Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
We have,
\[\frac{dy}{dx} = \log x\]
\[ \Rightarrow dy = \left( \log x \right)dx\]
Integrating both sides, we get
\[\int dy = \int\left( \log x \right)dx\]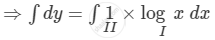
\[ \Rightarrow \int dy = \log x\int1 dx - \int\left[ \frac{d}{dx}\left( \log x \right)\int1 dx \right]dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = x\log x - \int\frac{x}{x}dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = x\log x - \int1dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = x\log x - x\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = x\left( \log x - 1 \right) + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = x\left( \log x - 1 \right) + C\]
\[\text{ So, } y = x\left( \log x - 1 \right) +\text{ C is defined for all }x \in R\text{ except }x = 0.\]
\[\text{ Hence, } y = x\left( \log x - 1 \right) +\text{ C, where } x \in R - \left\{ 0 \right\},\text{ is the solution to the given differential equation.}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Solve the equation for x: `sin^(-1) 5/x + sin^(-1) 12/x = pi/2, x != 0`
Show that Ax2 + By2 = 1 is a solution of the differential equation x \[\left\{ y\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} + \left( \frac{dy}{dx} \right)^2 \right\} = y\frac{dy}{dx}\]
Verify that y = cx + 2c2 is a solution of the differential equation
For the following differential equation verify that the accompanying function is a solution:
| Differential equation | Function |
|
\[x^3 \frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} = 1\]
|
\[y = ax + b + \frac{1}{2x}\]
|
Differential equation \[\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} - 3\frac{dy}{dx} + 2y = 0, y \left( 0 \right) = 1, y' \left( 0 \right) = 3\] Function y = ex + e2x
(1 + x) (1 + y2) dx + (1 + y) (1 + x2) dy = 0
Find the particular solution of the differential equation \[\frac{dy}{dx} = - 4x y^2\] given that y = 1, when x = 0.
(x2 − y2) dx − 2xy dy = 0
(x + 2y) dx − (2x − y) dy = 0
Solve the following initial value problem:-
\[dy = \cos x\left( 2 - y\text{ cosec }x \right)dx\]
The slope of a curve at each of its points is equal to the square of the abscissa of the point. Find the particular curve through the point (−1, 1).
Find the equation of the curve that passes through the point (0, a) and is such that at any point (x, y) on it, the product of its slope and the ordinate is equal to the abscissa.
Find the solution of the differential equation
\[x\sqrt{1 + y^2}dx + y\sqrt{1 + x^2}dy = 0\]
Integrating factor of the differential equation cos \[x\frac{dy}{dx} + y\] sin x = 1, is
Which of the following is the integrating factor of (x log x) \[\frac{dy}{dx} + y\] = 2 log x?
Verify that the function y = e−3x is a solution of the differential equation \[\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} + \frac{dy}{dx} - 6y = 0.\]
Solve the following differential equation.
x2y dx − (x3 + y3 ) dy = 0
Solve the following differential equation.
y dx + (x - y2 ) dy = 0
Solve the following differential equation.
`dy/dx + 2xy = x`
The solution of `dy/dx + x^2/y^2 = 0` is ______
Choose the correct alternative.
The integrating factor of `dy/dx - y = e^x `is ex, then its solution is
Solve `("d"y)/("d"x) = (x + y + 1)/(x + y - 1)` when x = `2/3`, y = `1/3`
Solve the following differential equation
`yx ("d"y)/("d"x)` = x2 + 2y2
Choose the correct alternative:
Differential equation of the function c + 4yx = 0 is
Choose the correct alternative:
General solution of `y - x ("d"y)/("d"x)` = 0 is
Solve the following differential equation
sec2 x tan y dx + sec2 y tan x dy = 0
Solution: sec2 x tan y dx + sec2 y tan x dy = 0
∴ `(sec^2x)/tanx "d"x + square` = 0
Integrating, we get
`square + int (sec^2y)/tany "d"y` = log c
Each of these integral is of the type
`int ("f'"(x))/("f"(x)) "d"x` = log |f(x)| + log c
∴ the general solution is
`square + log |tan y|` = log c
∴ log |tan x . tan y| = log c
`square`
This is the general solution.
Solve the following differential equation `("d"y)/("d"x)` = cos(x + y)
Solution: `("d"y)/("d"x)` = cos(x + y) ......(1)
Put `square`
∴ `1 + ("d"y)/("d"x) = "dv"/("d"x)`
∴ `("d"y)/("d"x) = "dv"/("d"x) - 1`
∴ (1) becomes `"dv"/("d"x) - 1` = cos v
∴ `"dv"/("d"x)` = 1 + cos v
∴ `square` dv = dx
Integrating, we get
`int 1/(1 + cos "v") "d"v = int "d"x`
∴ `int 1/(2cos^2 ("v"/2)) "dv" = int "d"x`
∴ `1/2 int square "dv" = int "d"x`
∴ `1/2* (tan("v"/2))/(1/2)` = x + c
∴ `square` = x + c
Integrating factor of the differential equation `"dy"/"dx" - y` = cos x is ex.
Solve: ydx – xdy = x2ydx.
