Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show that `2sin^-1(3/5) = tan^-1(24/7)`
उत्तर
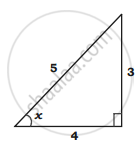
Let x = `sin^(-1)(3/5)`
sin x = `3/5`
tan x = `(3/4)`
x = `tan^(-1)(3/4)`
`sin^(-1)(3/5) = tan^(-1)(3/4)`
`2sin^(-1)(3/5) = 2tan^(-1)(3/4)`
= `tan^(-1)(3/4) + tan^(-1)(3/4)`
= `tan^(-1)(((3/4) + (3/4))/(1 - 3/4(3/4)))`
= `tan^(-1)((6/4)/(7/16))`
= `tan^(-1)(6/4 xx 16/7)`
= `tan^(-1)(24/7)`
`sin^(-1)(3/5) = tan^(-1)(24/7)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the principal value of `cot^(-1) (sqrt3)`
Find the value of the following:
If sin−1 x = y, then
Prove that:
`tan^-1 ((sqrt(1 + x) - sqrt(1 - x))/(sqrt(1 + x) + sqrt(1 - x))) = pi/4 - 1/2 cos^-1 x`, for `- 1/sqrt2 <= x <= 1`
[Hint: put x = cos 2θ]
Find the principal value of `sin^-1(1/sqrt2)`
`sin^-1 1/2-2sin^-1 1/sqrt2`
Find the domain of the following function:
`f(x)=sin^-1x^2`
Find the domain of the following function:
`f(x)sin^-1sqrt(x^2-1)`
Evaluate the following:
`tan^-1(-1/sqrt3)+tan^-1(-sqrt3)+tan^-1(sin(-pi/2))`
Find the set of values of `cosec^-1(sqrt3/2)`
Evaluate the following:
`cot^-1{2cos(sin^-1 sqrt3/2)}`
Prove that:
cot−1 7 + cot−1 8 + cot−1 18 = cot−1 3 .
In ΔABC, if a = 18, b = 24, c = 30 then find the values of tan `A/2`
Find the principal value of the following: `sin^-1 (1/2)`
Find the principal value of the following: cosec- 1(2)
Find the principal value of the following: cos- 1`(-1/2)`
Evaluate the following:
`cos^-1(1/2) + 2sin^-1(1/2)`
Evaluate the following:
`tan^-1 sqrt(3) - sec^-1 (-2)`
Evaluate the following:
`"cosec"^-1(-sqrt(2)) + cot^-1(sqrt(3))`
Prove the following:
`sin^-1(-1/2) + cos^-1(-sqrt(3)/2) = cos^-1(-1/2)`
Prove the following:
`2tan^-1(1/3) = tan^-1(3/4)`
Prove the following:
`tan^-1[sqrt((1 - cosθ)/(1 + cosθ))] = θ/(2)`, if θ ∈ (– π, π).
Find the principal solutions of the following equation:
cot 2θ = 0.
The principal value of sin−1`(1/2)` is ______
If `sin(sin^-1(1/5) + cos^-1(x))` = 1, then x = ______
Prove that `2 tan^-1 (3/4) = tan^-1(24/7)`
Evaluate:
`sin[cos^-1 (3/5)]`
Find the value of `cos^-1 (1/2) + tan^-1 (1/sqrt(3))`
If tan−1x + tan−1y + tan−1z = π, then show that `1/(xy) + 1/(yz) + 1/(zx)` = 1
Prove that sin `[tan^-1 ((1 - x^2)/(2x)) + cos^-1 ((1 - x^2)/(1 + x^2))]` = 1
Prove that cot−1(7) + 2 cot−1(3) = `pi/4`
Prove that `2 tan^-1 (1/8) + tan^-1 (1/7) + 2tan^-1 (1/5) = pi/4`
Find the principal value of the following:
cosec-1 (2)
Find the principal value of the following:
`sec^-1 (-sqrt2)`
Show that `tan^-1 (1/2) + tan^-1 (2/11) = tan^-1 (3/4)`
Solve `tan^-1 2x + tan^-1 3x = pi/4`
Prove that `tan^-1 (m/n) - tan^-1 ((m - n)/(m + n)) = pi/4`
Find the principal value of `cos^-1 sqrt(3)/2`
Find the principal value of `sec^-1 (- sqrt(2))`
A man standing directly opposite to one side of a road of width x meter views a circular shaped traffic green signal of diameter ‘a’ meter on the other side of the road. The bottom of the green signal Is ‘b’ meter height from the horizontal level of viewer’s eye. If ‘a’ denotes the angle subtended by the diameter of the green signal at the viewer’s eye, then prove that α = `tan^-1 (("a" + "b")/x) - tan^-1 ("b"/x)`
lf `sqrt3costheta + sintheta = sqrt2`, then the general value of θ is ______
In ΔABC, tan`A/2 = 5/6` and tan`C/2 = 2/5`, then ______
If `sin^-1(x/13) + cosec^-1(13/12) = pi/2`, then the value of x is ______
In Δ ABC, with the usual notations, if sin B sin C = `"bc"/"a"^2`, then the triangle is ______.
Which of the following function has period 2?
If `sin^-1 3/5 + cos^-1 12/13 = sin^-1 P`, then P is equal to ______
The principal value of `tan^{-1(sqrt3)}` is ______
In a triangle ABC, ∠C = 90°, then the value of `tan^-1 ("a"/("b + c")) + tan^-1("b"/("c + a"))` is ______.
`(sin^-1(-1/2) + tan^-1(-1/sqrt(3)))/(sec^-1 (-2/sqrt(3)) + cos^-1(1/sqrt(2))` = ______.
`sin{tan^-1((1 - x^2)/(2x)) + cos^-1((1 - x^2)/(1 + x^2))}` is equal to ______
The value of `cos(pi/4 + x) - cos(pi/4 - x)` is ______.
`cos^-1 4/5 + tan^-1 3/5` = ______.
If `3tan^-1x +cot^-1x = pi`, then xis equal to ______.
Solve for x `tan^-1((1 - x)/(1 + x)) = 1/2 tan^-1x, x > 0`
The equation tan–1x – cot–1x = `(1/sqrt(3))` has ______.
Show that `cos(2tan^-1 1/7) = sin(4tan^-1 1/3)`
Prove that `tan^-1 1/4 + tan^-1 2/9 = sin^-1 1/sqrt(5)`
When `"x" = "x"/2`, then tan x is ____________.
`"sin"^2 25° + "sin"^2 65°` is equal to ____________.
If `"x + y" = "x"/4` then (1+ tanx)(1 + tany) is equal to ____________.
If tan-1 3 + tan-1 x = tan-1 8, then x = ____________.
`"cos"^-1 1/2 + 2 "sin"^-1 1/2` is equal to ____________.
If tan-1 (x – 1) + tan-1 x + tan-1 (x + 1) = tan-1 3x, then the values of x are ____________.
If 6sin-1 (x2 – 6x + 8.5) = `pi`, then x is equal to ____________.
The value of `"cos"^-1 ("cos" ((33 pi)/5))` is ____________.
`"cos"^-1 ["cos" (2 "cot"^-1 (sqrt2 - 1))] =` ____________.
Find the value of sec2 (tan-1 2) + cosec2 (cot-1 3) ____________.
`"tan"(pi/4 + 1/2 "cos"^-1 "x") + "tan" (pi/4 - 1/2 "cos"^-1 "x") =` ____________.
`2"tan"^-1 ("cos x") = "tan"^-1 (2 "cosec x")`
If `"cot"^-1 (sqrt"cos" alpha) - "tan"^-1 (sqrt "cos" alpha) = "x",` then sinx is equal to ____________.
`"cos"^-1 ("cos" ((7pi)/6))` is equal to ____________.
`"tan"^-1 sqrt3 - "sec"^-1 (-2)` is equal to ____________.
The equation of the tangent to the curve given by x = a sin3t, y = bcos3t at a point where t = `pi/2` is
If a = `(2sin theta)/(1 + costheta + sintheta)`, then `(1 + sintheta - costheta)/(1 + sintheta)` is
Which of the following functions is inverse of itself?
sin 6θ + sin 4θ + sin 2θ = 0, then θ =
What is the value of `sin^-1(sin (3pi)/4)`?
What is the principal value of cosec–1(2).
Find the principal value of `tan^-1 (sqrt(3))`
Values of tan–1 – sec–1(–2) is equal to
`sin(tan^-1x), |x| < 1` is equal to
`2tan^-1 (cos x) = tan^-1 (2"cosec" x)`, then 'x' will be equal to
Value of `sin(pi/3 - sin^1 (- 1/2))` is equal to
What is the values of `cos^-1 (cos (7pi)/6)`
If `sin(sin^-1 1/5 + cos^-1 x) = 1`, the what will be the value of x?
`lim_(n→∞)tan{sum_(r = 1)^n tan^-1(1/(1 + r + r^2))}` is equal to ______.
If θ = `sin^-1((2x)/(1 + x^2)) + cos^-1((1 - x^2)/(1 + x^2))`, for `x ≥ 3/2` then the absolute value of `((cosθ + tanθ + 4)/secθ)` is ______.
Number of values of x satisfying the system of equations `sin^-1sqrt(2 + e^(-2x) - 2e^-x) + sec^-1sqrt(1 - x^2 + x^4) = π/2` and `5^(1+tan^-1x)` = 4 + [cos–1x] is ______ (where [.] denotes greatest integer function)
`cot^-1(sqrt(cos α)) - tan^-1 (sqrt(cos α))` = x, then sin x = ______.
If sin–1a + sin–1b + sin–1c = π, then find the value of `asqrt(1 - a^2) + bsqrt(1 - b^2) + csqrt(1 - c^2)`.
If ax + b (sec (tan–1 x)) = c and ay + b (sec.(tan–1 y)) = c, then `(x + y)/(1 - xy)` = ______.
If x ∈ R – {0}, then `tan^-1 ((sqrt(1 + x^2) + sqrt(1 - x^2))/(sqrt(1 + x^2) - sqrt(1 - x^2)))`
The value of cos (2cos–1 x + sin–1 x) at x = `1/5` is ______.
If tan–1 2x + tan–1 3x = `π/4`, then x = ______.
`(tan^-1 (sqrt(3)) - sec^-1(-2))/("cosec"^-1(-sqrt(2)) + cos^-1(-1/2))` is equal to ______.
sin [cot–1 (cos (tan–1 x))] = ______.
If cos–1 x > sin–1 x, then ______.
Prove that:
tan–1x + tan–1y = `π + tan^-1((x + y)/(1 - xy))`, provided x > 0, y > 0, xy > 1
The value of `tan(cos^-1 4/5 + tan^-1 2/3)` is ______.
