Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following initial value problem:-
\[\frac{dy}{dx} + y \tan x = 2x + x^2 \tan x, y\left( 0 \right) = 1\]
उत्तर
We have,
\[\frac{dy}{dx} + y \tan x = 2x + x^2 \tan x . . . . . \left( 1 \right)\]
Clearly, it is a linear differential equation of the form
\[\frac{dy}{dx} + Py = Q\]
\[\text{ where }P = \tan x\text{ and }Q = x^2 \cot x + 2x\]
\[ \therefore I . F . = e^{\int P\ dx} \]
\[ = e^{\int\tan x dx} \]
\[ = e^{log\left| \sec x \right|} = \sec x\]
\[\text{Multiplying both sides of }\left( 1 \right)\text{ by }I.F.= \sec x,\text{ we get }\]
\[\sec x\left( \frac{dy}{dx} + y\tan x \right) = \sec x\left( x^2 \tan x + 2x \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sec x\left( \frac{dy}{dx} + y\tan x \right) = x^2 \tan x \sec x + 2x \sec x\]
Integrating both sides with respect to x, we get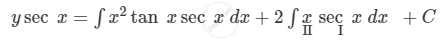
\[ \Rightarrow y \sec x = \int x^2 \tan x \sec x dx + 2sec x\int x dx - 2\int\left[ \frac{d}{dx}\left( sec x \right)\int x dx \right]dx + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow y \sec x = \int x^2 \tan x \sec\ x dx + x^2 \sec x - \int x^2 \tan x \sec x dx + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow y \sec x = x^2 \sec x + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = x^2 + C\cos x . . . . . \left( 2 \right)\]
Now,
\[y\left( 0 \right) = 1\]
\[ \therefore 1 = 0 + C\cos 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow C = 1\]
\[\text{Putting the value of C in }\left( 2 \right),\text{ we get }\]
\[y = x^2 + \cos x\]
\[\text{ Hence, }y = x^2 + \cos x\text{ is the required solution .}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the function y = A cos x + B sin x is a solution of the differential equation \[\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} + y = 0\]
Verify that y = \[\frac{a}{x} + b\] is a solution of the differential equation
\[\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} + \frac{2}{x}\left( \frac{dy}{dx} \right) = 0\]
Show that Ax2 + By2 = 1 is a solution of the differential equation x \[\left\{ y\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} + \left( \frac{dy}{dx} \right)^2 \right\} = y\frac{dy}{dx}\]
Differential equation \[\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} + y = 0, y \left( 0 \right) = 0, y' \left( 0 \right) = 1\] Function y = sin x
Differential equation \[\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} - \frac{dy}{dx} = 0, y \left( 0 \right) = 2, y'\left( 0 \right) = 1\]
Function y = ex + 1
Solve the differential equation \[\left( 1 + x^2 \right)\frac{dy}{dx} + \left( 1 + y^2 \right) = 0\], given that y = 1, when x = 0.
Find the particular solution of edy/dx = x + 1, given that y = 3, when x = 0.
In a bank principal increases at the rate of 5% per year. An amount of Rs 1000 is deposited with this bank, how much will it worth after 10 years (e0.5 = 1.648).
Solve the following differential equations:
\[\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{y}{x}\left\{ \log y - \log x + 1 \right\}\]
Solve the following initial value problem:-
\[\frac{dy}{dx} - 3y \cot x = \sin 2x; y = 2\text{ when }x = \frac{\pi}{2}\]
The rate of growth of a population is proportional to the number present. If the population of a city doubled in the past 25 years, and the present population is 100000, when will the city have a population of 500000?
Find the equation to the curve satisfying x (x + 1) \[\frac{dy}{dx} - y\] = x (x + 1) and passing through (1, 0).
At every point on a curve the slope is the sum of the abscissa and the product of the ordinate and the abscissa, and the curve passes through (0, 1). Find the equation of the curve.
The rate of increase of bacteria in a culture is proportional to the number of bacteria present and it is found that the number doubles in 6 hours. Prove that the bacteria becomes 8 times at the end of 18 hours.
The slope of the tangent at each point of a curve is equal to the sum of the coordinates of the point. Find the curve that passes through the origin.
Write the differential equation obtained by eliminating the arbitrary constant C in the equation x2 − y2 = C2.
The integrating factor of the differential equation (x log x)
\[\frac{dy}{dx} + y = 2 \log x\], is given by
The differential equation \[x\frac{dy}{dx} - y = x^2\], has the general solution
What is integrating factor of \[\frac{dy}{dx}\] + y sec x = tan x?
Integrating factor of the differential equation cos \[x\frac{dy}{dx} + y \sin x = 1\], is
Solve the following differential equation : \[y^2 dx + \left( x^2 - xy + y^2 \right)dy = 0\] .
If xmyn = (x + y)m+n, prove that \[\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{y}{x} .\]
y2 dx + (x2 − xy + y2) dy = 0
Determine the order and degree of the following differential equations.
| Solution | D.E |
| y = aex + be−x | `(d^2y)/dx^2= 1` |
Solve the following differential equation.
xdx + 2y dx = 0
Solve the following differential equation.
`xy dy/dx = x^2 + 2y^2`
Solve the following differential equation.
`dy/dx + y` = 3
Solve the following differential equation.
`dy/dx + 2xy = x`
Choose the correct alternative:
Solution of the equation `x("d"y)/("d"x)` = y log y is
Integrating factor of the differential equation `"dy"/"dx" - y` = cos x is ex.
