Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Show that `2sin^-1(3/5) = tan^-1(24/7)`
Solution
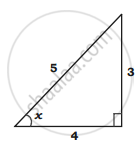
Let x = `sin^(-1)(3/5)`
sin x = `3/5`
tan x = `(3/4)`
x = `tan^(-1)(3/4)`
`sin^(-1)(3/5) = tan^(-1)(3/4)`
`2sin^(-1)(3/5) = 2tan^(-1)(3/4)`
= `tan^(-1)(3/4) + tan^(-1)(3/4)`
= `tan^(-1)(((3/4) + (3/4))/(1 - 3/4(3/4)))`
= `tan^(-1)((6/4)/(7/16))`
= `tan^(-1)(6/4 xx 16/7)`
= `tan^(-1)(24/7)`
`sin^(-1)(3/5) = tan^(-1)(24/7)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If `tan^-1((x-1)/(x-2))+cot^-1((x+2)/(x+1))=pi/4; `
Find the principal values of `sin^(-1) (-1/2)`
Find the principal value of `cos^(-1) (sqrt3/2)`
Find the principal value of cosec−1 (2)
Find the principal value of `cos^(-1) (-1/2)`
Find the principal value of `sec^(-1) (2/sqrt(3))`
Find the principal value of `cot^(-1) (sqrt3)`
Find the principal value of `cosec^(-1)(-sqrt2)`
`tan^(-1) sqrt3 - sec^(-1)(-2)` is equal to ______.
Find the value of the following:
`cos^(-1) (cos (13pi)/6)`
Find the value of the following:
`tan^(-1) (tan (7x)/6)`
Prove that:
`tan^-1 ((sqrt(1 + x) - sqrt(1 - x))/(sqrt(1 + x) + sqrt(1 - x))) = pi/4 - 1/2 cos^-1 x`, for `- 1/sqrt2 <= x <= 1`
[Hint: put x = cos 2θ]
`sin^-1 1/2-2sin^-1 1/sqrt2`
`sin^-1{cos(sin^-1 sqrt3/2)}`
Find the domain of the following function:
`f(x)sin^-1sqrt(x^2-1)`
Evaluate the following:
`tan^-1(tan (5pi)/6)+cos^-1{cos((13pi)/6)}`
In ΔABC, if a = 18, b = 24, c = 30 then find the values of cos `A/2`
In ΔABC, if a = 18, b = 24, c = 30 then find the values of tan `A/2`
In ΔABC, if a = 18, b = 24, c = 30 then find the values of sinA
In ΔABC prove that `sin "A"/(2). sin "B"/(2). sin "C"/(2) = ["A(ΔABC)"]^2/"abcs"`
Evaluate the following:
`"cosec"^-1(-sqrt(2)) + cot^-1(sqrt(3))`
Prove the following:
`sin^-1(1/sqrt(2)) -3sin^-1(sqrt(3)/2) = -(3π)/(4)`
Prove the following:
`sin^-1(3/5) + cos^-1(12/13) = sin^-1(56/65)`
Prove the following:
`2tan^-1(1/3) = tan^-1(3/4)`
Prove the following:
`tan^-1["cosθ + sinθ"/"cosθ - sinθ"] = pi/(4) + θ, if θ ∈ (- pi/4, pi/4)`
Find the principal solutions of the following equation:
sin 2θ = `− 1/(sqrt2)`
Find the principal solutions of the following equation:
cot 2θ = 0.
If `sin(sin^-1(1/5) + cos^-1(x))` = 1, then x = ______
Prove that `2 tan^-1 (3/4) = tan^-1(24/7)`
Find the value of `cos^-1 (1/2) + tan^-1 (1/sqrt(3))`
Prove that sin `[tan^-1 ((1 - x^2)/(2x)) + cos^-1 ((1 - x^2)/(1 + x^2))]` = 1
Find the principal value of the following:
cosec-1 (2)
Find the principal value of the following:
`sec^-1 (-sqrt2)`
Prove that:
2 tan-1 (x) = `sin^-1 ((2x)/(1 + x^2))`
Solve `tan^-1 2x + tan^-1 3x = pi/4`
Solve: tan-1 (x + 1) + tan-1 (x – 1) = `tan^-1 (4/7)`
Evaluate:
`cos[tan^-1 (3/4)]`
Evaluate: sin`[1/2 cos^-1 (4/5)]`
Prove that `tan^-1 (m/n) - tan^-1 ((m - n)/(m + n)) = pi/4`
Express `tan^-1 ((cos x - sin x)/(cos x + sin x))`, 0 < x < π in the simplest form.
Find the principal value of `sec^-1 (- sqrt(2))`
The value of cot `(tan^-1 2x + cot^-1 2x)` is ______
lf `sqrt3costheta + sintheta = sqrt2`, then the general value of θ is ______
sin[3 sin-1 (0.4)] = ______.
The principal value of `sin^-1 (sin (3pi)/4)` is ______.
The value of cot (- 1110°) is equal to ______.
In a triangle ABC, ∠C = 90°, then the value of `tan^-1 ("a"/("b + c")) + tan^-1("b"/("c + a"))` is ______.
The value of `sin^-1(cos (53pi)/5)` is ______
`sin{tan^-1((1 - x^2)/(2x)) + cos^-1((1 - x^2)/(1 + x^2))}` is equal to ______
`cos^-1 4/5 + tan^-1 3/5` = ______.
If `3tan^-1x +cot^-1x = pi`, then xis equal to ______.
The value of `sin^-1[cos(pi/3)] + sin^-1[tan((5pi)/4)]` is ______.
The domain of y = cos–1(x2 – 4) is ______.
The domain of the function defined by f(x) = sin–1x + cosx is ______.
The equation tan–1x – cot–1x = `(1/sqrt(3))` has ______.
Prove that `cot(pi/4 - 2cot^-1 3)` = 7
If 2 tan–1(cos θ) = tan–1(2 cosec θ), then show that θ = π 4, where n is any integer.
Show that `cos(2tan^-1 1/7) = sin(4tan^-1 1/3)`
Solve the following equation `cos(tan^-1x) = sin(cot^-1 3/4)`
All trigonometric functions have inverse over their respective domains.
`"sin"^2 25° + "sin"^2 65°` is equal to ____________.
`("cos" 8° - "sin" 8°)/("cos" 8° + "sin" 8°)` is equal to ____________.
If `"cos"^-1 "x + sin"^-1 "x" = pi`, then the value of x is ____________.
If tan-1 3 + tan-1 x = tan-1 8, then x = ____________.
`"sin"^-1 (-1/2)`
`"sin"^-1 (1/sqrt2)`
`2 "tan"^-1 ("cos x") = "tan"^-1 (2 "cosec x")`
`"tan"(pi/4 + 1/2 "cos"^-1 "x") + "tan" (pi/4 - 1/2 "cos"^-1 "x") =` ____________.
If `"sin"^-1("x"^2 - 7"x" + 12) = "n"pi, AA "n" in "I"`, then x = ____________.
If `"cot"^-1 (sqrt"cos" alpha) - "tan"^-1 (sqrt "cos" alpha) = "x",` then sinx is equal to ____________.
`"tan"^-1 sqrt3 - "sec"^-1 (-2)` is equal to ____________.
If a = `(2sin theta)/(1 + costheta + sintheta)`, then `(1 + sintheta - costheta)/(1 + sintheta)` is
If A = `[(cosx, sinx),(-sinx, cosx)]`, then A1 A–1 is
If `sqrt(2)` sec θ + tan θ = 1, then the general value of θ is
The inverse of `f(x) = sqrt(3x^2 - 4x + 5)` is
Domain and Rariges of cos–1 is:-
What will be the principal value of `sin^-1(-1/2)`?
`2tan^-1 (cos x) = tan^-1 (2"cosec" x)`, then 'x' will be equal to
If `sin(sin^-1 1/5 + cos^-1 x) = 1`, the what will be the value of x?
If f(x) = x5 + 2x – 3, then (f–1)1 (–3) = ______.
Find the principal value of `cot^-1 ((-1)/sqrt(3))`
`lim_(n→∞)tan{sum_(r = 1)^n tan^-1(1/(1 + r + r^2))}` is equal to ______.
Number of values of x satisfying the system of equations `sin^-1sqrt(2 + e^(-2x) - 2e^-x) + sec^-1sqrt(1 - x^2 + x^4) = π/2` and `5^(1+tan^-1x)` = 4 + [cos–1x] is ______ (where [.] denotes greatest integer function)
If ax + b (sec (tan–1 x)) = c and ay + b (sec.(tan–1 y)) = c, then `(x + y)/(1 - xy)` = ______.
If tan–1 2x + tan–1 3x = `π/4`, then x = ______.
Derivative of `tan^-1(x/sqrt(1 - x^2))` with respect sin–1(3x – 4x3) is ______.
If sin–1x – cos–1x = `π/6`, then x = ______.
Prove that:
tan–1x + tan–1y = `π + tan^-1((x + y)/(1 - xy))`, provided x > 0, y > 0, xy > 1
The value of `tan(cos^-1 4/5 + tan^-1 2/3)` is ______.
If tan 4θ = `tan(2/θ)`, then the general value of θ is ______.
