Topics
The Living World: Adaptations and Classification
- Biodiversity
- Adaptations and Its Types
- Adaptations of Plants
- Adaptation in Aquatic Plants (Hydrophytes)
- Adaptation in Desert Plants (Xerophytes)
- Adaptation in plants of snowy regions
- Adaptation in Forest Plants
- Adaptation in Grassland Plants (Mesophytes)
- Adaptation for Ingestion of Food in Plants
- Adaptation in Animals
- Adaptation in Aquatic Animals
- Adaptation in Forest and Grassland Animals
- Adaptation in Desert Animals
- Adaptation in animals of snowy regions
- Adaptation in Aerial Animals
- Adaptation in Reptiles
- Adaptation for Food in Animals
- Adaptation for Blending with the Surroundings
- Classification of Living Organisms
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- Nomenclature
Plants: Structure and Function
Properties of Natural Resources
Nutrition in Living Organisms
- Nutrients and Nutrition
- Autotrophic Plants
- Symbiotic Plants
- Heterotrophic Plants
- Insectivorous Plants
- Saprophytic Plants
- Role of nutrients and effects of their deficiency on plants
- Transport System in Plants
- Nitrogen Fixation
- Nutrition in Animals
- Mode of Nutrition in Animals
- Holozoic Nutrition
- Saprozoic Nutrition
- Parasitic Nutrition
Food Safety
Measurement of Physical Quantities
Motion, Force and Work
Static Electricity
Heat
Disaster Management
Cell Structure and Micro-organisms
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- Measurement and observation of cells
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Structure of the Cell
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Plasma Membrane
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell"
- Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”
- Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
- Plastids
- Microorganisms (Microbes) and Microbiology
- Useful micro-organisms
- Harmful Microorganisms
- Pathogens: Disease-producing Micro-organisms
The Muscular System and Digestive System in Human Beings
- Muscular System
- Muscles and Its Types
- Human Digestive System
- The Mouth and Buccal Cavity
- The Teeth and Its Structure
- The Salivary Glands
- The Food Pipe/Oesophagus
- Pharynx/Throat
- The Stomach
- The Small Intestine
- Pancreas
- Liver
- The Large Intestine
- Important Glands of the Digestive System
- Effects of Tobacco, Alcohol, Smoking, on the Digestive System
Changes – Physical and Chemical
- Changes-Physical and Chemical
- Classification of Change: Natural and Man-made Changes
- Classification of Change: Harmful and Useful Changes
- Classification of Change: Slow and Fast Changes
- Classification of Change: Reversible and Irreversible Changes
- Classification of Change: Periodic and Non-periodic Changes
- Classification of Change: Physical Changes
- Classification of Change: Chemical Changes
- Corrosion of Metals
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
Materials We Use
Natural Resources
Effects of Light
Sound: Production of Sound
Properties of a Magnetic Field
In the World of Stars
- Introduction
- Classification of Animals Based on Their Food
Introduction:
Holozoic nutrition is the process in which organisms eat solid food, break it down, and absorb nutrients.
- In unicellular animals like Amoeba, the entire process of nutrition happens inside a single cell. An amoeba doesn’t have hands or a mouth. Instead, it can take in food from any part of its body.
- When it finds food, it surrounds the food particle using extensions of its body called pseudopodia. Once the food is inside, it gets digested with the help of enzymes, and any undigested parts are left behind as the amoeba moves.
- Other unicellular organisms like Euglena and Paramecium also perform all nutrition steps inside their single cell.
In contrast, insects have different specialised mouthparts for feeding:
- Cockroaches and grasshoppers have jaw-like mouthparts to nibble and chew food.
- Butterflies use a long, tube-like structure called a proboscis to suck nectar.
- Mosquitoes and bedbugs have needle-like mouthparts to pierce skin and suck blood or other fluids.
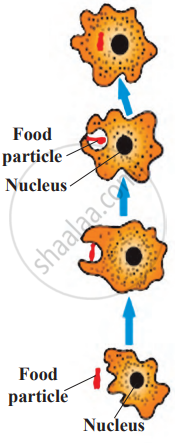
Amoeba
Classification of Animals Based on Their Food:
| Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Herbivores | Animals that eat plants directly. | Grazing animals-cows, goats, granivores (seed-eaters), pigeons, frugivores (fruit-eaters)-parrots, etc. |
| Carnivores | Animals that eat other animals. They indirectly depend on plants by eating herbivores or other animals. | Predators: lions Insectivores: frogs |
| Omnivores | Animals that eat both plants and animals. | Monkeys, chimpanzees, humans |
| Scavengers | Animals that feed on dead animals help to clean the environment. | Vultures, crows, hyenas |
| Decomposers | Microorganisms that break down dead bodies or organic materials, returning nutrients to the environment. | Bacteria, fungi |

Animals with different food habits
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
