Topics
Laws of Motion
- Motion and Rest
- Distance and Displacement
- Speed and Velocity
- Effect of Speed and Direction on Velocity
- Uniform and Non-uniform Motion
- Acceleration and Retardation
- Types of Acceleration
- Graphical Representation of Motion
- Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph
- Velocity - Time Graphs
- Equations of Motion by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Velocity - Time Relation by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Displacement - Time Relation by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Displacement - Velocity Relation by Graphical Method
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Newton's First Law of Motion
- Newton's Second Law of Motion
- Newton's Third Law of Motion
- Conservation of Linear Momentum and Its Principle
Work and Energy
Current Electricity
- Electricity
- Potential and Potential Difference
- Free Electrons
- Electric Current
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Resistance and Resistivity of a Conductor
- Electric Circuit
- Symbols and Functions of Various Components of an Electric Circuits
- Conductors and Insulators
- Experimental Verification of Ohm’s Law
- System of Resistors
- Resistors in Series
- Resistors in Parallel
- Domestic Electrical Connections
- Precautions to Be Taken While Using Electricity
Measurement of Matter
- Laws of Chemical Combination
- Law of Conservation of Matter (Law of Conservation of Mass)
- Law of Constant Proportions (Law of Definite Proportions)
- Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
- Atomic Mass
- Symbols Used to Represent Atoms of Different Elements
- Molecules of Elements and Compounds
- Molecular Mass
- Mole Concept
- Avogadro’s Number
- Valency
- Variable Valency
- Ions (Radicals) and Its Types
- Chemical Formulae of Compounds
Acids, Bases and Salts
- Concept of Acid, Base, and Salt
- Ionic Compounds
- Dissociation of Ionic Compounds
- Arrhenius Theory of Acids and Bases
- Basicity and Acidity
- Ph of Solution
- Universal Indicators
- Neutralization Reaction
- Reactions of Acids
- Reactions of Bases
- Salts
- Classification of Salts
- Water of Crystallization
- Ionic Compounds
- Electrolysis
- Electrolysis of Water
Classification of Plants
Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
Useful and Harmful Microbes
Environmental Management
- Weather and Climate
- Importance of Weather in the Living World
- Meteorology
- India Meteorological Department
- Solid Waste Management
- Waste and Its Categories
- Biodegradable Waste
- Non-Biodegradable Wastes
- Harmful effects of solid waste
- Necessity of Solid Waste Management
- 7 Principles of Solid Waste Management
- Period Required for Degradation of Waste
- Disaster Management
- First Aid and Emergency Action
- Methods of Transporting Victims/Patients Safely
Information Communication Technology
Reflection of Light
- Introduction to Light
- Mirrors
- Plane Mirror
- Spherical Mirrors
- Concave Mirror
- Convex Mirror
- Terms Related to Spherical Mirrors
- Rules for Drawing Ray Diagrams
- Image Formation by Concave Mirror
- Image Formation by Convex Mirror
- Divergence and Convergence of Light
- Sign Convention
- Mirror Equation/Formula
- Linear Magnification (M) Due to Spherical Mirrors
Study of Sound
Carbon : An Important Element
- Carbon: A Versatile Element
- Properties of Carbon
- Allotropy and Allotropes of Carbon
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Diamond
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Graphite
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Fullerene
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Coal
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Charcoal
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Coke
- Hydrocarbons
- Solubility of Carbon
- Reaction of Carbon
- Carbon Dioxide
- Fire Extinguisher
- Methane
- Biogas Plant
Substances in Common Use
- Important Salts in Daily Life
- Properties and Uses of Sodium Chloride
- Preparation and Uses of Baking Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Bleaching Powder
- Preparation and Uses of Washing Soda
- Some Crystalline Salts
- Soap
- Radioactivity
- Nature of Radioactive Radiation
- Characteristics of Alpha, Beta and Gamma Rays
- Uses of Radioactive Isotopes
- Hazards of Radioactive Substances and Radiation
- Chemical Substances in Day to Day Life
- Food Colours and Essences
- Dye
- Artificial Colours
- Deodorant
- Teflon
- Powder Coating
- Anodizing
- Ceramic
Life Processes in Living Organisms
- Transportation in Living Organisms
- Transportation in Plant
- Transportation of Water in Plants
- Transportation of Food and Other Substances in Plants
- Excretion
- Excretion in Plants
- Human Excretory System
- Dialysis and Artificial Kidney
- Control and Co-ordination
- Control and Co-ordination in Plants
- Control and Co-ordination in Human Being
- Nervous Control
- Human Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Chemical Control
- Endocrine Glands: Location and Important Functions
Heredity and Variation
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Inherited Traits and Expression of Traits
- Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity
- Types of Chromosomes
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- Monohybrid Cross
- Dihybrid Cross
- Genetic Disorders
- Disorders Due to Chromosomal Abnormalities
- Diseases Occuring Due to Mutation in Single Gene (Monogenic Disorders)
- Mitochondrial Disorder
- Disorders Due to Mutations in Multiple Genes : (Polygenic Disorders)
Introduction to Biotechnology
- Tissues - “The Teams of Workers”
- Animal Tissues
- Epithelial Tissue
- Connective Tissue
- Muscular Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
- Plant Tissues
- Meristems or Meristematic Tissues
- Permanent Tissue
- Simple Permanent Tissues (Supporting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Biotechnology
- Tissue Culture
- Changes in Agricultural Management Due to Biotechnology
- Application of Biotechnology in Floriculture, Nurseries and Forestry
- Agritourism
- Animal Husbandry (Livestock)
- Dairy Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Sericulture
Observing Space : Telescopes
- Floriculture, Nurseries and Forestry
- Application of Biotechnology in Floriculture, Nurseries, and Forestry
Floriculture, Nurseries and Forestry:
1. Floriculture
Floriculture is a branch of horticulture that focuses on the cultivation, production, and management of flowering plants and ornamental plants. It involves growing flowers for decorative purposes, landscaping, and commercial use, including cut flowers, potted plants, and garden displays. Floriculture plays a significant role in beautification and the flower trade.
2. Nurseries
Nurseries play a crucial role in large-scale gardening, afforestation, and reforestation by supplying seedlings in large numbers. It is a specialised facility or space where plants are propagated, grown, and nurtured until they are ready for transplantation or sale. They serve as centres for cultivating a wide variety of plants, including flowers, trees, shrubs, and vegetables, under controlled conditions to ensure healthy growth. Nurseries are essential for landscaping, gardening, and commercial farming.
3. Forestry
Forestry is the science and practice of managing forests for sustainable use and conservation. It includes the cultivation, protection, and utilisation of trees and forest resources to meet environmental, economic, and social needs. Forestry plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance, combating climate change, and supporting industries like timber and paper production.
Application of Biotechnology in Floriculture, Nurseries, and Forestry:
- Plants bearing excellent flowers or fruits can be grown on a large scale in a shorter time.
- Plants can be produced even without natural pollination or germination, such as orchids and pitcher plants.
- Bioreactors enable the growth of cells in a nutritive, pathogen-free medium for mass production.
- Tissue culture requires minimal resources and produces large numbers of seedlings in a short time.
- Plants produced via tissue culture or genetic modification are often disease-free, with virus-free plantlets derived from the meristem.
- Rare and endangered plants can be propagated and preserved using tissue culture, protecting them from extinction.
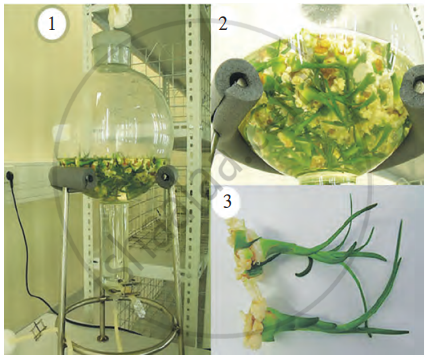
Bioreactor and production of plantlets
