Topics
Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land
- Natural Resources
- Atmosphere and Its Layers
- Air Around Us
- Composition and Components of Air
- Importance of Air
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Water: Our Lifeline
- Availability of Water
- Composition of Water
- Importance of Water
- Scarcity of Water
- Land
- Soil Formation
- The Importance of Conserving Earth’s Natural Resources
The Living World
Diversity in Living Things and Their Classification
Disaster Management
Substances in the Surroundings –Their States and Properties
Substances in Daily Use
Nutrition and Diet
- Nutrients and Nutrition
- Component of Food
- Carbohydrates
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Carbohydrates
- Fats (Lipids)
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Fats
- Proteins
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Proteins
- Vitamin and Minerals
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Vitamin
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Minerals
- Fibre
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Fibre
- Water
- Diseases Due to Deficiency of Water
- A Balanced Diet
- Nourishment and Malnutrition
- Food Adulteration
Our Skeletal System and the Skin
Motion and Types of Motion
Force and Types of Force
Work and Energy
- Force, displacement and work
- Energy
- The relationship between work and energy
- Forms of Energy
- Mechanical Energy
- Power Plants Based on Thermal Energy
- Light Energy
- Sound energy
- Chemical Energy
- Transformation of Energy
- Energy Resources
- Conventional energy resources or non-renewable energy resources
- Non-conventional energy resources or renewable energy resources
- Energy saving and green energy
Simple Machines
Sound
Light and the Formation of Shadows
Fun with Magnets
The Universe
- Introduction
- Experiment
Introduction:
Gravitational force is the force that the Earth uses to pull all objects toward itself. This is why when something is thrown upward, it eventually falls back down to the ground.
- For example, when a ball is thrown up, it reaches a certain height and then comes back down because of the Earth's gravitational pull.
- The stronger the gravitational force on an object, the harder it is to lift.
- Gravitational force also works in space. It keeps the planets in the solar system revolving around the sun.
- Gravity also acts between planets and their moons, keeping the moons in orbit around the planets.
Discovery of Gravitational Force:
In the 17th century, Sir Isaac Newton discovered the concept of gravitation. The earth’s gravitational force acts in a direction opposite to that of an object moving upwards. Hence, the speed of that object goes on decreasing till, in the end, it becomes zero. Then the object starts falling down instead of going up any further. While falling, its speed goes on increasing all the time due to gravitational force.
Experiment:
1. Aim: To observe the difference in sound when a stone is dropped from different heights and understand the effect of gravitational force on objects of different weights. Effect of Height and Weight on Gravitational Force.
2. Requirements: A small stone, a bucket of water, and two sacks (one empty, one full)
3. Procedure
I. Stone experiment:
- Take a small stone and a bucket of water.
- Drop the stone into the water from a height of about 20 cm.
- Observe and listen to the sound made when the stone hits the water.
- Now, drop the same stone into the water from a height of about 100 cm.
- Again, observe and listen to the sound produced.
II. Sack experiment:
- Take two sacks—one empty and the other full.
- Lift the empty sack and notice how much effort is needed.
- Then, lift the full sack and observe the difference in the effort required.
4. Conclusion:
- For the stone experiment: Dropping the stone from a greater height produces a louder sound because the stone gains more speed as it falls due to the effect of gravitational force. This means that the greater the height, the more speed and force the stone has when it hits the water.
- For the sack experiment: The empty sack is easier to lift because it weighs less, meaning the gravitational force acting on it is smaller. The full sack requires more effort to lift because it is heavier, and the gravitational force on it is greater. This shows that greater force is needed to lift heavier objects.

Dropping a stone in water
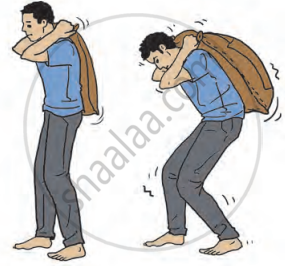
Carrying a load
