Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If f : Q → Q is defined as f(x) = x2, then f−1 (9) is equal to
Options
(a) 3
(b) −3
(c) {−3, 3}
(d) ϕ
Solution
(c) {−3, 3}
If f : A → B, such that y ∈ B, then
In other words,
Then, f (x) = 9
⇒ x2 = 9
⇒ x = ± 3
∴ \[f^{- 1}\] {9} = {- 3, 3}.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
f, g, h are three function defined from R to R as follow:
(iii) h(x) = x2 + 1
Find the range of function.
If f(x) = x2 − 3x + 4, then find the values of x satisfying the equation f(x) = f(2x + 1).
If \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{1 - x}\] , show that f[f[f(x)]] = x.
If \[f\left( x \right) = \begin{cases}x^2 , & \text{ when } x < 0 \\ x, & \text{ when } 0 \leq x < 1 \\ \frac{1}{x}, & \text{ when } x \geq 1\end{cases}\]
find: (a) f(1/2), (b) f(−2), (c) f(1), (d)
If \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{2x}{1 + x^2}\] , show that f(tan θ) = sin 2θ.
Let f and g be two real functions defined by \[f\left( x \right) = \sqrt{x + 1}\] and \[g\left( x \right) = \sqrt{9 - x^2}\] . Then, describe function:
(viii) \[\frac{5}{8}\]
If f(x) = loge (1 − x) and g(x) = [x], then determine function:
(iii) \[\frac{f}{g}\]
Let A and B be two sets such that n(A) = p and n(B) = q, write the number of functions from A to B.
Let f and g be two functions given by
f = {(2, 4), (5, 6), (8, −1), (10, −3)} and g = {(2, 5), (7, 1), (8, 4), (10, 13), (11, −5)}.
Find the domain of f + g
Find the set of values of x for which the functions f(x) = 3x2 − 1 and g(x) = 3 + x are equal.
If A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {x, y}, then the number of functions that can be defined from A into B is
If \[f\left( x \right) = \log \left( \frac{1 + x}{1 - x} \right)\] , then \[f\left( \frac{2x}{1 + x^2} \right)\] is equal to
Let f(x) = x, \[g\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{x}\] and h(x) = f(x) g(x). Then, h(x) = 1
If f : R → R be given by for all \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{4^x}{4^x + 2}\] x ∈ R, then
The domain of definition of the function f(x) = log |x| is
The domain of the function \[f\left( x \right) = \sqrt{5 \left| x \right| - x^2 - 6}\] is
If \[\left[ x \right]^2 - 5\left[ x \right] + 6 = 0\], where [.] denotes the greatest integer function, then
The range of \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{1 - 2\cos x}\] is
If f(m) = m2 − 3m + 1, find f(−3)
If f(x) = ax2 + bx + 2 and f(1) = 3, f(4) = 42, find a and b.
If f(x) = `{(x^2 + 3"," x ≤ 2),(5x + 7"," x > 2):},` then find f(2)
Check if the relation given by the equation represents y as function of x:
x + y2 = 9
If f(x) = `("a" - x)/("b" - x)`, f(2) is undefined, and f(3) = 5, find a and b
Express the area A of circle as a function of its diameter d
lf f(x) = 3(4x+1), find f(– 3)
Write the following expression as a single logarithm.
`1/3 log (x - 1) + 1/2 log (x)`
Select the correct answer from given alternatives.
If log10(log10(log10x)) = 0 then x =
The equation logx2 16 + log2x 64 = 3 has,
Answer the following:
Find the domain of the following function.
f(x) = 5–xPx–1
Answer the following:
Find the range of the following function.
f(x) = |x – 5|
Answer the following:
Find (f ° g) (x) and (g ° f) (x)
f(x) = `x/(x + 1)`, g(x) = `x/(1 - x)`
Given the function f: x → x2 – 5x + 6, evaluate f(2)
A graph representing the function f(x) is given in it is clear that f(9) = 2
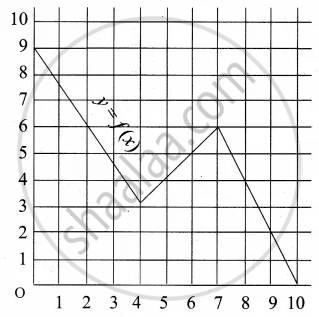
Describe the following Domain
The function f and g are defined by f(x) = 6x + 8; g(x) = `(x - 2)/3`
Write an expression for gf(x) in its simplest form
Let f and g be two functions given by f = {(2, 4), (5, 6), (8, – 1), (10, – 3)} g = {(2, 5), (7, 1), (8, 4), (10, 13), (11, – 5)} then. Domain of f + g is ______.
Find the range of the following functions given by f(x) = `3/(2 - x^2)`
If f(x) = y = `(ax - b)/(cx - a)`, then prove that f(y) = x.
Range of f(x) = `1/(1 - 2 cosx)` is ______.
If f(x) = x3 – 1 and domain of f = {0, 1, 2, 3}, then domain of f–1 is ______.
If f : R – {2} `rightarrow` R i s a function defined by f(x) = `(x^2 - 4)/(x - 2)`, then its range is ______.
