Topics
Number Systems
Number Systems
Polynomials
Algebra
Coordinate Geometry
Linear Equations in Two Variables
Geometry
Coordinate Geometry
Introduction to Euclid’S Geometry
Mensuration
Statistics and Probability
Lines and Angles
- Introduction to Lines and Angles
- Basic Terms and Definitions
- Intersecting Lines and Non-intersecting Lines
- Introduction to Parallel Lines
- Pairs of Angles
- Parallel Lines and a Transversal
- Angle Sum Property of a Triangle
Triangles
- Concept of Triangles
- Congruence of Triangles
- Criteria for Congruence of Triangles
- Properties of a Triangle
- Some More Criteria for Congruence of Triangles
- Inequalities in a Triangle
Quadrilaterals
- Concept of Quadrilaterals
- Properties of a Quadrilateral
- Types of Quadrilaterals
- Another Condition for a Quadrilateral to Be a Parallelogram
- Theorem of Midpoints of Two Sides of a Triangle
- Property: The Opposite Sides of a Parallelogram Are of Equal Length.
- Theorem: A Diagonal of a Parallelogram Divides It into Two Congruent Triangles.
- Theorem : If Each Pair of Opposite Sides of a Quadrilateral is Equal, Then It is a Parallelogram.
- Property: The Opposite Angles of a Parallelogram Are of Equal Measure.
- Theorem: If in a Quadrilateral, Each Pair of Opposite Angles is Equal, Then It is a Parallelogram.
- Property: The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. (at the point of their intersection)
- Theorem : If the Diagonals of a Quadrilateral Bisect Each Other, Then It is a Parallelogram
Circles
Areas - Heron’S Formula
Surface Areas and Volumes
Statistics
Algebraic Expressions
Algebraic Identities
Area
Constructions
- Introduction of Constructions
- Basic Constructions
- Some Constructions of Triangles
Probability
Formula
- Volume of a Cuboid = l × b × h
Notes
Volume of a Cuboid:
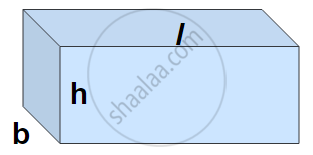
Volume of a Cuboid = Measure of the space occupied by the cuboid.
The area of the plane region occupied by each rectangle × height.
Volume of a Cuboid = base area × height = length × breadth × height.
Volume of a Cuboid = l × b × h, where l, b, and h are respectively the length, breadth, and height of the cuboid.
Example
Find the height of a cuboid whose volume is 275 cm3 and the base area is 25 cm2.
Volume of a cuboid = Base area × Height
Hence height of the cuboid = `"Volume of cuboid"/"Base area"`
=`275/25`
= 11 cm
Height of the cuboid is 11 cm.
Example
A godown is in the form of a cuboid of measures 60 m × 40 m × 30 m. How many cuboidal boxes can be stored in it if the volume of one box is 0.8 m3?
Volume of one box = 0.8 m3
Volume of godown = 60 × 40 × 30 = 72000 m3
Number of boxes that can be stored in the godown = `"Volume of the godown"/"Volume of one box"`
= `(60 xx 40 xx 30)/(0.8)`
= 90,000
Hence the number of cuboidal boxes that can be stored in the godown is 90,000.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Shaalaa.com | Problems on Mensuration - Part 2
to track your progress
