| Procedure | Information | Working |
|---|---|---|
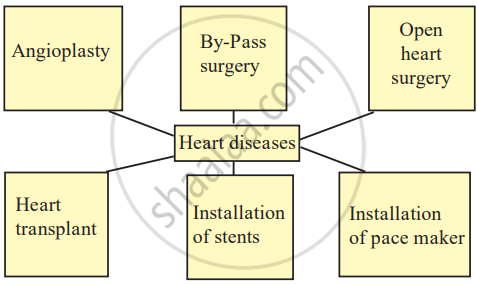
| Angioplasty | A procedure to open up blocked or narrowed blood vessels in the heart. | A small balloon is inserted into the blocked artery and inflated to widen it. A stent is often placed to keep the artery open. |
| Bypass Surgery | A surgery that creates a new route for blood to flow around a blocked artery. | Surgeons use a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body to bypass the blockage, restoring blood flow to the heart. |
| Open Heart Surgery | A surgery where the chest is opened and the heart is operated on directly. | Used to repair heart defects, replace or repair heart valves, or perform bypass surgery. |
| Heart Transplant | A surgical procedure where a failing heart is replaced with a healthy donor heart. | Done when the heart is too damaged to be repaired or if severe heart failure occurs, providing a new lease on life. |
| Installation of Stents | Placing a small, expandable tube called a stent in a blocked artery. | The stent helps maintain proper blood flow to the heart, especially after angioplasty. |
| Installation of Pacemaker | A small electronic device placed in the chest to control abnormal heart rhythms. | The pacemaker sends electrical impulses to ensure the heart beats at a regular and appropriate rate. |
Topics
Living World and Classification of Microbes
Health and Diseases
Force and Pressure
- Force
- Types of Force: Contact Force
- Types of Force: Non-Contact Force
- Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
- Inertia and Mass
- Types of Inertia
- Thrust and Pressure
- Pressure on Solids
- Pressure of liquid
- Gas Pressure
- Atmospheric Pressure
- Buoyancy Force (Upthrust Force)
- Archimedes Principle
- Density of substance and Relative density
Current Electricity and Magnetism
Inside the Atom
Composition of Matter
- Matter (Substance)
- Characteristics of Particles (Molecules) of Matter
- States of Matter
- The Solid State
- The Liquid State
- The Gaseous State
- Elements
- Types of Element: Metals
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Type of Element: Metalloid
- Compound
- Types of Compound
- Mixture
- Types of Mixtures
- Solution
- Suspension Solution
- Colloidal Solution
- Molecular Formula of Compounds
- Valency
Metals and Nonmetals
- Types of Element: Metals
- Physical Properties of Metals
- Chemical Properties of Metal
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Physical Properties of Non-metal
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Chemical Properties of Non-metal
- Type of Element: Metalloid
- Uses of metals and nonmetals
- Nobel Metal
- Purity of Gold
- Corrosion of Metals
- Alloy
Pollution
- Pollution and Its Types
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Air Pollution
- Prevention of Air Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Effects of Water Pollution
- Prevention of Water Pollution
- Soil Pollution and its Causes
- Effects of Soil Pollution
- Prevention of Soil Pollution
- Relationship of Soil Pollution with Air and Water Pollution
- Laws for Control, Regulation, and Prevention of Pollution by Indian Government
Disaster Management
Cell and Cell Organelles
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Structure of the Cell
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Plasma Membrane
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell"
- Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”
- Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”
- Plastids
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
Human Body and Organ System
- Human Body
- Human Organ System
- Mechanism of respiration-Breathing
- Human Respiratory System
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Human Heart
- Blood Vessels
- Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart)
- Heart Beat - Heart Sounds "LUBB" and "DUP"
- Blood
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Functions of Blood
- Blood Transfusion and Blood Groups (ABO and Rh system)
- Blood Pressure (B.P.)
- Heart Related Conditions
Introduction to Acid and Base
Chemical Change and Chemical Bond
Measurement and Effects of Heat
Sound
Reflection of Light
Man Made Materials
Ecosystems
Life Cycle of Stars
- Introduction of Heart Diseases
- Common Reasons for a Heart Attack
- First Aid for Heart Disease
- Treatment of Heart Diseases
Introduction of Heart Diseases:
Heart diseases occur when the heart’s efficiency decreases due to a lack of adequate blood, oxygen, and nutrient supply to the heart muscles. When the heart does not get enough of these essentials, it needs to work much harder, causing stress. If this situation becomes severe, it can lead to a heart attack. During a heart attack, the heart muscle is damaged, and immediate medical attention is crucial to save the person’s life.
Symptoms Not to Be Ignored:
- Severe chest pain.
- Pains in the shoulder, neck, and arms.
- Cramps in the hand, uneasiness, and tremors.
Common Reasons for a Heart Attack:
- Smoking: It damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease.
- Alcoholism: Excessive drinking can raise blood pressure and lead to heart problems.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the heart and blood vessels.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure puts strain on the heart, making it work harder.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the risk of developing heart disease.
- Lack of Physical Exercise: Inactivity weakens the heart and circulatory system.
- Heredity: A family history of heart disease can increase the risk.
- Mental Stress, Anger, and Anxiety: Emotional stress can cause spikes in blood pressure and strain the heart.
First Aid for Heart Disease:
When a person is having a heart attack, quick and proper action is critical.
- Call for Emergency Help: Dial 108 to get an ambulance immediately. It is important to get medical professionals to the scene as soon as possible.
- Check for Consciousness: Gently shake the person’s shoulders to see if they are conscious. If they are unresponsive, you must take action.
- Position the Patient: Lay the person flat on their back on a hard surface to ensure proper support.
- Perform Compression-Only Life Support (C.O.L.S.)
- Press the centre of the chest (thorax) hard and fast with both hands at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute.
- Make sure to press at least 30 times in a continuous rhythm. This helps keep blood circulating until medical help arrives.
Treatment of Heart Diseases:
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
