Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
We have,
\[\frac{dy}{dx} = \log x\]
\[ \Rightarrow dy = \left( \log x \right)dx\]
Integrating both sides, we get
\[\int dy = \int\left( \log x \right)dx\]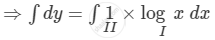
\[ \Rightarrow \int dy = \log x\int1 dx - \int\left[ \frac{d}{dx}\left( \log x \right)\int1 dx \right]dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = x\log x - \int\frac{x}{x}dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = x\log x - \int1dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = x\log x - x\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = x\left( \log x - 1 \right) + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = x\left( \log x - 1 \right) + C\]
\[\text{ So, } y = x\left( \log x - 1 \right) +\text{ C is defined for all }x \in R\text{ except }x = 0.\]
\[\text{ Hence, } y = x\left( \log x - 1 \right) +\text{ C, where } x \in R - \left\{ 0 \right\},\text{ is the solution to the given differential equation.}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If 1, `omega` and `omega^2` are the cube roots of unity, prove `(a + b omega + c omega^2)/(c + s omega + b omega^2) = omega^2`
Verify that \[y = ce^{tan^{- 1}} x\] is a solution of the differential equation \[\left( 1 + x^2 \right)\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} + \left( 2x - 1 \right)\frac{dy}{dx} = 0\]
For the following differential equation verify that the accompanying function is a solution:
| Differential equation | Function |
|
\[x\frac{dy}{dx} + y = y^2\]
|
\[y = \frac{a}{x + a}\]
|
(sin x + cos x) dy + (cos x − sin x) dx = 0
C' (x) = 2 + 0.15 x ; C(0) = 100
Solve the following differential equation:
(xy2 + 2x) dx + (x2 y + 2y) dy = 0
Solve the following differential equation:
\[\text{ cosec }x \log y \frac{dy}{dx} + x^2 y^2 = 0\]
Solve the following differential equation:
\[y e^\frac{x}{y} dx = \left( x e^\frac{x}{y} + y^2 \right)dy, y \neq 0\]
Solve the differential equation \[\left( 1 + x^2 \right)\frac{dy}{dx} + \left( 1 + y^2 \right) = 0\], given that y = 1, when x = 0.
\[x^2 \frac{dy}{dx} = x^2 + xy + y^2 \]
Solve the following initial value problem:-
\[\left( 1 + y^2 \right) dx + \left( x - e^{- \tan^{- 1} y} \right) dx = 0, y\left( 0 \right) = 0\]
Solve the following initial value problem:-
\[\frac{dy}{dx} + y \tan x = 2x + x^2 \tan x, y\left( 0 \right) = 1\]
Experiments show that radium disintegrates at a rate proportional to the amount of radium present at the moment. Its half-life is 1590 years. What percentage will disappear in one year?
Find the curve for which the intercept cut-off by a tangent on x-axis is equal to four times the ordinate of the point of contact.
Find the equation of the curve which passes through the point (3, −4) and has the slope \[\frac{2y}{x}\] at any point (x, y) on it.
In the following verify that the given functions (explicit or implicit) is a solution of the corresponding differential equation:-
`y=sqrt(a^2-x^2)` `x+y(dy/dx)=0`
The price of six different commodities for years 2009 and year 2011 are as follows:
| Commodities | A | B | C | D | E | F |
|
Price in 2009 (₹) |
35 | 80 | 25 | 30 | 80 | x |
| Price in 2011 (₹) | 50 | y | 45 | 70 | 120 | 105 |
The Index number for the year 2011 taking 2009 as the base year for the above data was calculated to be 125. Find the values of x andy if the total price in 2009 is ₹ 360.
For the following differential equation find the particular solution.
`dy/ dx = (4x + y + 1),
when y = 1, x = 0
The solution of `dy/ dx` = 1 is ______
Solve
`dy/dx + 2/ x y = x^2`
Solve `("d"y)/("d"x) = (x + y + 1)/(x + y - 1)` when x = `2/3`, y = `1/3`
Solve the following differential equation y2dx + (xy + x2) dy = 0
Solve the following differential equation
sec2 x tan y dx + sec2 y tan x dy = 0
Solution: sec2 x tan y dx + sec2 y tan x dy = 0
∴ `(sec^2x)/tanx "d"x + square` = 0
Integrating, we get
`square + int (sec^2y)/tany "d"y` = log c
Each of these integral is of the type
`int ("f'"(x))/("f"(x)) "d"x` = log |f(x)| + log c
∴ the general solution is
`square + log |tan y|` = log c
∴ log |tan x . tan y| = log c
`square`
This is the general solution.
The differential equation (1 + y2)x dx – (1 + x2)y dy = 0 represents a family of:
