Topics
The Living World: Adaptations and Classification
- Biodiversity
- Adaptations and Its Types
- Adaptations of Plants
- Adaptation in Aquatic Plants (Hydrophytes)
- Adaptation in Desert Plants (Xerophytes)
- Adaptation in plants of snowy regions
- Adaptation in Forest Plants
- Adaptation in Grassland Plants (Mesophytes)
- Adaptation for Ingestion of Food in Plants
- Adaptation in Animals
- Adaptation in Aquatic Animals
- Adaptation in Forest and Grassland Animals
- Adaptation in Desert Animals
- Adaptation in animals of snowy regions
- Adaptation in Aerial Animals
- Adaptation in Reptiles
- Adaptation for Food in Animals
- Adaptation for Blending with the Surroundings
- Classification of Living Organisms
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- Nomenclature
Plants: Structure and Function
Properties of Natural Resources
Nutrition in Living Organisms
- Nutrients and Nutrition
- Autotrophic Plants
- Symbiotic Plants
- Heterotrophic Plants
- Insectivorous Plants
- Saprophytic Plants
- Role of nutrients and effects of their deficiency on plants
- Transport System in Plants
- Nitrogen Fixation
- Nutrition in Animals
- Mode of Nutrition in Animals
- Holozoic Nutrition
- Saprozoic Nutrition
- Parasitic Nutrition
Food Safety
Measurement of Physical Quantities
Motion, Force and Work
Static Electricity
Heat
Disaster Management
Cell Structure and Micro-organisms
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- Measurement and observation of cells
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Structure of the Cell
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Plasma Membrane
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell"
- Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”
- Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
- Plastids
- Microorganisms (Microbes) and Microbiology
- Useful micro-organisms
- Harmful Microorganisms
- Pathogens: Disease-producing Micro-organisms
The Muscular System and Digestive System in Human Beings
- Muscular System
- Muscles and Its Types
- Human Digestive System
- The Mouth and Buccal Cavity
- The Teeth and Its Structure
- The Salivary Glands
- The Food Pipe/Oesophagus
- Pharynx/Throat
- The Stomach
- The Small Intestine
- Pancreas
- Liver
- The Large Intestine
- Important Glands of the Digestive System
- Effects of Tobacco, Alcohol, Smoking, on the Digestive System
Changes – Physical and Chemical
- Changes-Physical and Chemical
- Classification of Change: Natural and Man-made Changes
- Classification of Change: Harmful and Useful Changes
- Classification of Change: Slow and Fast Changes
- Classification of Change: Reversible and Irreversible Changes
- Classification of Change: Periodic and Non-periodic Changes
- Classification of Change: Physical Changes
- Classification of Change: Chemical Changes
- Corrosion of Metals
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
Materials We Use
Natural Resources
Effects of Light
Sound: Production of Sound
Properties of a Magnetic Field
In the World of Stars
Sky Watching:
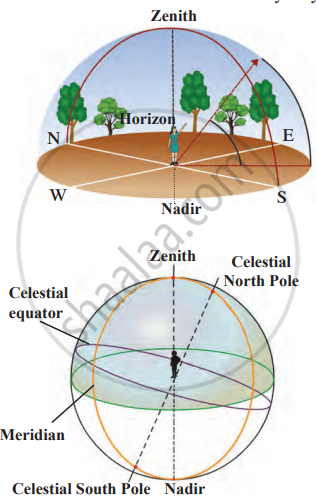
1. Horizon: The horizon is the line where the sky seems to meet the ground. When you stand still and turn around, the horizon looks like a circle surrounding you.
2. Celestial Sphere: The sky appears like a giant sphere around the Earth, called the celestial sphere, on which stars and planets seem to move.
3. Zenith and Nadir:
- Zenith: The point directly above your head on the celestial sphere.
- Nadir: The point directly under your feet on the celestial sphere.
4. Celestial Poles: When Earth's rotation axis is extended into the sky, it intersects the celestial sphere at the North and South celestial poles.
5. Meridian: A circle passing through the celestial poles, zenith, and nadir is called the meridian.
6. Celestial Equator: If Earth's equator is extended outward, it forms the celestial equator on the celestial sphere.
7. Ecliptic: The ecliptic is the path the Sun seems to follow on the celestial sphere throughout the year, caused by Earth’s orbit around the Sun.
8. Sky and Space:
- Sky: The part of the atmosphere and beyond that looks like a roof above us.
- Space: The empty area between stars and planets, containing gas, dust, and star clusters.
9. Motion of Celestial Bodies:
- The Sun, Moon, and stars rise in the east and set in the west because Earth rotates from west to east.
- Stars rise 4 minutes earlier each day, and the Sun moves 1 degree daily, while the Moon moves 12–13 degrees daily, due to their motion relative to Earth.
Virtual sphere
