In the past, it was believed that bacteria of the Bacillus type spoilt meat, but the specific type was unknown. Van Ermengem discovered that Clostridium botulinum, an anaerobic bacterium, is responsible for food poisoning. Ida Bengston obtained higher education in biochemistry at Chicago University. She conducted important research on the toxin responsible for gas gangrene and the antitoxin useful for treating it. While she was researching the dreaded disease called typhus, she herself contracted the infection. But she overcame it and continued her research. For this work, she was honoured with the ‘Typhus Medal’ in 1947.
Topics
Laws of Motion
- Motion and Rest
- Distance and Displacement
- Speed and Velocity
- Effect of Speed and Direction on Velocity
- Uniform and Non-uniform Motion
- Acceleration and Retardation
- Types of Acceleration
- Graphical Representation of Motion
- Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph
- Velocity - Time Graphs
- Equations of Motion by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Velocity - Time Relation by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Displacement - Time Relation by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Displacement - Velocity Relation by Graphical Method
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Newton's First Law of Motion
- Newton's Second Law of Motion
- Newton's Third Law of Motion
- Conservation of Linear Momentum and Its Principle
Work and Energy
Current Electricity
- Electricity
- Potential and Potential Difference
- Free Electrons
- Electric Current
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Resistance and Resistivity of a Conductor
- Electric Circuit
- Symbols and Functions of Various Components of an Electric Circuits
- Conductors and Insulators
- Experimental Verification of Ohm’s Law
- System of Resistors
- Resistors in Series
- Resistors in Parallel
- Domestic Electrical Connections
- Precautions to Be Taken While Using Electricity
Measurement of Matter
- Laws of Chemical Combination
- Law of Conservation of Matter (Law of Conservation of Mass)
- Law of Constant Proportions (Law of Definite Proportions)
- Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
- Atomic Mass
- Symbols Used to Represent Atoms of Different Elements
- Molecules of Elements and Compounds
- Molecular Mass
- Mole Concept
- Avogadro’s Number
- Valency
- Variable Valency
- Ions (Radicals) and Its Types
- Chemical Formulae of Compounds
Acids, Bases and Salts
- Concept of Acid, Base, and Salt
- Ionic Compounds
- Dissociation of Ionic Compounds
- Arrhenius Theory of Acids and Bases
- Basicity and Acidity
- Ph of Solution
- Universal Indicators
- Neutralization Reaction
- Reactions of Acids
- Reactions of Bases
- Salts
- Classification of Salts
- Water of Crystallization
- Ionic Compounds
- Electrolysis
- Electrolysis of Water
Classification of Plants
Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
Useful and Harmful Microbes
Environmental Management
- Weather and Climate
- Importance of Weather in the Living World
- Meteorology
- India Meteorological Department
- Solid Waste Management
- Waste and Its Categories
- Biodegradable Waste
- Non-Biodegradable Wastes
- Harmful effects of solid waste
- Necessity of Solid Waste Management
- 7 Principles of Solid Waste Management
- Period Required for Degradation of Waste
- Disaster Management
- First Aid and Emergency Action
- Methods of Transporting Victims/Patients Safely
Information Communication Technology
Reflection of Light
- Introduction to Light
- Mirrors
- Plane Mirror
- Spherical Mirrors
- Concave Mirror
- Convex Mirror
- Terms Related to Spherical Mirrors
- Rules for Drawing Ray Diagrams
- Image Formation by Concave Mirror
- Image Formation by Convex Mirror
- Divergence and Convergence of Light
- Sign Convention
- Mirror Equation/Formula
- Linear Magnification (M) Due to Spherical Mirrors
Study of Sound
Carbon : An Important Element
- Carbon: A Versatile Element
- Properties of Carbon
- Allotropy and Allotropes of Carbon
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Diamond
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Graphite
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Fullerene
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Coal
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Charcoal
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Coke
- Hydrocarbons
- Solubility of Carbon
- Reaction of Carbon
- Carbon Dioxide
- Fire Extinguisher
- Methane
- Biogas Plant
Substances in Common Use
- Important Salts in Daily Life
- Properties and Uses of Sodium Chloride
- Preparation and Uses of Baking Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Bleaching Powder
- Preparation and Uses of Washing Soda
- Some Crystalline Salts
- Soap
- Radioactivity
- Nature of Radioactive Radiation
- Characteristics of Alpha, Beta and Gamma Rays
- Uses of Radioactive Isotopes
- Hazards of Radioactive Substances and Radiation
- Chemical Substances in Day to Day Life
- Food Colours and Essences
- Dye
- Artificial Colours
- Deodorant
- Teflon
- Powder Coating
- Anodizing
- Ceramic
Life Processes in Living Organisms
- Transportation in Living Organisms
- Transportation in Plant
- Transportation of Water in Plants
- Transportation of Food and Other Substances in Plants
- Excretion
- Excretion in Plants
- Human Excretory System
- Dialysis and Artificial Kidney
- Control and Co-ordination
- Control and Co-ordination in Plants
- Control and Co-ordination in Human Being
- Nervous Control
- Human Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Chemical Control
- Endocrine Glands: Location and Important Functions
Heredity and Variation
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Inherited Traits and Expression of Traits
- Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity
- Types of Chromosomes
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- Monohybrid Cross
- Dihybrid Cross
- Genetic Disorders
- Disorders Due to Chromosomal Abnormalities
- Diseases Occuring Due to Mutation in Single Gene (Monogenic Disorders)
- Mitochondrial Disorder
- Disorders Due to Mutations in Multiple Genes : (Polygenic Disorders)
Introduction to Biotechnology
- Tissues - “The Teams of Workers”
- Animal Tissues
- Epithelial Tissue
- Connective Tissue
- Muscular Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
- Plant Tissues
- Meristems or Meristematic Tissues
- Permanent Tissue
- Simple Permanent Tissues (Supporting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Biotechnology
- Tissue Culture
- Changes in Agricultural Management Due to Biotechnology
- Application of Biotechnology in Floriculture, Nurseries and Forestry
- Agritourism
- Animal Husbandry (Livestock)
- Dairy Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Sericulture
Observing Space : Telescopes
- An Introduction to Scientists
- Other Harmful Microorganisms
- Diseases Caused by Virus
- Diseases Caused by Bacteria
- Diseases Caused by Protozoa
- Diseases Caused by Fungi
An Introduction to Scientists:
Other Harmful Microorganisms:
Diseases Caused by Virus:
1. AIDS
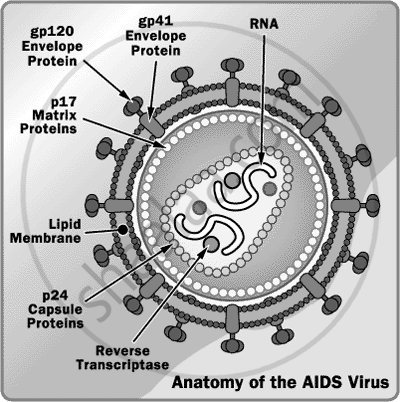
Virus
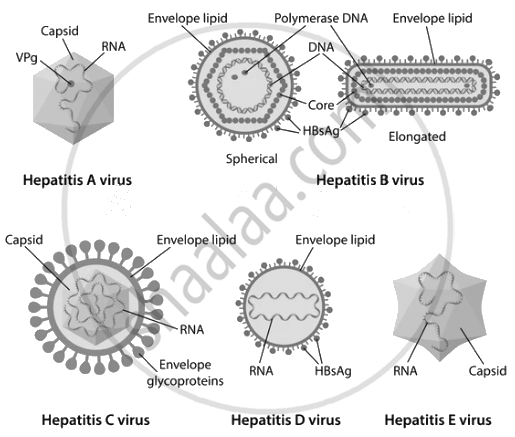
2. Hepatitis
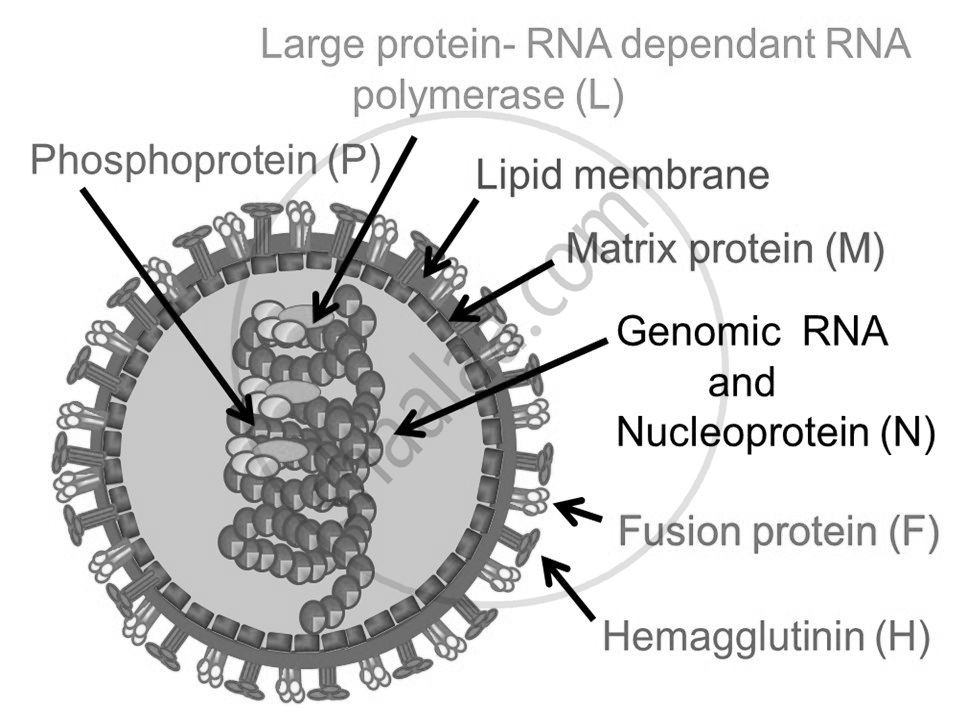
3. Influenza
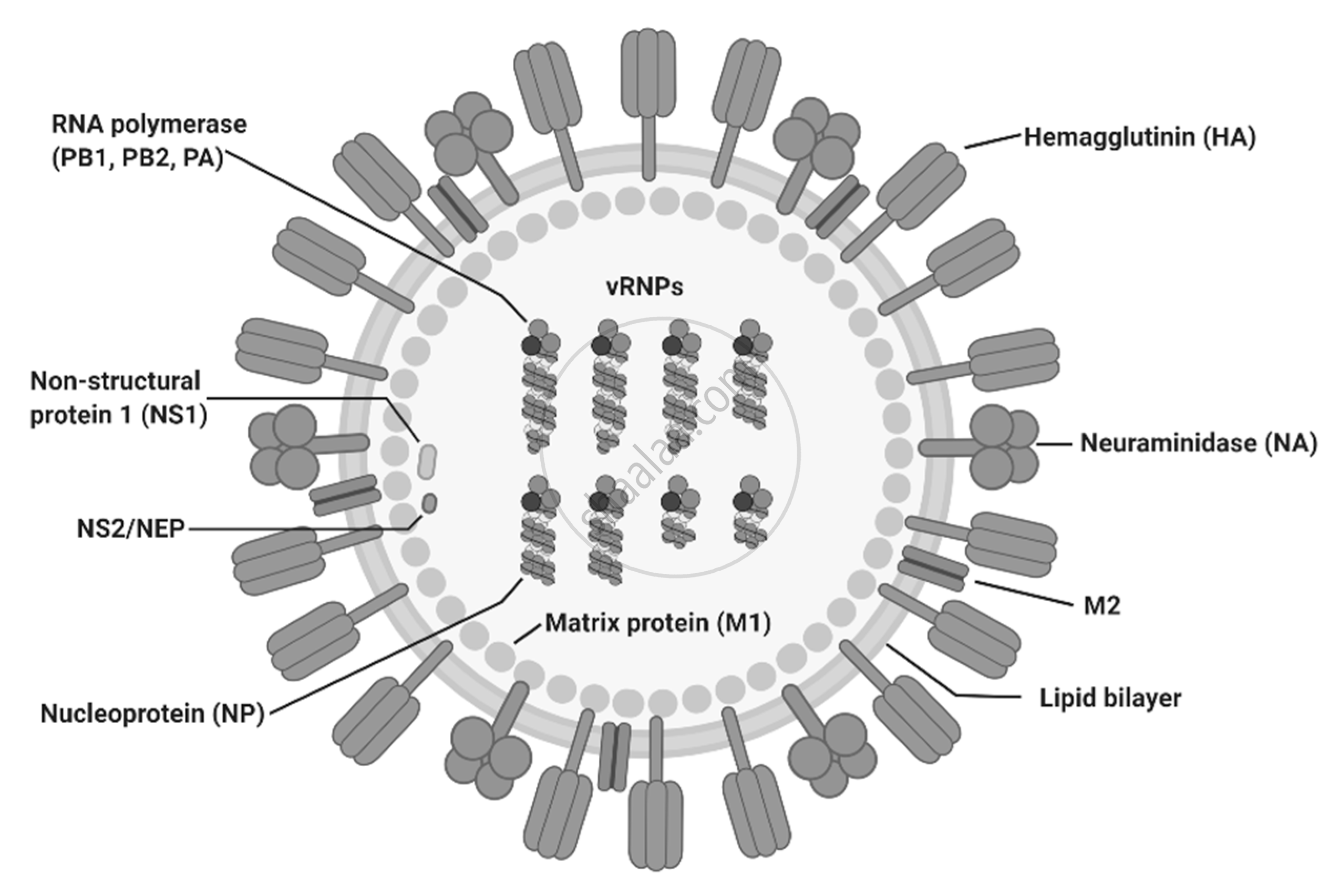
Influenza A virus
4. Dengue
Dengue is caused by a virus and is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes, primarily Aedes aegypti. The virus causes flu-like symptoms, including high fever, severe headaches, joint and muscle pain, skin rashes, and fatigue. In severe cases, it can lead to dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome, which can be life-threatening. Preventive measures include maintaining cleanliness in surroundings, eliminating stagnant water where mosquitoes breed (such as in containers, old tires, and open tanks), and using mosquito control methods like insecticides and mosquito nets. Wearing protective clothing and applying mosquito repellents can also reduce the risk of bites. Public awareness and community efforts to control mosquito populations are critical for preventing the spread of dengue.

Dengue virus
5. Measles
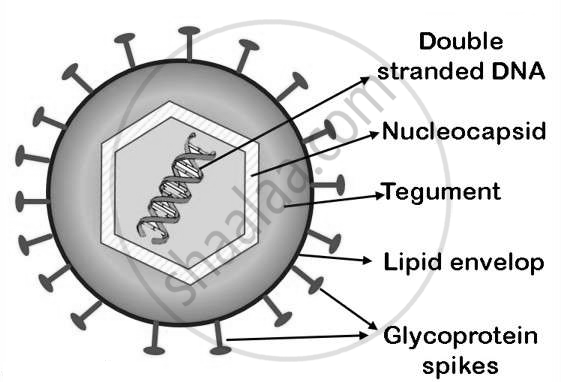
Varicella-Zoster Virus
Diseases Caused by Bacteria:
1. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a respiratory disease caused primarily by bacterial pathogens, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae. It spreads through droplets released into the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, making it highly contagious in close-contact settings. Pneumonia affects the lungs, leading to symptoms like fever, cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain, which can range from mild to severe depending on the individual's health and immunity. Preventive measures include vaccination, particularly for children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems, as they are at higher risk. Maintaining proper hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and wearing masks in crowded places, can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Additionally, strengthening immunity through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and timely medical check-ups can help in preventing severe outcomes of pneumonia. Early diagnosis and appropriate medical treatment, including antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia, are essential for managing and recovering from the illness effectively.
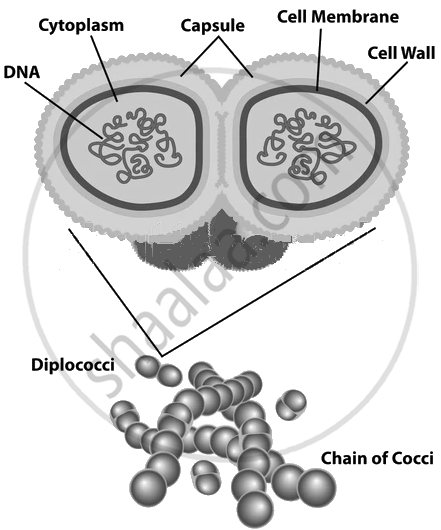
Streptococcus pneumoniae
2. Leprosy
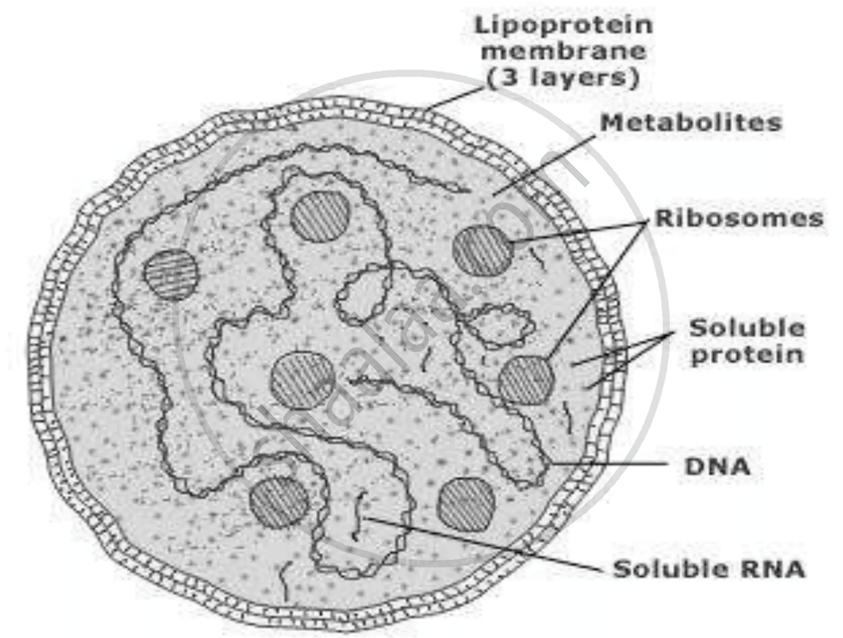
Mycobacterium leprae
3. Cholera
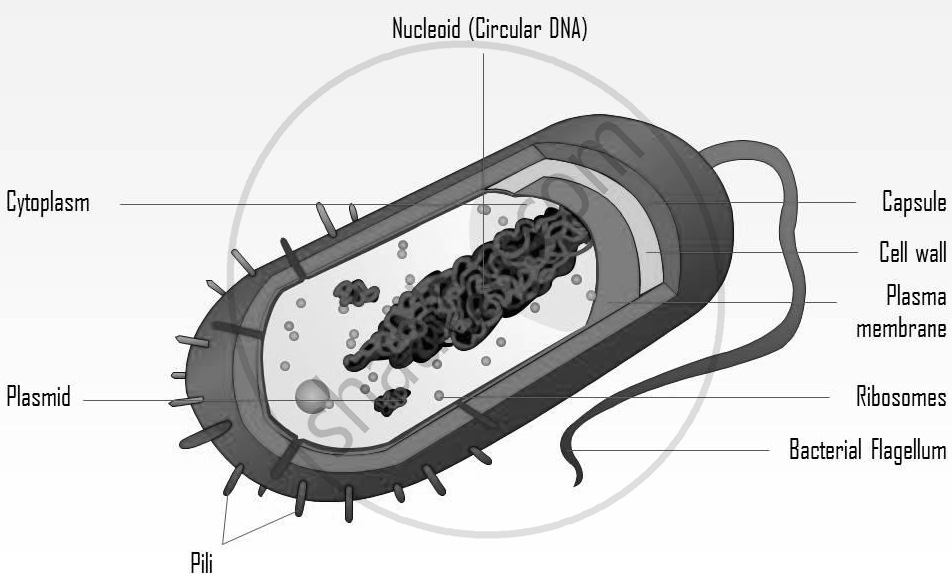
Vibrio cholerae
Diseases Caused by Protozoa:
Malaria
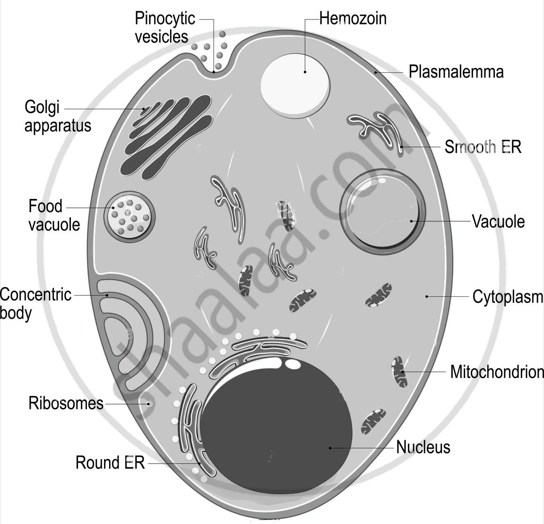
Plasmodium falciparum
Diseases Caused by Fungi:
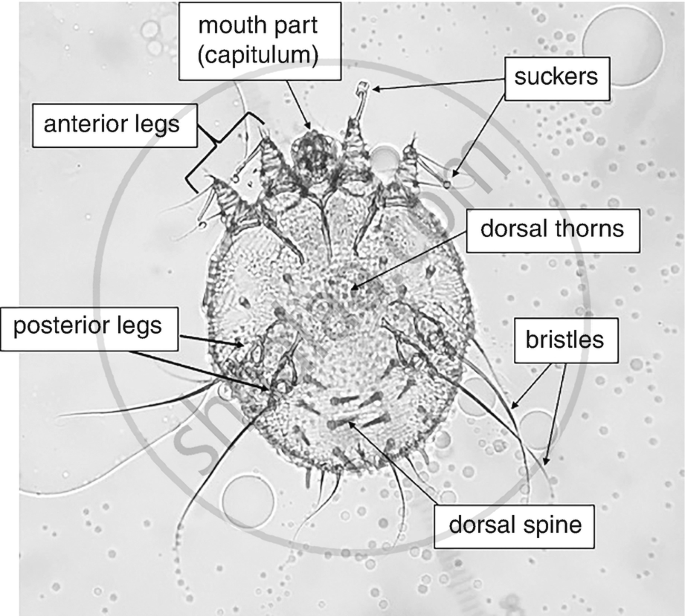
Sarcoptes scabiei
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.