Advertisements
Chapters
2: Banking (Recurring Deposit Account)
3: Shares and Dividend
4: Linear Inequations (In one variable)
5: Quadratic Equations
6: Solving (simple) Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations)
7: Ratio and Proportion (Including Properties and Uses)
8: Remainder and Factor Theorems
9: Matrices
10: Arithmetic Progression
11: Geometric Progression
12: Reflection
13: Section and Mid-Point Formula
14: Equation of a Line
15: Similarity (With Applications to Maps and Models)
16: Loci (Locus and Its Constructions)
17: Circles
18: Tangents and Intersecting Chords
19: Constructions (Circles)
20: Cylinder, Cone and Sphere
21: Trigonometrical Identities
22: Height and Distances
23: Graphical Representation
24: Measure of Central Tendency(Mean, Median, Quartiles and Mode)
▶ 25: Probability
![Selina solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 25 - Probability Selina solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 25 - Probability - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-10-icse_6:8bf8c01058454f579d37da35940563b5.png)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 25: Probability
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 25 of CISCE Selina for Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE 25 Probability Exercise 25 (A) [Page 386]
A coin is tossed once. Find the probability of getting a tail.
A coin is tossed once. Find the probability of not getting a tail.
A bag contains 3 white, 5 black and 2 red balls, all of the same shape and size. A ball is drawn from the bag without looking into it, find the probability that the ball drawn
a black ball.
A bag contains 3 white, 5 black and 2 red balls, all of the same shape and size. A ball is drawn from the bag without looking into it, find the probability that the ball drawn
a red ball.
A bag contains 3 white, 5 black and 2 red balls, all of the same shape and size. A ball is drawn from the bag without looking into it, find the probability that the ball drawn White ball.
A bag contains 3 white, 5 black and 2 red balls, all of the same shape and size. A ball is drawn from the bag without looking into it, find the probability that the ball drawn is:
not a red ball.
A bag contains 3 white, 5 black and 2 red balls, all of the same shape and size. A ball is drawn from the bag without looking into it, find the probability that the ball drawn
not a black ball.
In a single throw of a dice, find the probability of getting a number greater than 4.
In a single throw of a dice, find the probability of getting a number less than or equal to 4.
In a single throw of a dice, find the probability of getting a number not greater than 4.
In a single throw of a dice, find the probability that the number will be an even number.
In a single throw of a dice, find the probability that the number will not be an even number.
In a single throw of a dice, find the probability that the number will be an odd number.
From a well-shuffled deck of 52 playing-cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn will be a black card.
From a well-shuffled deck of 52 playing-cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn will not be a red card.
From a well-shuffled deck of 52 playing-cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn will be a red card.
From a well-shuffled deck of 52 playing-cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn will be a face card.
From a well-shuffled deck of 52 playing-cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn will be a face card of red colour.
If A and B are two complementary events then what is the relation between P(A) and P(B)?
If the probability of happening of an event A is 0.46. What will be the probability of not happening of the event A?
In a T.T. match between Geeta and Ritu, the probability of the winning of Ritu is 0.73. Find the probability of:
- winning of Geeta.
- not winning of Ritu.
In a T.T. match between Geeta and Ritu, the probability of the winning of Ritu is 0.73. Find the probability of not winning of Ritu.
In a race between Mahesh and John, the probability that John will lose the race is 0.54. Find the probability of:
- winning of Mahesh
- winning of John
Write the probability of a sure event.
Write the probability of an event which is impossible.
For an event E, write a relation representing the range of values of P(E).
In a single throw of a dice, find the probability of getting 5.
In a single throw of a dice, find the probability of getting 8.
In a single throw of a dice, find the probability of getting a number less than 8.
In a single throw of a dice, find the probability of getting a prime number.
A dice is thrown once. Find the probability of getting an even number.
A dice is thrown once. Find the probability of getting a number between 3 and 8.
A dice is thrown once. Find the probability of getting an even number or a multiple of 3.
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
- `3/5`
- 2.7
- 43%
- – 0.6
- – 3.2
- 0.35
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
2.7
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
43%
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
– 0.6
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
–3.2
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
0.35
A bag contains six identical black balls. A child withdraws one ball from the bag without looking into it. What is the probability that he takes out a white ball?
A bag contains six identical black balls. A child withdraws one ball from the bag without looking into it. What is the probability that he takes out a black ball?
A single letter is selected at random from the word ‘Probability’. Find the probability that it is a vowel.
Ramesh chooses a date at random in January for a party.
| January | |||||
| Mon | 6 | 13 | 20 | 27 | |
| Tue | 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | |
| Wed | 1 | 8 | 15 | 22 | 29 |
| Thurs | 2 | 9 | 16 | 23 | 30 |
| Fri | 3 | 10 | 17 | 24 | 31 |
| Sat | 4 | 11 | 18 | 25 | |
| Sun | 5 | 12 | 19 | 26 | |
Find the probability that he chooses:
- a Wednesday
- a Friday
- a Tuesday or a Saturday.
Selina solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE 25 Probability Exercise 25 (B) [Page 393]
Nine cards (identical in all respects) are numbered 2 to 10. A card is selected from them at random. Find the probability that the card selected will be an even number.
Nine cards (identical in all respects) are numbered 2 to 10. A card is selected from them at random. Find the probability that the card selected will be a multiple of 3.
Nine cards (identical in all respects) are numbered 2 to 10. A card is selected from them at random. Find the probability that the card selected will be an even number and a multiple of 3.
Nine cards (identical in all respects) are numbered 2 to 10. A card is selected from them at random. Find the probability that the card selected will be an even number or a multiple of 3.
Hundred identical cards are numbered from 1 to 100. The cards are well shuffled and then a card is drawn. Find the probability that the number on the card drawn is a multiple of 5.
Hundred identical cards are numbered from 1 to 100. The cards are well shuffled and then a card is drawn. Find the probability that the number on the card drawn is a multiple of 6.
Hundred identical cards are numbered from 1 to 100. The cards are well shuffled and then a card is drawn. Find the probability that the number on the card drawn is between 40 and 60.
Hundred identical cards are numbered from 1 to 100. The cards are well shuffled and then a card is drawn. Find the probability that the number on the card drawn is greater than 85.
Hundred identical cards are numbered from 1 to 100. The cards are well shuffled and then a card is drawn. Find the probability that the number on the card drawn is less than 48.
From 25 identical cards, numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ......, 24, 25; one card is drawn at random. Find the probability that the number on the card drawn is a multiple of 3.
From 25 identical cards, numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ……, 24, 25: one card is drawn at random. Find the probability that the number on the card drawn is a multiple of 5.
From 25 identical cards, numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ......, 24, 25; one card is drawn at random. Find the probability that the number on the card drawn is a multiple of 3 and 5.
From 25 identical cards, numbered 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ......, 24, 25; one card is drawn at random. Find the probability that the number on the card drawn is a multiple of 3 or 5.
A dice is thrown once. Find the probability of getting a number less than 3.
A die is thrown once. Find the probability of getting a number greater than or equal to 4.
A dice is thrown once. Find the probability of getting a number less than 8.
A dice is thrown once. Find the probability of getting a number greater than 6.
A book contains 85 pages. A page is chosen at random. What is the probability that the sum of the digits on the page is 8?
A pair of dice is thrown. Find the probability of getting a sum of 10 or more, if 5 appears on the first dice.
If two coins are tossed once, what is the probability of getting both heads.
If two coins are tossed once, what is the probability of getting at least one head.
If two coins are tossed once, what is the probability of getting both heads or both tails.
Two dice are rolled together. Find the probability of getting a total of at least 10.
Two dice are rolled together. Find the probability of getting a multiple of 2 on one die and an odd number on the other die.
A card is drawn from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is a spade.
A card is drawn from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is a red card.
A card is drawn from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is a face card.
A card is drawn from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is 5 of heart or diamond.
A card is drawn from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is jack or queen.
A card is drawn from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is ace and king.
A card is drawn from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is a red and a king.
A card is drawn from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is a red or a king.
A bag contains 16 coloured balls. Six are green, 7 are red and 3 are white. A ball is chosen, without looking into the bag. Find the probability that the ball chosen is red.
A bag contains 16 coloured balls. Six are green, 7 are red and 3 are white. A ball is chosen, without looking into the bag. Find the probability that the ball chosen is not red.
A bag contains 16 coloured balls. Six are green, 7 are red and 3 are white. A ball is chosen, without looking into the bag. Find the probability that the ball chosen is white.
A bag contains 16 coloured balls. Six are green, 7 are red and 3 are white. A ball is chosen, without looking into the bag. Find the probability that the ball chosen is not white.
A bag contains 16 coloured balls. Six are green, 7 are red and 3 are white. A ball is chosen, without looking into the bag. Find the probability that the ball chosen is green or red.
A bag contains 16 coloured balls. Six are green, 7 are red and 3 are white. A ball is chosen, without looking into the bag. Find the probability that the ball chosen is white or green.
A bag contains 16 coloured balls. Six are green, 7 are red and 3 are white. A ball is chosen, without looking into the bag. Find the probability that the ball chosen is green or red or white.
A ball is drawn at random from a box containing 12 white, 16 red and 20 green balls. Determine the probability that the ball drawn is white.
A ball is drawn at random from a box containing 12 white, 16 red and 20 green balls. Determine the probability that the ball drawn is red.
A ball is drawn at random from a box containing 12 white, 16 red and 20 green balls. Determine the probability that the ball drawn is not green.
A ball is drawn at random from a box containing 12 white, 16 red and 20 green balls. Determine the probability that the ball drawn is red or white.
A card is drawn from a pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is a red card.
A card is drawn from a pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is a black card.
A card is drawn from a pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is a spade.
A card is drawn from a pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is an ace.
A card is drawn from a pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is a black ace.
A card is drawn from a pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is ace of diamonds.
A card is drawn from a pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is not a club.
A card is drawn from a pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is a queen or a jack.
Thirty identical cards are marked with numbers 1 to 30. If one card is drawn at random, find the probability that it is a multiple of 4 or 6.
Thirty identical cards are marked with numbers 1 to 30. If one card is drawn at random, find the probability that it is a multiple of 3 and 5.
Thirty identical cards are marked with numbers 1 to 30. If one card is drawn at random, find the probability that it is a multiple of 3 or 5.
In a single throw of two dice, find the probability of a doublet.
In a single throw of two dice, find the probability of a number less than 3 on each dice.
In a single throw of two dice, find the probability of an odd number as a sum.
In a single throw of two dice, find the probability of a total of at most 10.
In a single throw of two dice, find the probability of an odd number on one dice and a number less than or equal to 4 on the other dice.
Selina solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE 25 Probability Exercise 25 (C) [Pages 394 - 396]
A bag contains 3 red balls, 4 blue balls and 1 yellow ball, all the balls being identical in shape and size. If a ball is taken out of the bag without looking into it; find the probability that the ball is yellow.
A bag contains 3 red balls, 4 blue balls and 1 yellow ball, all the balls being identical in shape and size. If a ball is taken out of the bag without looking into it; find the probability that the ball is red.
A bag contains 3 red balls, 4 blue balls and 1 yellow ball, all the balls being identical in shape and size. If a ball is taken out of the bag without looking into it; find the probability that the ball is not yellow.
A bag contains 3 red balls, 4 blue balls and 1 yellow ball, all the balls being identical in shape and size. If a ball is taken out of the bag without looking into it; find the probability that the ball is neither yellow nor red.
A dice is thrown once. What is the probability of getting a number greater than 2?
A dice is thrown once. What is the probability of getting a number less than or equal to 2?
From a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn is a face card.
From a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn is not a face card.
From a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn is a queen of black card.
From a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn is a card with number 5 or 6.
From a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn is a card with number less than 8.
From a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn is a card with number between 2 and 9.
In a match between A and B; the probability of winning of A is 0.83. What is the probability of winning of B?
In a match between A and B; the probability of losing the match is 0.49 for B. What is the probability of winning of A?
A and B are friends. Ignoring the leap year, find the probability that both friends will have different birthdays?
A and B are friends. Ignoring the leap year, find the probability that both friends will have the same birthday?
A man tosses two different coins (one of Rs 2 and another of Rs 5) simultaneously. What is the probability that he gets at least one head?
A man tosses two different coins (one of Rs 2 and another of Rs 5) simultaneously. What is the probability that he gets at most one head?
A box contains 7 red balls, 8 green balls and 5 white balls. A ball is drawn at random from the box. Find the probability that the ball is white.
A box contains 7 red balls, 8 green balls and 5 white balls. A ball is drawn at random from the box. Find the probability that the ball is neither red nor white.
All the three face cards of spades are removed from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. A card is then drawn at random from the remaining pack. Find the probability of getting a black face card.
All the three face cards of spades are removed from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. A card is then drawn at random from the remaining pack. Find the probability of getting a queen.
All the three face cards of spades are removed from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. A card is then drawn at random from the remaining pack. Find the probability of getting a black card.
In a musical chairs game, a person has been advised to stop playing the music at any time within 40 seconds after its start. What is the probability that the music will stop within the first 15 seconds?
In a bundle of 50 shirts, 44 are good, 4 have minor defects and 2 have major defects. What is the probability that it is acceptable to a trader who accepts only a good shirt?
In a bundle of 50 shirts, 44 are good, 4 have minor defects and 2 have major defects. What is the probability that it is acceptable to a trader who rejects only a shirt with major defects?
Two dice are thrown at the same time. Find the probability that the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top of the dice is 8.
Two dice are thrown at the same time. Find the probability that the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top of the dice is 13.
Two dice are thrown at the same time. Find the probability that the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top of the dice is less than or equal to 12.
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
`3/7`
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
0.82
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
37%
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
–2.4
If P(E) = 0.59; find P(not E).
A bag contains a certain number of red balls. A ball is drawn. Find the probability that the ball drawn is black.
A bag contains a certain number of red balls. A ball is drawn. Find the probability that the ball drawn is red.
The probability that two boys do not have the same birthday is 0.897. What is the probability that the two boys have the same birthday?
A bag contains 10 red balls, 16 white balls and 8 green balls. A ball is drawn out of the bag at random. What is the probability that the ball drawn will be not red?
A bag contains 10 red balls, 16 white balls and 8 green balls. A ball is drawn out of the bag at random. What is the probability that the ball drawn will be neither red nor green?
A bag contains 10 red balls, 16 white balls and 8 green balls. A ball is drawn out of the bag at random. What is the probability that the ball drawn will be white or green?
A bag contains twenty Rs 5 coins, fifty Rs 2 coins and thirty Re 1 coins. If it is equally likely that one of the coins will fall down when the bag is turned upside down, what is the probability that the coin will be a Re 1 coin?
A bag contains twenty Rs 5 coins, fifty Rs 2 coins and thirty Re 1 coins. If it is equally likely that one of the coins will fall down when the bag is turned upside down, what is the probability that the coin will not be a Rs 2 coin?
A bag contains twenty Rs 5 coins, fifty Rs 2 coins and thirty Re 1 coins. If it is equally likely that one of the coins will fall down when the bag is turned upside down, what is the probability that the coin will neither be a Rs 5 coin nor be a Re 1 coin?
A game consists of spinning an arrow which comes to rest pointing at one of the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12; as shown below.
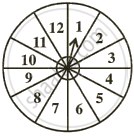
If the outcomes are equally likely, find the probability that the pointer will point at:
- 6
- an even number.
- a prime number.
- a number greater than 8.
- a number less than or equal to 9.
- a number between 3 and 11.
One card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting a queen of red color.
One card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting a black face card.
One card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting the jack or the queen of the hearts.
One card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting a diamond.
One card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting a diamond or a spade.
From a deck of 52 cards, all the face cards are removed and then the remaining cards are shuffled. Now one card is drawn from the remaining deck. Find the probability that the card drawn is a black card.
From a deck of 52 cards, all the face cards are removed and then the remaining cards are shuffled. Now one card is drawn from the remaining deck. Find the probability that the card drawn is 8 of red color.
From a deck of 52 cards, all the face cards are removed and then the remaining cards are shuffled. Now one card is drawn from the remaining deck. Find the probability that the card drawn is a king of black color.
Seven cards:- the eight, the nine, the ten, jack, queen, king and ace of diamonds are well shuffled. One card is then picked up at random.
What is the probability that the card drawn is the eight or the king?
Seven cards:- the eight, the nine, the ten, jack, queen, king and ace of diamonds are well shuffled. One card is then picked up at random.
If the king is drawn and put aside, what is the probability that the second card picked up is:
- an ace?
- a king?
A box contains 150 bulbs out of which 15 are defective. It is not possible to just look at a bulb and tell whether or not it is defective. One bulb is taken out at random from this box. Calculate the probability that the bulb taken out is a good one.
A box contains 150 bulbs out of which 15 are defective. It is not possible to just look at a bulb and tell whether or not it is defective. One bulb is taken out at random from this box. Calculate the probability that the bulb taken out is a defective one.
4 defective pens are accidentally mixed with 16 good ones. It is not possible to just look at a pen and tell whether or not it is defective. One pen is drawn at random from the lot. What is the probability that the pen is defective?
Suppose the pen drawn in (i) is defective and is not replaced. Now one more pen is drawn at random from the rest. What is the probability that this pen is:
- defective
- not defective?
A bag contains 100 identical marble stones which are numbered 1 to 100. If one stone is drawn at random from the bag, find the probability that it bears a perfect square number.
A bag contains 100 identical marble stones which are numbered 1 to 100. If one stone is drawn at random from the bag, find the probability that it bears a number divisible by 4.
A bag contains 100 identical marble stones which are numbered 1 to 100. If one stone is drawn at random from the bag, find the probability that it bears a number divisible by 5.
A bag contains 100 identical marble stones which are numbered 1 to 100. If one stone is drawn at random from the bag, find the probability that it bears a number divisible by 4 or 5.
A bag contains 100 identical marble stones which are numbered 1 to 100. If one stone is drawn at random from the bag, find the probability that it bears a number divisible by 4 and 5.
A circle with diameter 20 cm is drawn somewhere on a rectangular piece of paper with length 40 cm and width 30 cm. This paper is kept horizontal on table top and a dice, very small in size, is dropped on the rectangular paper without seeing towards it. If the dice falls and lands on the paper only, find the probability that it will fall and land inside the circle.
A circle with diameter 20 cm is drawn somewhere on a rectangular piece of paper with length 40 cm and width 30 cm. This paper is kept horizontal on table top and a dice, very small in size, is dropped on the rectangular paper without seeing towards it. If the dice falls and lands on the paper only, find the probability that it will fall and land outside the circle.
Two dice (each bearing numbers 1 to 6) are rolled together. Find the probability that the sum of the numbers on the upper-most faces of two dice is 4 or 5.
Two dice (each bearing numbers 1 to 6) are rolled together. Find the probability that the sum of the numbers on the upper-most faces of two dice is 7, 8 or 9.
Two dice (each bearing numbers 1 to 6) are rolled together. Find the probability that the sum of the numbers on the upper-most faces of two dice is between 5 and 8.
Two dice (each bearing numbers 1 to 6) are rolled together. Find the probability that the sum of the numbers on the upper-most faces of two dice is more than 10.
Two dice (each bearing numbers 1 to 6) are rolled together. Find the probability that the sum of the numbers on the upper-most faces of two dice is less than 6.
Three coins are tossed together. Write all the possible outcomes. Now, find the probability of getting exactly two heads.
Three coins are tossed together. Write all the possible outcomes. Now, find the probability of getting at least two heads.
Three coins are tossed together. Write all the possible outcomes. Now, find the probability of getting at most two heads.
Three coins are tossed together. Write all the possible outcomes. Now, find the probability of getting all tails.
Three coins are tossed together. Write all the possible outcomes. Now, find the probability of getting at least one tail.
Two dice are thrown simultaneously. What is the probability that:
- 4 will not come up either time?
- 4 will come up at least once?
Cards marked with numbers 1, 2, 3 ......... 20 are well shuffled and a card is drawn at random. What is the probability that the number on the card is a prime number?
Cards marked with numbers 1, 2, 3 ......... 20 are well shuffled and a card is drawn at random. What is the probability that the number on the card is divisible by 3?
Cards marked with numbers 1, 2, 3 ......... 20 are well shuffled and a card is drawn at random. What is the probability that the number on the card is a perfect square?
Offices in Delhi are open for five days in a week (Monday to Friday). Two employees of an office remain absent for one day in the same particular week. Find the probability that they remain absent on the same day.
Offices in Delhi are open for five days in a week (Monday to Friday). Two employees of an office remain absent for one day in the same particular week. Find the probability that they remain absent on consecutive day.
Offices in Delhi are open for five days in a week (Monday to Friday). Two employees of an office remain absent for one day in the same particular week. Find the probability that they remain absent on different days.
A box contains some black balls and 30 white balls. If the probability of drawing a black ball is two-fifths of a white ball; find the number of black balls in the box.
From a pack of 52 playing cards, all cards whose numbers are multiples of 3 are removed. A card is now drawn at random. What is the probability that the card drawn is a face card (King, Jack or Queen).
From a pack of 52 playing cards, all cards whose numbers are multiples of 3 are removed. A card is now drawn at random. What is the probability that the card drawn is an even numbered red card?
A die has 6 faces marked by the given numbers, as shown below.
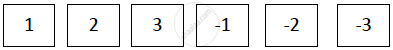
The die is thrown once. What is the probability of getting
1) a positive integer
2) an integer greater than −3.
3) the smallest integer.
A bag contains 5 white balls, 6 red balls and 9 green balls. A ball is drawn at random from the bag. Find the probability that the ball drawn is
- a green ball.
- a white or a red ball.
- neither a green ball nor a white ball.
A game of numbers has cards marked with 11, 12, 13, ....., 40. A card is drawn at random. Find the probability that the number on the card drawn is a perfect square.
Sixteen cards are labelled as a, b, c, ............... m, n, o, p. They are put in a box and shuffled. A boy is asked to draw a card from the box. What is the probability that the card drawn is:
- a vowel.
- a consonant.
- none of the letters of the word median.
A box contains a certain number of balls. On each of 60% balls, letter A is marked. On each of 30% balls, letter B is marked and on each of remaining balls, letter C is marked. A ball is drawn from the box at random. Find the probability that the ball drawn is:
- marked C
- A or B
- neither B nor C
A box contains a certain number of balls. Some of these balls are marked A, some are marked B and the remaining are marked C. When a ball is drawn at random from the box P(A) = `1/3` and P(B) = `1/4`. If there are 40 balls in the box which are marked C, find the number of balls in the box.
Solutions for 25: Probability
![Selina solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 25 - Probability Selina solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 25 - Probability - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-10-icse_6:8bf8c01058454f579d37da35940563b5.png)
Selina solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 25 - Probability
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 25 (Probability) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 25 Probability are Probability - A Theoretical Approach, Sample Space, Type of Event - Complementry, Simple Problems on Single Events, Random Experiments, Basic Ideas of Probability, Measurement of Probability, Probability - A Theoretical Approach, Sample Space, Type of Event - Complementry, Simple Problems on Single Events, Random Experiments, Basic Ideas of Probability, Measurement of Probability.
Using Selina Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Probability exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 25, Probability Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
