Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solution
\[\frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{e^x \left( \sin^2 x + \sin 2x \right)}{y\left( 2\log y + 1 \right)}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y\left( 2\log y + 1 \right)dy = e^x \left( \sin^2 x + \sin 2x \right)dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( 2y \log y + y \right)dy = \left( e^x \sin^2 x + e^x \sin 2x \right)dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2y \log y\ dy + y\ dy = e^x \sin^2 x dx + e^x \sin 2x dx\]
Integrating both sides, we get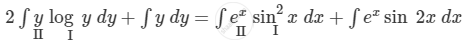
\[ \Rightarrow 2\left[ \log y\int y\ dy - \int\left\{ \frac{d}{dy}\left( \log y \right)\int y dy \right\} \right]dy + \int y dy = \sin^2 x\int e^x\ dx - \int\left[ \frac{d}{dx}\left( \sin^2 x \right)\int e^x dx \right]dx + \int e^x \sin 2x\ dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\left[ \log y \left( \frac{y^2}{2} \right) - \int\left( \frac{1}{y} \right)\frac{y^2}{2}dy \right] + \int y\ dy = \sin^2 x e^x - \int\left[ 2\sin x\cos x e^x \right]dx + \int e^x \sin 2x\ dx + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow y^2 \log y - \int y\ dy + \int y\ dy = e^x \sin^2 x - \int e^x \sin 2x\ dx + \int e^x \sin 2x\ dx + C\]
\[ \Rightarrow y^2 \log y = e^x \sin^2 x + C\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Verify that \[y = e^{m \cos^{- 1} x}\] satisfies the differential equation \[\left( 1 - x^2 \right)\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2} - x\frac{dy}{dx} - m^2 y = 0\]
Differential equation \[\frac{dy}{dx} = y, y\left( 0 \right) = 1\]
Function y = ex
(sin x + cos x) dy + (cos x − sin x) dx = 0
tan y \[\frac{dy}{dx}\] = sin (x + y) + sin (x − y)
Solve the following differential equation:
(xy2 + 2x) dx + (x2 y + 2y) dy = 0
Find the particular solution of the differential equation
(1 – y2) (1 + log x) dx + 2xy dy = 0, given that y = 0 when x = 1.
(x + y) (dx − dy) = dx + dy
x2 dy + y (x + y) dx = 0
Solve the following initial value problem:-
\[y' + y = e^x , y\left( 0 \right) = \frac{1}{2}\]
Solve the following initial value problem:-
\[\frac{dy}{dx} - 3y \cot x = \sin 2x; y = 2\text{ when }x = \frac{\pi}{2}\]
Solve the following initial value problem:-
\[\frac{dy}{dx} + y\cot x = 2\cos x, y\left( \frac{\pi}{2} \right) = 0\]
Show that the equation of the curve whose slope at any point is equal to y + 2x and which passes through the origin is y + 2 (x + 1) = 2e2x.
Find the equation of the curve which passes through the origin and has the slope x + 3y− 1 at any point (x, y) on it.
At every point on a curve the slope is the sum of the abscissa and the product of the ordinate and the abscissa, and the curve passes through (0, 1). Find the equation of the curve.
Define a differential equation.
Which of the following differential equations has y = C1 ex + C2 e−x as the general solution?
Choose the correct option from the given alternatives:
The differential equation `"y" "dy"/"dx" + "x" = 0` represents family of
In each of the following examples, verify that the given function is a solution of the corresponding differential equation.
| Solution | D.E. |
| y = ex | `dy/ dx= y` |
Solve the following differential equation.
`dy/dx = x^2 y + y`
Solve the following differential equation.
(x2 − y2 ) dx + 2xy dy = 0
A solution of a differential equation which can be obtained from the general solution by giving particular values to the arbitrary constants is called ___________ solution.
y2 dx + (xy + x2)dy = 0
`xy dy/dx = x^2 + 2y^2`
The function y = ex is solution ______ of differential equation
Verify y = `a + b/x` is solution of `x(d^2y)/(dx^2) + 2 (dy)/(dx)` = 0
y = `a + b/x`
`(dy)/(dx) = square`
`(d^2y)/(dx^2) = square`
Consider `x(d^2y)/(dx^2) + 2(dy)/(dx)`
= `x square + 2 square`
= `square`
Hence y = `a + b/x` is solution of `square`
An appropriate substitution to solve the differential equation `"dx"/"dy" = (x^2 log(x/y) - x^2)/(xy log(x/y))` is ______.
Solve the differential equation `"dy"/"dx" + 2xy` = y
