Topics
Laws of Motion
- Motion and Rest
- Distance and Displacement
- Speed and Velocity
- Effect of Speed and Direction on Velocity
- Uniform and Non-uniform Motion
- Acceleration and Retardation
- Types of Acceleration
- Graphical Representation of Motion
- Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph
- Velocity - Time Graphs
- Equations of Motion by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Velocity - Time Relation by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Displacement - Time Relation by Graphical Method
- Derivation of Displacement - Velocity Relation by Graphical Method
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Newton's First Law of Motion
- Newton's Second Law of Motion
- Newton's Third Law of Motion
- Conservation of Linear Momentum and Its Principle
Work and Energy
Current Electricity
- Electricity
- Potential and Potential Difference
- Free Electrons
- Electric Current
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Resistance and Resistivity of a Conductor
- Electric Circuit
- Symbols and Functions of Various Components of an Electric Circuits
- Conductors and Insulators
- Experimental Verification of Ohm’s Law
- System of Resistors
- Resistors in Series
- Resistors in Parallel
- Domestic Electrical Connections
- Precautions to Be Taken While Using Electricity
Measurement of Matter
- Laws of Chemical Combination
- Law of Conservation of Matter (Law of Conservation of Mass)
- Law of Constant Proportions (Law of Definite Proportions)
- Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter
- Atomic Mass
- Symbols Used to Represent Atoms of Different Elements
- Molecules of Elements and Compounds
- Molecular Mass
- Mole Concept
- Avogadro’s Number
- Valency
- Variable Valency
- Ions (Radicals) and Its Types
- Chemical Formulae of Compounds
Acids, Bases and Salts
- Concept of Acid, Base, and Salt
- Ionic Compounds
- Dissociation of Ionic Compounds
- Arrhenius Theory of Acids and Bases
- Basicity and Acidity
- Ph of Solution
- Universal Indicators
- Neutralization Reaction
- Reactions of Acids
- Reactions of Bases
- Salts
- Classification of Salts
- Water of Crystallization
- Ionic Compounds
- Electrolysis
- Electrolysis of Water
Classification of Plants
Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
Useful and Harmful Microbes
Environmental Management
- Weather and Climate
- Importance of Weather in the Living World
- Meteorology
- India Meteorological Department
- Solid Waste Management
- Waste and Its Categories
- Biodegradable Waste
- Non-Biodegradable Wastes
- Harmful effects of solid waste
- Necessity of Solid Waste Management
- 7 Principles of Solid Waste Management
- Period Required for Degradation of Waste
- Disaster Management
- First Aid and Emergency Action
- Methods of Transporting Victims/Patients Safely
Information Communication Technology
Reflection of Light
- Introduction to Light
- Mirrors
- Plane Mirror
- Spherical Mirrors
- Concave Mirror
- Convex Mirror
- Terms Related to Spherical Mirrors
- Rules for Drawing Ray Diagrams
- Image Formation by Concave Mirror
- Image Formation by Convex Mirror
- Divergence and Convergence of Light
- Sign Convention
- Mirror Equation/Formula
- Linear Magnification (M) Due to Spherical Mirrors
Study of Sound
Carbon : An Important Element
- Carbon: A Versatile Element
- Properties of Carbon
- Allotropy and Allotropes of Carbon
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Diamond
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Graphite
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Fullerene
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Coal
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Charcoal
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Coke
- Hydrocarbons
- Solubility of Carbon
- Reaction of Carbon
- Carbon Dioxide
- Fire Extinguisher
- Methane
- Biogas Plant
Substances in Common Use
- Important Salts in Daily Life
- Properties and Uses of Sodium Chloride
- Preparation and Uses of Baking Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Bleaching Powder
- Preparation and Uses of Washing Soda
- Some Crystalline Salts
- Soap
- Radioactivity
- Nature of Radioactive Radiation
- Characteristics of Alpha, Beta and Gamma Rays
- Uses of Radioactive Isotopes
- Hazards of Radioactive Substances and Radiation
- Chemical Substances in Day to Day Life
- Food Colours and Essences
- Dye
- Artificial Colours
- Deodorant
- Teflon
- Powder Coating
- Anodizing
- Ceramic
Life Processes in Living Organisms
- Transportation in Living Organisms
- Transportation in Plant
- Transportation of Water in Plants
- Transportation of Food and Other Substances in Plants
- Excretion
- Excretion in Plants
- Human Excretory System
- Dialysis and Artificial Kidney
- Control and Co-ordination
- Control and Co-ordination in Plants
- Control and Co-ordination in Human Being
- Nervous Control
- Human Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Chemical Control
- Endocrine Glands: Location and Important Functions
Heredity and Variation
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Inherited Traits and Expression of Traits
- Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity
- Types of Chromosomes
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- Monohybrid Cross
- Dihybrid Cross
- Genetic Disorders
- Disorders Due to Chromosomal Abnormalities
- Diseases Occuring Due to Mutation in Single Gene (Monogenic Disorders)
- Mitochondrial Disorder
- Disorders Due to Mutations in Multiple Genes : (Polygenic Disorders)
Introduction to Biotechnology
- Tissues - “The Teams of Workers”
- Animal Tissues
- Epithelial Tissue
- Connective Tissue
- Muscular Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
- Plant Tissues
- Meristems or Meristematic Tissues
- Permanent Tissue
- Simple Permanent Tissues (Supporting Tissue)
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Biotechnology
- Tissue Culture
- Changes in Agricultural Management Due to Biotechnology
- Application of Biotechnology in Floriculture, Nurseries and Forestry
- Agritourism
- Animal Husbandry (Livestock)
- Dairy Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Sericulture
Observing Space : Telescopes
- Optical Telescopes
- Refracting and Reflecting Telescopes
- Types of Reflecting Telescopes
Optical Telescopes:
An optical telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by gathering and focusing light from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. It helps create magnified images for direct viewing, photography, or data collection through electronic sensors.
Working:
- Optical telescopes primarily use two or more lenses.
- The main lens, called the objective lens, is designed to collect as much light as possible from a distant object.
- A larger objective lens ensures more light is gathered, enabling a clearer and brighter image.
- The light collected by the objective lens is directed to a smaller lens, known as the eyepiece.
- The eyepiece magnifies the image, making it larger and easier to observe.
- When light passes through a lens, it changes direction due to a process called refraction. This occurs as light enters and exits the lens.
- Telescopes that rely on refraction for image formation are called refracting telescopes.
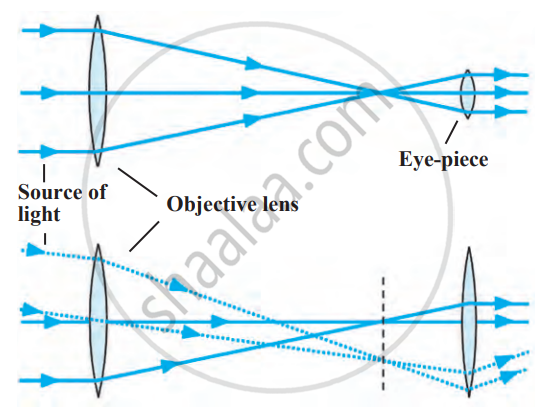
Refracting telescope
Refracting and Reflecting Telescopes:
Refracting telescopes are useful for observing space, but they have limitations
- The objective lens must be very large to collect more light, which makes it heavy and difficult to manufacture without distortion.
- Larger lenses increase the length of the telescope, making it cumbersome to handle.
- Lenses cause chromatic aberration, where colours in the image appear distorted.
To address these challenges, reflecting telescopes are used. These telescopes use concave mirrors instead of lenses.
- Large mirrors are easier to build and can be made by combining smaller pieces.
- Mirrors are lighter than lenses of the same size.
- Images formed by mirrors are free from chromatic aberration.
Reflecting telescopes enable the observation of distant stars and galaxies that are invisible to the human eye.
Types of Reflecting Telescopes:
1. Newtonian Telescope
- Light from space is collected by a concave mirror.
- It is then deflected by a small flat (plane) mirror to the side.
- The light passes through an eyepiece, producing a magnified image.
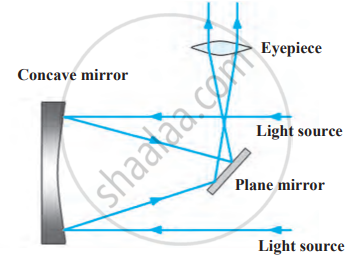
The Newtonian telescope
2. Cassegrain Telescope
- Light is collected by a concave mirror and reflected back toward a smaller convex mirror.
- The light passes through a hole in the concave mirror and then through an eyepiece located at the back, creating a magnified image.
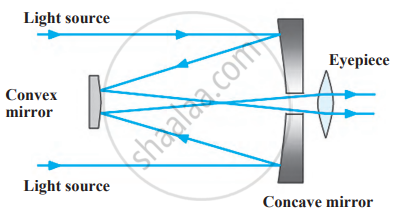
The Cassegrain telescope
In India, several reflecting telescopes with concave mirrors of 2-meter diameter have been in use for years. The largest optical telescope in India, and also in Asia, has a 3.6-meter-diameter mirror. It is located at the Aryabhatt Research Institute of Experimental Sciences in Nainital.

