Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Compound Interest (Without using formula)
3: Compound Interest (Using Formula)
4: Expansions (Including Substitution)
5: Factorisation
6: Simultaneous (Linear) Equations (Including Problems)
7: Indices (Exponents)
8: Logarithms
9: Triangles [Congruency in Triangles]
10: Isosceles Triangles
11: Inequalities
12: Mid-point and Its Converse [ Including Intercept Theorem]
13: Pythagoras Theorem [Proof and Simple Applications with Converse]
14: Rectilinear Figures [Quadrilaterals: Parallelogram, Rectangle, Rhombus, Square and Trapezium]
15: Construction of Polygons (Using ruler and compass only)
16: Area Theorems [Proof and Use]
17: Circle
18: Statistics
19: Mean and Median (For Ungrouped Data Only)
20: Area and Perimeter of Plane Figures
21: Solids [Surface Area and Volume of 3-D Solids]
22: Trigonometrical Ratios [Sine, Consine, Tangent of an Angle and their Reciprocals]
23: Trigonometrical Ratios of Standard Angles [Including Evaluation of an Expression Involving Trigonometric Ratios]
24: Solution of Right Triangles [Simple 2-D Problems Involving One Right-angled Triangle]
25: Complementary Angles
▶ 26: Co-ordinate Geometry
27: Graphical Solution (Solution of Simultaneous Linear Equations, Graphically)
28: Distance Formula
![Selina solutions for Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 26 - Co-ordinate Geometry Selina solutions for Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 26 - Co-ordinate Geometry - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-mathematics-english-class-9-icse_6:b313c06da7fb4b0f885a06c3b5e4e4fa.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 26: Co-ordinate Geometry
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 26 of CISCE Selina for Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE 26 Co-ordinate Geometry Exercise 26 (A) [Pages 315 - 316]
For the equation given below; name the dependent and independent variables.
y = `(4)/(3)x` - 7
For the equation given below; name the dependent and independent variables.
x = 9y + 4
For the equation given below; name the dependent and independent variables.
x = `(5y + 3)/(2)`
For each equation given below; name the dependent and independent variables.
y = `(1)/(7)` (6x + 5)
Plot the following points on the same graph paper:
(i) (8, 7)
(ii) (3, 6)
(iii) (0, 4)
(iv) (0, -4)
(v) (3, -2)
(vi) (-2, 5)
(vii) (-3, 0)
(viii) (5, 0)
(ix) (-4, -3)
Find the values of x and y if:
(x - 1, y + 3) = (4, 4)
Find the values of x and y if:
(3x + 1, 2y - 7) = (9, - 9)
Find the values of x and y if:
(5x - 3y, y - 3x) = (4, -4)
Use the graph given alongside, to find the coordinates of the point (s) satisfying the given condition:
(i) The abscissa is 2.
(ii)The ordinate is 0.
(iii) The ordinate is 3.
(iv) The ordinate is -4.
(v) The abscissa is 5.
(vi) The abscissa is equal to the ordinate.
(vii) The ordinate is half of the abscissa.

State, true or false:
The ordinate of a point is its x-co-ordinate.
True
False
State, true or false:
The origin is in the first quadrant.
True
False
State, true or false:
The y-axis is the vertical number line.
True
False
State, true or false:
Every point is located in one of the four quadrants.
True
False
State, true or false:
If the ordinate of a point is equal to its abscissa; the point lies either in the first quadrant or in the second quadrant.
True
False
State, true or false:
The origin (0, 0) lies on the x-axis.
True
False
State, true or false:
The point (a, b) lies on the y-axis if b = 0.
True
False
In the following, find the coordinates of the point whose abscissa is the solution of the first equation and ordinate is the solution of the second equation:
3 - 2x = 7; 2y + 1 = 10 - 2`(1)/(2)`y.
In the following, find the co-ordinates of the point whose abscissa is the solution of the first equation and ordinate is the solution of the second equation:
`(2"a")/(3) - 1 = "a"/(2); (15 - 4"b")/(7) = (2"b" - 1)/(3)`.
In the following, find the co-ordinates of the point whose abscissa is the solution of the first equation and ordinate is the solution of the second equation:
`5x - (5 - x) = (1)/(2) (3 - x); 4 -3y = (4 + y)/(3)`
In the following, the coordinates of the three vertices of a rectangle ABCD are given. By plotting the given points; find, in case, the coordinates of the fourth vertex:
A(2, 0), B(8, 0) and C(8, 4).
In the following, the coordinates of the three vertices of a rectangle ABCD are given. By plotting the given points; find, in case, the coordinates of the fourth vertex:
A (4, 2), B(-2, 2) and D(4, -2).
In the following, the coordinates of the three vertices of a rectangle ABCD are given. By plotting the given points; find, in case, the coordinates of the fourth vertex:
A (- 4, - 6), C(6, 0) and D(- 4, 0).
In the following, the coordinates of the three vertices of a rectangle ABCD are given. By plotting the given points; find, in case, the coordinates of the fourth vertex:
B (10, 4), C(0, 4) and D(0, -2).
A (- 2, 2), B(8, 2) and C(4, - 4) are the vertices of a parallelogram ABCD. By plotting the given points on a graph paper; find the co-ordinates of the fourth vertex D.
Also, form the same graph, state the co-ordinates of the mid-points of the sides AB and CD.
A (-2, 4), C(4, 10) and D(-2, 10) are the vertices of a square ABCD. Use the graphical method to find the co-ordinates of the fourth vertex B. Also, find:
(i) The co-ordinates of the mid-point of BC;
(ii) The co-ordinates of the mid-point of CD and
(iii) The co-ordinates of the point of intersection of the diagonals of the square ABCD.
By plotting the following points on the same graph paper. Check whether they are collinear or not:
(i) (3, 5), (1, 1) and (0, -1)
(ii) (-2, -1), (-1, -4) and (-4, 1)
Plot point A(5, -7). From point A, draw AM perpendicular to the x-axis and AN perpendicular to the y-axis. Write the coordinates of points M and N.
In square ABCD; A = (3, 4), B = (-2, 4) and C = (-2, -1). By plotting these points on a graph paper, find the co-ordinates of vertex D. Also, find the area of the square.
In rectangle OABC; point O is the origin, OA = 10 units along x-axis and AB = 8 units. Find the co-ordinates of vertices A, B and C.
Selina solutions for Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE 26 Co-ordinate Geometry Exercise 26 (B) [Page 320]
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
x = 3
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
x + 3 = 0
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
x - 5 = 0
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
2x - 7 = 0
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
y = 4
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
y + 6 = 0
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
y - 2 = 0
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
3y + 5 = 0
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
2y - 5 = 0
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
y = 0
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
x = 0
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
y = 3x
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
y = - x
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
y = - 2x
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
y = x
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
5x+ y = 0.
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
x + 2y = 0
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
4x - y = 0
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
3x + 2y = 0
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
x = - 2y
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
y = 2x + 3
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
y = `(2x)/(3) - 1`
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
y = - x + 4
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
y = `4x - (5)/(2)`
Draw the graph for the each linear equation given below:
y = `(3x)/(2) + (2)/(3)`
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
2x - 3y = 4
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
`(x - 1)/(3) - (y + 2)/(2) = 0`
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
x - 3 = `(2)/(5)(y + 1)`
Draw the graph for the linear equation given below:
x + 5y + 2 = 0
Draw the graph for the equation given below:
3x + 2y = 6
Draw the graph for the equation given below:
2x - 5y = 10
Draw the graph for the equation given below:
`(1)/(2) x + (2)/(3) y = 5`.
Draw the graph for the equation given below:
`(2x - 1)/(3) - (y - 2)/(5) = 0`
For the linear equation, given above, draw the graph and then use the graph drawn (in the following case) to find the area of a triangle enclosed by the graph and the co-ordinates axes:
3x - (5 - y) = 7
For the linear equation, given above, draw the graph and then use the graph drawn (in the following case) to find the area of a triangle enclosed by the graph and the co-ordinates axes:
7 - 3 (1 - y) = -5 + 2x
For the pair of linear equations given below, draw graphs and then state, whether the lines drawn are parallel or perpendicular to each other.
y = 3x - 1
y = 3x + 2
For the pair of linear equations given below, draw graphs and then state, whether the lines drawn are parallel or perpendicular to each other.
y = x - 3
y = - x + 5
For the pair of linear equations given below, draw graphs and then state, whether the lines drawn are parallel or perpendicular to each other.
2x - 3y = 6
`x/(2) + y/(3) = 1`
For the pair of linear equations given below, draw graphs and then state, whether the lines drawn are parallel or perpendicular to each other.
3x + 4y = 24
`x/(4) + y/(3) = 1`
On the same graph paper, plot the graph of y = x - 2, y = 2x + 1 and y = 4 from x= - 4 to 3.
On the same graph paper, plot the graphs of y = 2x - 1, y = 2x and y = 2x + 1 from x = - 2 to x = 4. Are the graphs (lines) drawn parallel to each other?
The graph of 3x + 2y = 6 meets the x=axis at point P and the y-axis at point Q. Use the graphical method to find the co-ordinates of points P and Q.
Draw the graph of equation x + 2y - 3 = 0. From the graph, find:
(i) x1, the value of x, when y = 3
(ii) x2, the value of x, when y = - 2.
Draw the graph of the equation 3x - 4y = 12.
Use the graph drawn to find:
(i) y1, the value of y, when x = 4.
(ii) y2, the value of y, when x = 0.
Draw the graph of equation `x/(4) + y/(5) = 1` Use the graph drawn to find:
(i) x1, the value of x, when y = 10
(ii) y1, the value of y, when x = 8.
Use the graphical method to show that the straight lines given by the equations x + y = 2, x - 2y = 5 and `x/(3) + y = 0` pass through the same point.
Selina solutions for Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE 26 Co-ordinate Geometry Exercise 26 (C) [Page 323]
In the following, find the inclination of line AB:
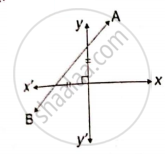
In the following, find the inclination of line AB:
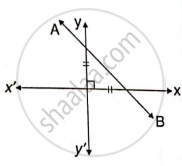
In the following, find the inclination of line AB:
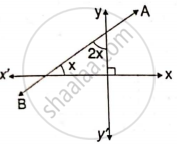
Write the inclination of a line which is: Parallel to the x-axis.
Write the inclination of a line which is: Perpendicular to the x-axis.
Write the inclination of a line which is: Parallel to the y-axis.
Write the inclination of a line which is: Perpendicular to the y-axis.
Write the slope of the line whose inclination is: 0°.
Write the slope of the line whose inclination is: 30°
Write the slope of the line whose inclination is: 45°.
Write the slope of the line whose inclination is: 60°
Find the inclination of the line whose slope is: 0
Find the inclination of the line whose slope is: 1
Find the inclination of the line whose slope is: `sqrt(3)`
Find the inclination of the line whose slope is: `(1)/sqrt(3)`
Write the slope of the line which is: Parallel to the x-axis.
Write the slope of the line which is: Perpendicular to the x-axis.
Write the slope of the line which is: Parallel to the y-axis.
Write the slope of the line which is: Perpendicular to the y-axis.
For the equation given below, find the slope and the y-intercept:
x + 3y + 5 = 0
For the equation given below, find the slope and the y-intercept:
3x - y - 8 = 0
For the equation given below, find the slope and the y-intercept:
5x = 4y + 7
For the equation given below, find the slope and the y-intercept:
x= 5y - 4
For the equation given below, find the slope and the y-intercept:
y = 7x - 2
For the equation given below, find the slope and the y-intercept:
3y = 7
For the equation given below, find the slope and the y-intercept:
4y + 9 = 0
Find the equation of the line whose:
Slope = 2 and y-intercept = 3
Find the equation of the line whose:
Slope = 5 and y-intercept = - 8
Find the equation of the line whose:
slope = - 4 and y-intercept = 2
Find the equation of the line whose:
slope = - 3 and y-intercept = - 1
Find the equation of the line whose:
slope = 0 and y-intercept = - 5
Find the equation of the line whose:
slope = 0 and y-intercept = 0
Draw the line 3x + 4y = 12 on a graph paper. From the graph paper, read the y-intercept of the line.
Draw the line 2x - 3y - 18 = 0 on a graph paper. From the graph paper, read the y-intercept of the line.
Draw the graph of the line x + y = 5. Use the graph paper drawn to find the inclination and the y-intercept of the line.
Solutions for 26: Co-ordinate Geometry
![Selina solutions for Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 26 - Co-ordinate Geometry Selina solutions for Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 26 - Co-ordinate Geometry - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-mathematics-english-class-9-icse_6:b313c06da7fb4b0f885a06c3b5e4e4fa.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 26 - Co-ordinate Geometry
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE 26 (Co-ordinate Geometry) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 26 Co-ordinate Geometry are Dependent and Independent Variables, Ordered Pair, Co-ordinates of Points, Quadrants and Sign Convention, Plotting of Points, Graph, Graphs of Linear Equations, Inclination and Slope, Y-intercept, Finding the Slope and the Y-intercept of a Given Line, Coordinate Geometry, Cartesian Coordinate System.
Using Selina Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE solutions Co-ordinate Geometry exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 26, Co-ordinate Geometry Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
