 3. Calculate:
(i) `("area"(Δ"ADE"))/("area"(Δ"ABC")`
(i) `("area"("trapeziumEDBC"))/("area"(Δ"ABC"))`
In ΔABC, AB = 8cm, AC = 10cm and ∠B = 90°. P and Q are the points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that PQ = 3cm ad ∠PQA = 90. Find: The area of ΔAQP.
The scale of a map is 1 : 50000. The area of a city is 40 sq km which is to be represented on the map. Find: The area of land represented on the map.
A man whose eye-level is 2 m above the ground wishes to find the height of a tree. He places a mirror horizontally on the ground 20 m from the tree and finds that if he stands at a point C which is 4 m from the mirror B, he can see the reflection of the top of the tree. How height is the tree?
In the given figure, UB || AT and CU ≡ CB Prove that ΔCUB ~ ΔCAT and hence ΔCAT is isosceles.
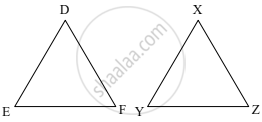
In ΔDEF and ΔXYZ, `"DE"/"XY" = "FE"/"YZ"` and ∠E ≅ ∠Y. _______ test gives similarity between ΔDEF and ΔXYZ.
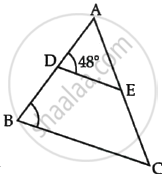
In figure, if AD = 6 cm, DB = 9 cm, AE = 8 cm and EC = 12 cm and ∠ADE = 48°. Find ∠ABC.