Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
x cos2 y dx = y cos2 x dy
उत्तर
We have,
\[x \cos {}^2 y dx = y \cos {}^2 x dy\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{x}{\cos^2 x}dx = \frac{y}{\cos^2 y}dy\]
\[ \Rightarrow x \sec^2 x dx = y \sec^2 y dy\]
Integrating both sides, we get 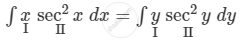
\[ \Rightarrow x\int \sec^2 x dx - \int\left\{ \frac{d}{dx}\left( x \right)\int \sec^2 x dx \right\}dx = y\int \sec^2 y dy - \int\left\{ \frac{d}{dy}\left( y \right)\int \sec^2 y dy \right\}dy\]
\[ \Rightarrow x \tan x - \int\tan x dx = y \tan y - \int\tan y dy\]
\[ \Rightarrow x \tan x - \log \left| \sec x \right| = y \tan y - \log \left| \sec y \right| + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow x \tan x - y \tan y = \log \left| \sec x \right| - \log \left| \sec y \right| + C\]
\[\text{ Hence, }x \tan x - y \tan y = \log \left| \sec x \right| - \log \left| \sec y \right| +\text{C is the required solution.} \]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the function y = A cos 2x − B sin 2x is a solution of the differential equation \[\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} + 4y = 0\].
For the following differential equation verify that the accompanying function is a solution:
| Differential equation | Function |
|
\[x^3 \frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} = 1\]
|
\[y = ax + b + \frac{1}{2x}\]
|
Differential equation \[\frac{dy}{dx} + y = 2, y \left( 0 \right) = 3\] Function y = e−x + 2
Differential equation \[\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} - y = 0, y \left( 0 \right) = 2, y' \left( 0 \right) = 0\] Function y = ex + e−x
Differential equation \[\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} - 2\frac{dy}{dx} + y = 0, y \left( 0 \right) = 1, y' \left( 0 \right) = 2\] Function y = xex + ex
(ey + 1) cos x dx + ey sin x dy = 0
y (1 + ex) dy = (y + 1) ex dx
Find the particular solution of the differential equation \[\frac{dy}{dx} = - 4x y^2\] given that y = 1, when x = 0.
In a bank principal increases at the rate of r% per year. Find the value of r if ₹100 double itself in 10 years (loge 2 = 0.6931).
If y(x) is a solution of the different equation \[\left( \frac{2 + \sin x}{1 + y} \right)\frac{dy}{dx} = - \cos x\] and y(0) = 1, then find the value of y(π/2).
x2 dy + y (x + y) dx = 0
Solve the following initial value problem:
\[\frac{dy}{dx} + y \cot x = 4x\text{ cosec }x, y\left( \frac{\pi}{2} \right) = 0\]
The decay rate of radium at any time t is proportional to its mass at that time. Find the time when the mass will be halved of its initial mass.
The tangent at any point (x, y) of a curve makes an angle tan−1(2x + 3y) with x-axis. Find the equation of the curve if it passes through (1, 2).
What is integrating factor of \[\frac{dy}{dx}\] + y sec x = tan x?
The integrating factor of the differential equation \[\left( 1 - y^2 \right)\frac{dx}{dy} + yx = ay\left( - 1 < y < 1 \right)\] is ______.
Find the particular solution of the differential equation `"dy"/"dx" = "xy"/("x"^2+"y"^2),`given that y = 1 when x = 0
Form the differential equation from the relation x2 + 4y2 = 4b2
For each of the following differential equations find the particular solution.
(x − y2 x) dx − (y + x2 y) dy = 0, when x = 2, y = 0
For each of the following differential equations find the particular solution.
`y (1 + logx)dx/dy - x log x = 0`,
when x=e, y = e2.
Solve the following differential equation.
`x^2 dy/dx = x^2 +xy - y^2`
Choose the correct alternative.
The differential equation of y = `k_1 + k_2/x` is
x2y dx – (x3 + y3) dy = 0
Solve the differential equation sec2y tan x dy + sec2x tan y dx = 0
Choose the correct alternative:
General solution of `y - x ("d"y)/("d"x)` = 0 is
Solve the following differential equation
`y log y ("d"x)/("d"y) + x` = log y
Find the particular solution of the following differential equation
`("d"y)/("d"x)` = e2y cos x, when x = `pi/6`, y = 0.
Solution: The given D.E. is `("d"y)/("d"x)` = e2y cos x
∴ `1/"e"^(2y) "d"y` = cos x dx
Integrating, we get
`int square "d"y` = cos x dx
∴ `("e"^(-2y))/(-2)` = sin x + c1
∴ e–2y = – 2sin x – 2c1
∴ `square` = c, where c = – 2c1
This is general solution.
When x = `pi/6`, y = 0, we have
`"e"^0 + 2sin pi/6` = c
∴ c = `square`
∴ particular solution is `square`
Solve `x^2 "dy"/"dx" - xy = 1 + cos(y/x)`, x ≠ 0 and x = 1, y = `pi/2`
Solve the differential equation `"dy"/"dx" + 2xy` = y
The differential equation (1 + y2)x dx – (1 + x2)y dy = 0 represents a family of:
