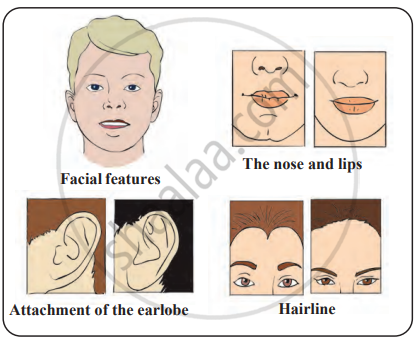
1. Inherited traits
Inherited traits are encoded in our DNA and passed on to the next generation, such as eye colour, height, skin tone, and hair colour. Variations arising from reproduction can also be inherited and may enhance an organism's survival. In sexually reproducing individuals, there are two copies of each gene. If these copies differ, the trait that is visibly expressed is called the dominant trait, while the one not expressed is the recessive trait. These variations can contribute to survival advantages or lead to genetic drift within a species.
2. Acquired Traits
Acquired traits are characteristics that an individual develops during their lifetime, either through personal effort or external influences. Unlike inherited traits, acquired traits are not encoded in DNA and cannot be passed on to the next generation. Examples include skills such as dancing or cooking.