Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the principal and general solutions of the equation sec x = 2
Solution
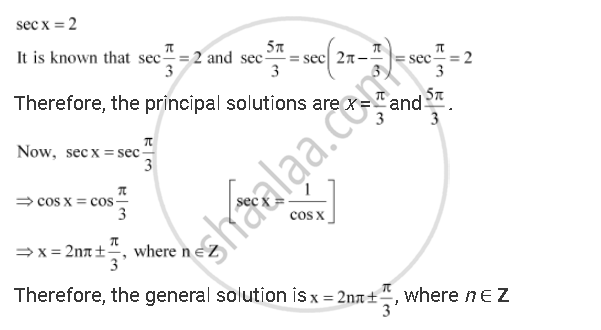
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the general solution of the equation cos 3x + cos x – cos 2x = 0
If \[\sin x = \frac{a^2 - b^2}{a^2 + b^2}\], then the values of tan x, sec x and cosec x
If \[T_n = \sin^n x + \cos^n x\], prove that \[\frac{T_3 - T_5}{T_1} = \frac{T_5 - T_7}{T_3}\]
Prove that: cos 24° + cos 55° + cos 125° + cos 204° + cos 300° = \[\frac{1}{2}\]
Prove that: tan (−225°) cot (−405°) −tan (−765°) cot (675°) = 0
Prove that:
\[\frac{\cos (2\pi + x) cosec (2\pi + x) \tan (\pi/2 + x)}{\sec(\pi/2 + x)\cos x \cot(\pi + x)} = 1\]
Prove that
In a ∆A, B, C, D be the angles of a cyclic quadrilateral, taken in order, prove that cos(180° − A) + cos (180° + B) + cos (180° + C) − sin (90° + D) = 0
Find x from the following equations:
\[cosec\left( \frac{\pi}{2} + \theta \right) + x \cos \theta \cot\left( \frac{\pi}{2} + \theta \right) = \sin\left( \frac{\pi}{2} + \theta \right)\]
Prove that:
\[\sin \frac{13\pi}{3}\sin\frac{2\pi}{3} + \cos\frac{4\pi}{3}\sin\frac{13\pi}{6} = \frac{1}{2}\]
Prove that:
If sec \[x = x + \frac{1}{4x}\], then sec x + tan x =
If \[f\left( x \right) = \cos^2 x + \sec^2 x\], then
Find the general solution of the following equation:
Solve the following equation:
Solve the following equation:
Solve the following equation:
Solve the following equation:
\[\cot x + \tan x = 2\]
Solve the following equation:
\[5 \cos^2 x + 7 \sin^2 x - 6 = 0\]
Solve the following equation:
sin x tan x – 1 = tan x – sin x
Solve the following equation:
3tanx + cot x = 5 cosec x
Solve the following equation:
3 – 2 cos x – 4 sin x – cos 2x + sin 2x = 0
Solve the following equation:
3sin2x – 5 sin x cos x + 8 cos2 x = 2
Write the set of values of a for which the equation
If cos x = k has exactly one solution in [0, 2π], then write the values(s) of k.
Write the number of points of intersection of the curves
If \[2 \sin^2 x = 3\cos x\]. where \[0 \leq x \leq 2\pi\], then find the value of x.
The number of solution in [0, π/2] of the equation \[\cos 3x \tan 5x = \sin 7x\] is
The smallest positive angle which satisfies the equation
If \[\cot x - \tan x = \sec x\], then, x is equal to
A value of x satisfying \[\cos x + \sqrt{3} \sin x = 2\] is
If \[\sqrt{3} \cos x + \sin x = \sqrt{2}\] , then general value of x is
Solve the following equations:
2cos 2x – 7 cos x + 3 = 0
Choose the correct alternative:
If tan α and tan β are the roots of x2 + ax + b = 0 then `(sin(alpha + beta))/(sin alpha sin beta)` is equal to
Choose the correct alternative:
If f(θ) = |sin θ| + |cos θ| , θ ∈ R, then f(θ) is in the interval
If a cosθ + b sinθ = m and a sinθ - b cosθ = n, then show that a2 + b2 = m2 + n2
Find the general solution of the equation sinx – 3sin2x + sin3x = cosx – 3cos2x + cos3x
In a triangle ABC with ∠C = 90° the equation whose roots are tan A and tan B is ______.
