Topics
Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land
- Natural Resources
- Atmosphere and Its Layers
- Air Around Us
- Composition and Components of Air
- Importance of Air
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Water: Our Lifeline
- Availability of Water
- Composition of Water
- Importance of Water
- Scarcity of Water
- Land
- Soil Formation
- The Importance of Conserving Earth’s Natural Resources
The Living World
Diversity in Living Things and Their Classification
Disaster Management
Substances in the Surroundings –Their States and Properties
Substances in Daily Use
Nutrition and Diet
- Nutrients and Nutrition
- Component of Food
- Carbohydrates
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Carbohydrates
- Fats (Lipids)
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Fats
- Proteins
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Proteins
- Vitamin and Minerals
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Vitamin
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Minerals
- Fibre
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Fibre
- Water
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Water
- A Balanced Diet
- Nourishment and Malnutrition
- Food Adulteration
Our Skeletal System and the Skin
Motion and Types of Motion
Force and Types of Force
Work and Energy
- Force, displacement and work
- Energy
- The relationship between work and energy
- Forms of Energy
- Mechanical Energy
- Heat Energy (Thermal Energy)
- Light Energy
- Sound energy
- Chemical Energy
- Transformation of Energy
- Energy Resources
- Conventional energy resources or non-renewable energy resources
- Non-conventional energy resources or renewable energy resources
- Energy saving and green energy
Simple Machines
Sound
Light and the Formation of Shadows
Fun with Magnets
The Universe
- Introduction
- Experiment
- Food is necessary for growth
Introduction:
| Type of Growth | Description |
|---|---|
| Human Growth | Babies grow into adults (women or men). |
| Gain in height, weight, and strength during growth. | |
| Full growth takes 18 to 21 years. | |
| Animal Growth | Animals grow into adults over a specific period. |
| For example, hens, cows, and dogs have different growth periods. | |
| Unlike humans, animals have varying growth times. | |
| Plant Growth | Plants grow in the width and height of their stems. |
| Some plants grow branches, while others do not. | |
| Plants continue to grow as long as they live, unlike animals that stop growing. |
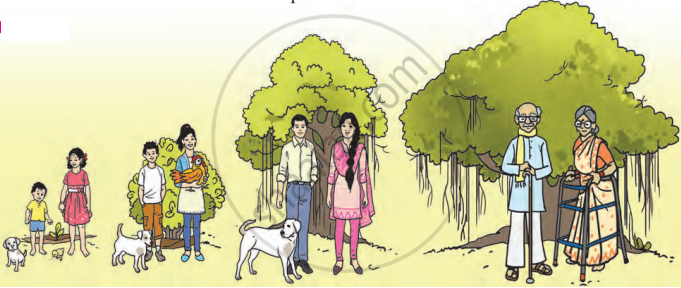
Growth in living things

Growth in banyan and coconut trees
Experiment
1. Aim: To observe and measure the growth of a potted sapling over ten to fifteen days.
2. Requirements: potted sapling, thread, peg or nail, and measuring scale.
3. Procedure
- Tie a thread to the tip of the sapling.
- Stretch the thread upwards and tie it to a peg or nail above the plant.
- Ensure the thread remains taut and observe the setup daily for 10–15 days.
4. Observations
- After 10–15 days, the plant's tip is no longer aligned with the thread's original position.
- The plant tip has risen above the thread, indicating vertical growth.
- Any changes in the width of the stem or the formation of new branches can also be noted.
5. Conclusion: The distance between the tip and the thread indicates that the sapling has grown taller. This experiment demonstrates that a plant's growth occurs in both height and width, and some may develop branches.
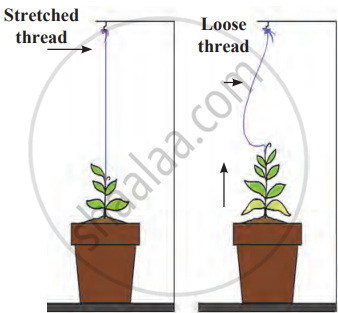
Sapling in a pot
Food is necessary for growth:
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Plants (Photosynthesis) | Plants make food using sunlight, water, soil nutrients, and carbon dioxide. |
| This process is called photosynthesis, which requires chlorophyll (which gives plants a green colour). | |
| During photosynthesis, plants release oxygen into the air. | |
| Animals (Food Search) | Animals cannot make their food because they lack chlorophyll. |
| Herbivores (e.g., goats, sheep, horses) eat plants like grass. | |
| Carnivores (e.g., tigers and lions) hunt other animals that live on plants. |
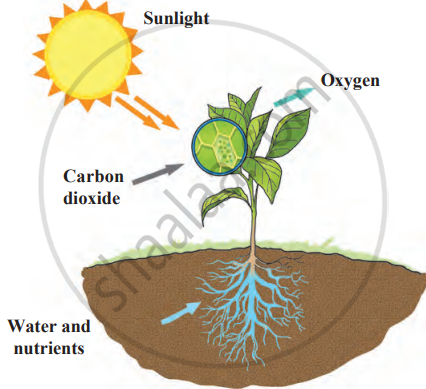
Photosynthesis

Intake of food by animals
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
