Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following differential equation:-
\[\frac{dy}{dx} - y = \cos x\]
उत्तर
We have,
\[\frac{dy}{dx} - y = \cos x\]
\[\text{Comparing with }\frac{dy}{dx} + Py = Q,\text{ we get}\]
\[P = - 1 \]
\[Q = \cos x\]
Now,
\[ I . F . = e^{- 1\int dx} = e^{- x} \]
Solution is given by,
\[y \times I . F . = \int\cos x \times I . F . dx + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow y e^{- x} = \int e^{- x} \cos x dx + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow y e^{- x} = I + C . . . . . \left( 1 \right)\]
Where,

\[ \Rightarrow I = \cos x\int e^{- x} dx - \int\left[ \frac{d}{dx}\left( \cos x \right)\int e^{- x} dx \right]dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow I = - \cos x e^{- x} - \int\sin x e^{- x} dx\]
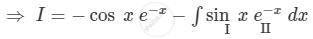
\[ \Rightarrow I = - \cos x e^{- x} - \sin x\int e^{- x} dx + \int\left[ \frac{d}{dx}\left( \sin x \right)\int e^{- x} dx \right]dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow I = - \cos x e^{- x} + \sin x e^{- x} - \int\left[ \cos x e^{- x} \right]dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow I = - \cos x e^{- x} + \sin x e^{- x} - I ..........\left[\text{Using (2)} \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2I = - \cos x e^{- x} + \sin x e^{- x} \]
\[ \Rightarrow I = \frac{1}{2}\left( - \cos x + \sin x \right) e^{- x} . . . . . . . . \left( 3 \right)\]
From (1) and (3), we get
\[ \therefore y e^{- x} = \left( \sin x - \cos x \right) e^{- x} + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \frac{1}{2}\left( \sin x - \cos x \right) + C e^x\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Solve the differential equation cos(x +y) dy = dx hence find the particular solution for x = 0 and y = 0.
The solution of the differential equation dy/dx = sec x – y tan x is:
(A) y sec x = tan x + c
(B) y sec x + tan x = c
(C) sec x = y tan x + c
(D) sec x + y tan x = c
If x = Φ(t) differentiable function of ‘ t ' then prove that `int f(x) dx=intf[phi(t)]phi'(t)dt`
Verify that the given function (explicit or implicit) is a solution of the corresponding differential equation:
y = cos x + C : y′ + sin x = 0
Verify that the given function (explicit or implicit) is a solution of the corresponding differential equation:
y = x sin x : xy' = `y + x sqrt (x^2 - y^2)` (x ≠ 0 and x > y or x < -y)
Solve the differential equation `[e^(-2sqrtx)/sqrtx - y/sqrtx] dx/dy = 1 (x != 0).`
if `y = sin^(-1) (6xsqrt(1-9x^2))`, `1/(3sqrt2) < x < 1/(3sqrt2)` then find `(dy)/(dx)`
The general solution of the differential equation \[\frac{dy}{dx} + y \] cot x = cosec x, is
The solution of the differential equation \[2x\frac{dy}{dx} - y = 3\] represents
Which of the following differential equations has y = x as one of its particular solution?
Write the solution of the differential equation \[\frac{dy}{dx} = 2^{- y}\] .
(x + y − 1) dy = (x + y) dx
\[\frac{dy}{dx} - y \cot x = cosec\ x\]
\[\frac{dy}{dx} - y \tan x = - 2 \sin x\]
\[\frac{dy}{dx} - y \tan x = e^x \sec x\]
(1 + y + x2 y) dx + (x + x3) dy = 0
(x2 + 1) dy + (2y − 1) dx = 0
\[\frac{dy}{dx} + 5y = \cos 4x\]
\[x\frac{dy}{dx} + x \cos^2 \left( \frac{y}{x} \right) = y\]
\[\left( 1 + y^2 \right) + \left( x - e^{- \tan^{- 1} y} \right)\frac{dy}{dx} = 0\]
For the following differential equation, find the general solution:- \[\frac{dy}{dx} = \sqrt{4 - y^2}, - 2 < y < 2\]
For the following differential equation, find the general solution:- \[\frac{dy}{dx} + y = 1\]
For the following differential equation, find a particular solution satisfying the given condition:- \[\frac{dy}{dx} = y \tan x, y = 1\text{ when }x = 0\]
Solve the following differential equation:-
\[\frac{dy}{dx} + \left( \sec x \right) y = \tan x\]
Find the equation of a curve passing through the point (0, 0) and whose differential equation is \[\frac{dy}{dx} = e^x \sin x.\]
Solve the differential equation : `("x"^2 + 3"xy" + "y"^2)d"x" - "x"^2 d"y" = 0 "given that" "y" = 0 "when" "x" = 1`.
Solution of the differential equation `"dx"/x + "dy"/y` = 0 is ______.
The general solution of the differential equation x(1 + y2)dx + y(1 + x2)dy = 0 is (1 + x2)(1 + y2) = k.
y = x is a particular solution of the differential equation `("d"^2y)/("d"x^2) - x^2 "dy"/"dx" + xy` = x.
Solve: `y + "d"/("d"x) (xy) = x(sinx + logx)`
Solution of the differential equation tany sec2xdx + tanx sec2ydy = 0 is ______.
The solution of the equation (2y – 1)dx – (2x + 3)dy = 0 is ______.
Which of the following is the general solution of `("d"^2y)/("d"x^2) - 2 ("d"y)/("d"x) + y` = 0?
The solution of the differential equation ydx + (x + xy)dy = 0 is ______.
General solution of `("d"y)/("d"x) + y` = sinx is ______.
The solution of the differential equation `("d"y)/("d"x) = (x + 2y)/x` is x + y = kx2.
The differential equation of all parabolas that have origin as vertex and y-axis as axis of symmetry is ______.
If the solution curve of the differential equation `(dy)/(dx) = (x + y - 2)/(x - y)` passes through the point (2, 1) and (k + 1, 2), k > 0, then ______.
